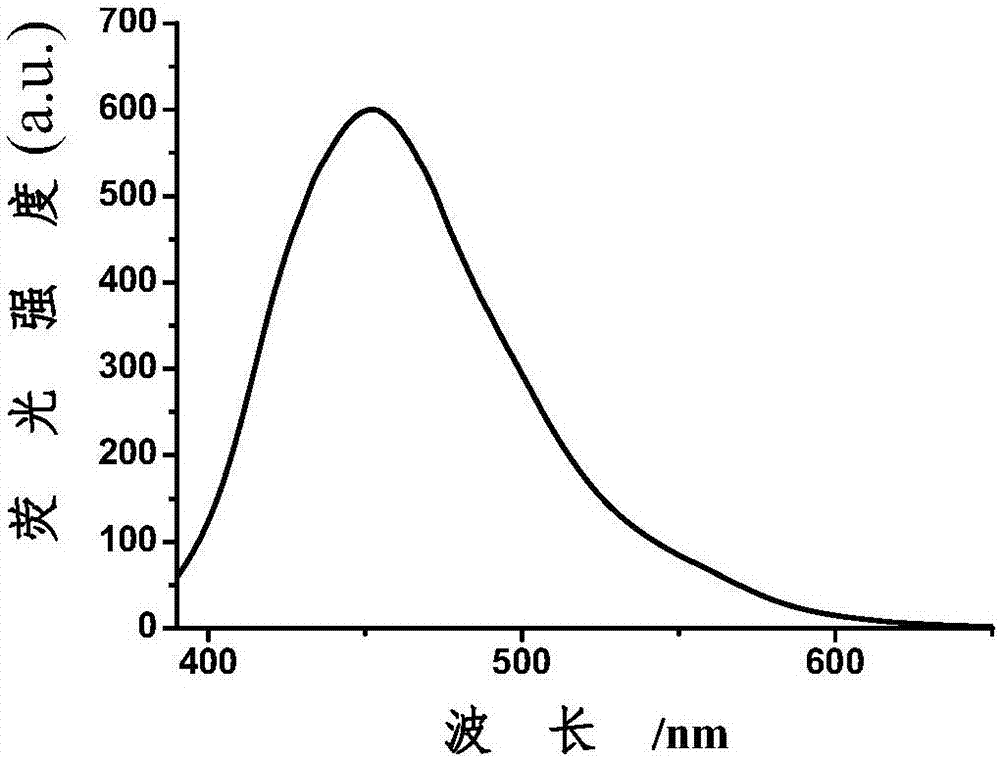
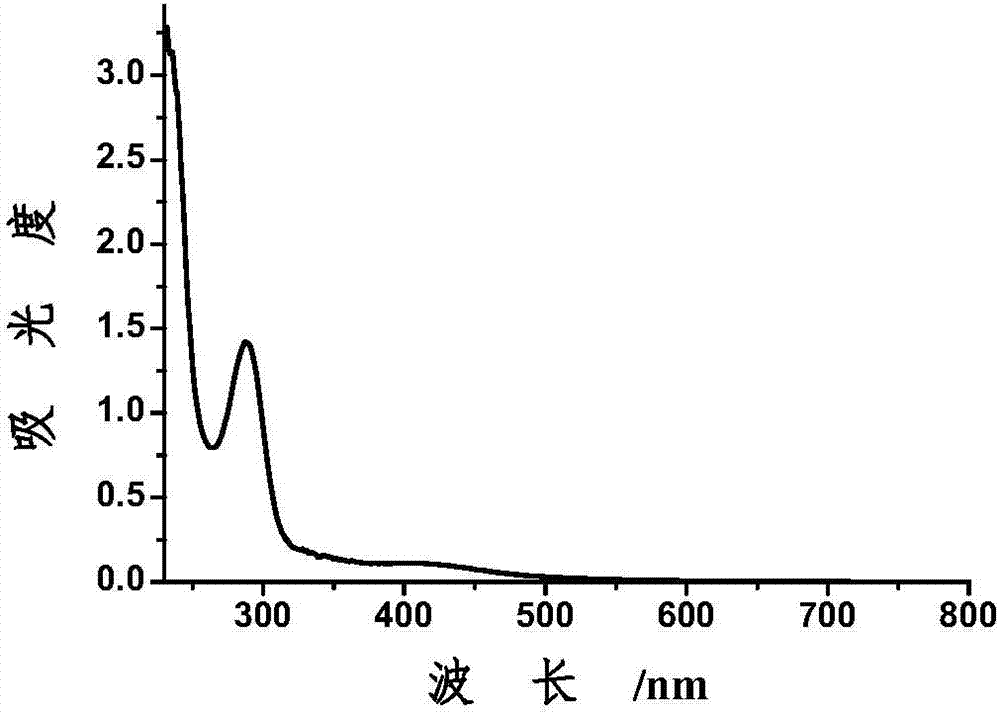
Pulse potential preparation method for nitrogen-doped fluorescent carbon dots
A fluorescent carbon dot, nitrogen doping technology, applied in the field of carbon nanomaterials, can solve the problem of lack of new electrochemical methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Use the CHI760E electrochemical workstation to control the potential, adopt a two-electrode system, the platinum plate is the working electrode and the counter electrode, and add a mixture of ethanol, o-phenylenediamine and water into a 200mL beaker as the electrolyte. The substances of these three reactants The volume ratio is 100:1:80. Set the parameters of the pulse potentiometric method and start the reaction: the high potential is 5V, the low potential is 3V, the pulse width is 5s, and the number of cycles is 720 times; after the reaction, the solution turns from colorless to yellow, and after standing for a while, take the supernatant Add hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH to be neutral, then centrifuge at 6000r / min for 5min, concentrate the supernatant by rotary evaporation, and finally use a dialysis bag with a cutoff of 3500 in deionized water to dialyze the concentrated solution for 48h to obtain nitrogen-doped fluorescent carbon point of aqueous solution.
Embodiment 2
[0021] The difference between Example 2 and Example 1 is that a mixture of ethanol, o-phenylenediamine and water is added in a 200mL beaker as the electrolyte, and the ratio of the amount of these three reactants is 90:1:70 . Set the parameters of the pulse potentiometric method and start the reaction: the high potential is 9V, the low potential is 5V, the pulse width is 5s, and the number of cycles is 720 times; after the reaction, the solution turns from colorless to yellow, and after standing for a while, take the supernatant Add hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH to be neutral, then centrifuge at 5000r / min for 10min, concentrate the supernatant by rotary evaporation, and finally use a dialysis bag with a cutoff of 1000 in deionized water to dialyze the concentrated solution for 48h to obtain nitrogen-doped fluorescent carbon point of aqueous solution.
Embodiment 3
[0023] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is that in the beaker of 200mL, add the mixed solution of citric acid, o-phenylenediamine and water as electrolyte, the ratio of the amount of these three reactants is 110:1: 80. Set the parameters of the pulse potentiometric method and start the reaction: the high potential is 9V, the low potential is 5V, the pulse width is 10s, and the number of cycles is 600 times; after the reaction, the solution changes from colorless to brownish-yellow. Add hydrochloric acid to the solution to adjust the pH to be neutral, then centrifuge at 6000r / min for 10min, concentrate the supernatant by rotary evaporation, and finally use a dialysis bag with a cutoff of 1000 in deionized water to dialyze the concentrated solution for 48 hours to obtain nitrogen-doped fluorescence Aqueous solution of carbon dots.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com