Application of folium artemisiae argyi pigment dye to cellulose fiber one-bath mordant dyeing process
A technology of cellulose fiber and mugwort leaves, which is applied in the application field of mugwort leaf pigment dyes in the same-bath mordant dyeing process of cellulose fibers, to achieve the effect of reducing a large amount of consumption and simplifying the ethanol solvent extraction process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
[0031] After the prepared mugwort leaves are washed and dried, the walls are broken with a wall breaking machine to obtain a dark green paste liquid, which releases the unique aroma of mugwort. Take 100g of pasty liquid each time, use ethanol as solvent to dissolve according to the ratio in the table, and then filter with suction to get the filtrate. Prepare dyes according to the mass ratio of pasty liquid and ethanol solvent as 1:1, 1:2, 1:3, and 1:4, take equal amounts (100g) of dyes, and directly match the same amount under the same conditions Cotton fabric (2.5g) was dyed, and the results are shown in the table below:
[0032]
[0033] Combining the state and color of the dyeing liquor after filtration and the effect of direct dyeing of the fabric, further through the determination of parameters such as dyeing depth, dry and wet rubbing fastness, staining, and discoloration, the mass ratio of the pasty liquid to the ethanol solvent is determined as 1:2, the dye liquor ...
Embodiment
[0035] Same bath mordant method:
[0036] At room temperature, take mugwort leaf pigment to prepare 300ml of dyeing solution, the mass concentration of mugwort leaf pigment is 33%, add mordant, dyeing accelerator salt, after the chemical material is uniform, raise the temperature to 80°C (3°C / min), add pure cotton for bleaching Twill fabric 10g, liquor ratio 1:30, after dyeing, add color-fixing salt, keep warm for 15 minutes, wash with water, and dry.
[0037] Direct staining method:
[0038] At room temperature, take mugwort leaf pigment and make dye solution 300ml, the mass concentration of mugwort leaf pigment is 33%, add dyeing accelerator salt, heat up to 65°C (2°C / min), add mordant and 10g of pure cotton bleached twill fabric, liquor ratio The ratio is 1:30. After the dyeing is completed, add color-fixing salt and keep warm for 15 minutes to fix the color. After dyeing, wash with water and dry.
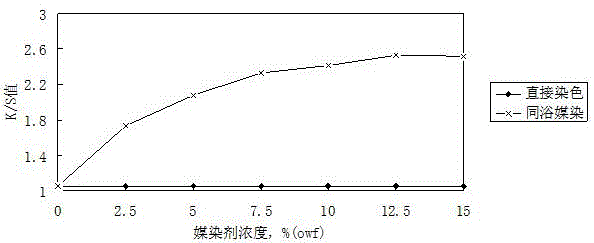
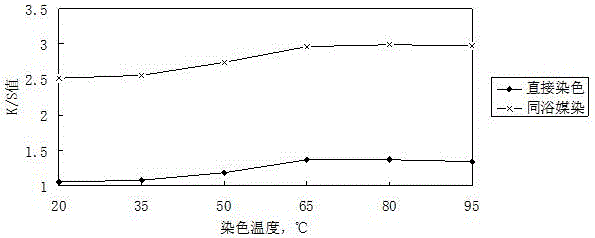
[0039] According to the manual attached figure 1 The relationship betwee...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com