Quantitative measurement method based on integral averaging in pulse infrared heat wave technology
An infrared thermal wave and integral averaging technology, which is applied in measurement devices, material thermal development, material defect testing, etc. The effect of small randomness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0127] Embodiment 1. Using reflective pulsed infrared thermal wave technology to measure defect depth
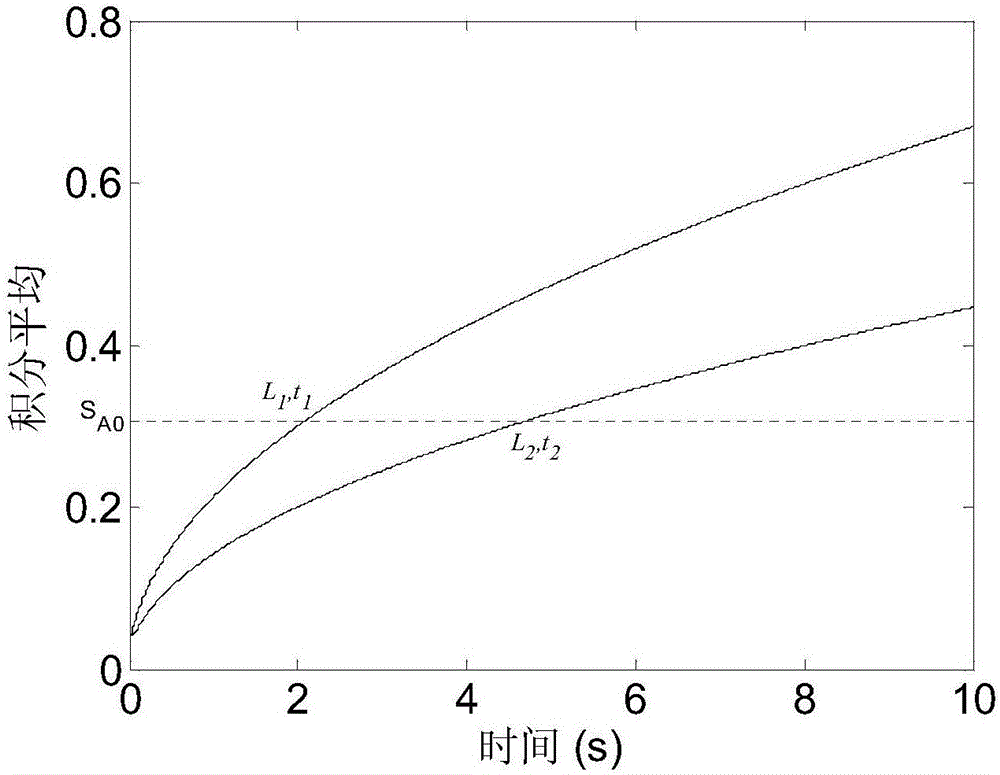
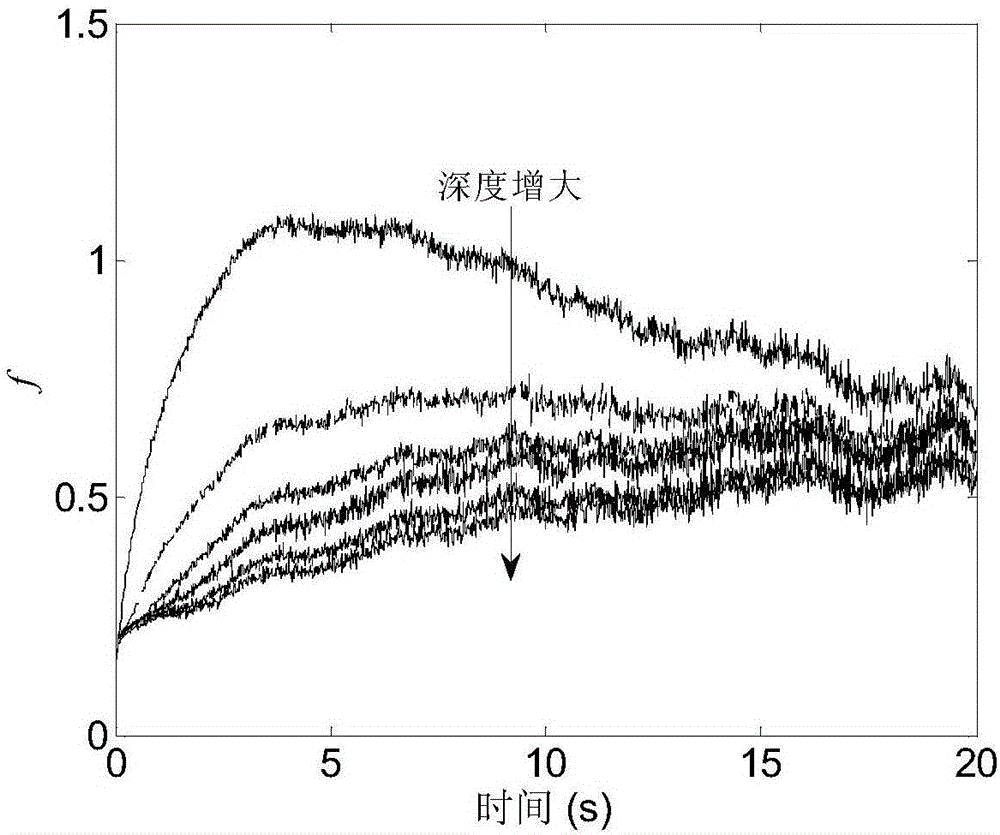
[0128] Using the first stainless steel standard specimen, extract the cooling curve of each flat-bottomed hole center pixel in the heat map of the stainless steel specimen, normalize it with the first frame, and then multiply it by the square root of the corresponding time to obtain a new time series f, such as image 3 shown. The sequence S is obtained by taking the integral average of the sequence f A ,Such as Figure 4 shown. refer to figure 1 , theoretically the integral average curve should be a monotonically increasing sequence, but Figure 4 The second half of the curve corresponding to the middle 1mm hole is monotonously decreasing, which is caused by the small depth of the defect and the obvious three-dimensional thermal diffusion, while the other curves can be regarded as a monotonically increasing sequence within the shown time period. Depend on Figure 4 It...
Embodiment 2
[0129] Embodiment 2. Measuring the thickness of the test piece by the transmission pulse infrared thermal wave technology
[0130] Still using the first stainless steel standard specimen, first obtain the infrared heat map sequence by the transmission experimental scheme, extract the temperature rise curve of each flat-bottomed hole center pixel in the heat map of the stainless steel specimen, and the results are shown in Figure 6 middle. Since the same test piece is used in the transmissive scheme and the reflective scheme in the present invention, the diameter of the flat-bottomed hole is relatively small and the depth of the flat-bottomed hole and the thickness of the test piece have a large difference. There will be certain difficulties, leading to Figure 6 The curves of the two holes of 5-6mm in the center basically have no temperature rise. Therefore, only four holes of 1-4 mm are processed in the following processing. The new time series f is obtained by normalizin...
Embodiment 3
[0131] Embodiment 3. Measuring the thickness of the second layer of the double-layer medium by using the reflective pulsed infrared thermal wave technology
[0132] Using the second standard test piece, one 1.1mm hole is filled with water as a reference hole, and different amounts of water are injected into the other 1.1mm holes for reflective pulsed infrared thermal wave experiments. Extract the cooling curve of the center pixel of the water hole in the heat map of the stainless steel specimen and the corresponding cooling curve of the full water hole as reference curves, and normalize with the first frame. The normalized cooling curve of different water volumes minus the normalized cooling curve of the full water hole is obtained to obtain the thermal contrast curve, and then multiplied by the square root of the corresponding time to obtain the f time series. The sequence S is obtained by taking the integral average of the sequence f A ,Such as Figure 9 shown. choose S ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com