Method for culturing soil aggregate microorganisms in situ
A soil aggregate and in-situ culture technology, which is applied in the field of in-situ culture of soil aggregate microorganisms, can solve the problems of little research on the distribution characteristics of microbial biomass, and achieve the effects of stable microbial properties of soil aggregates, simple operation, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
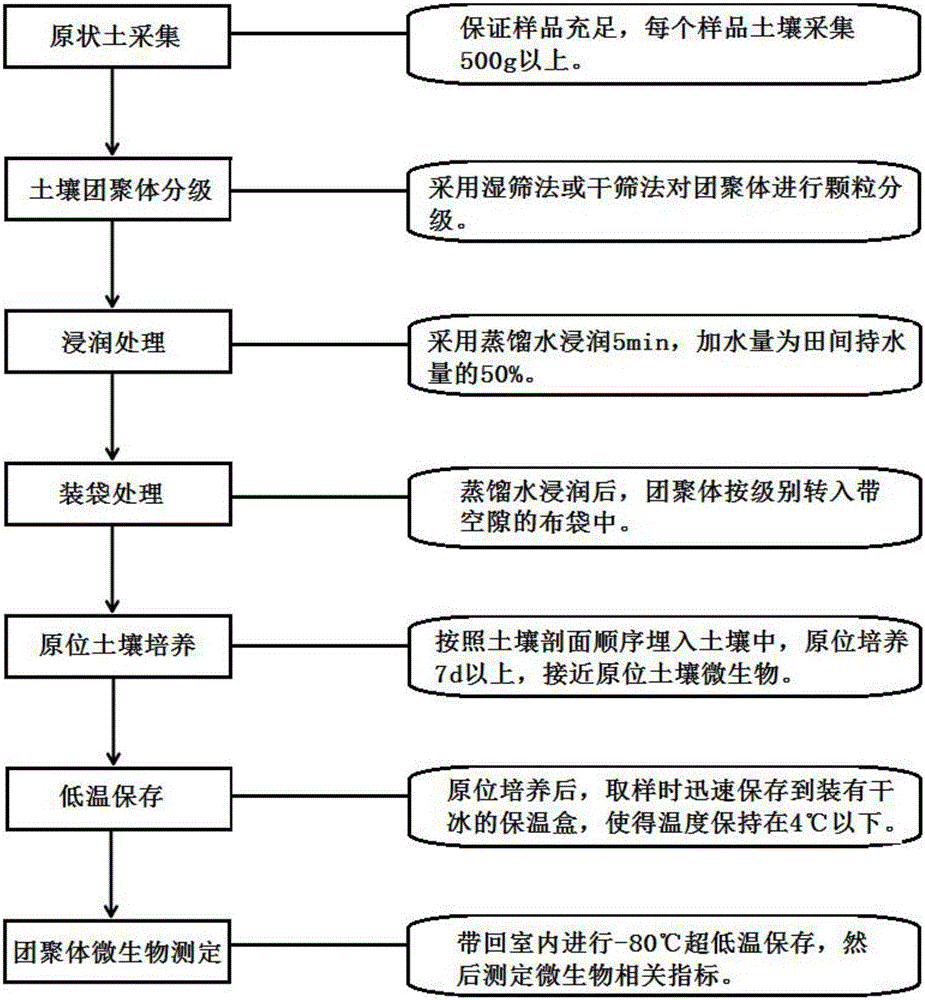
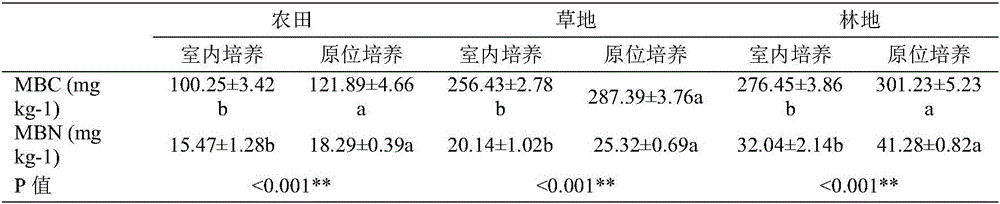
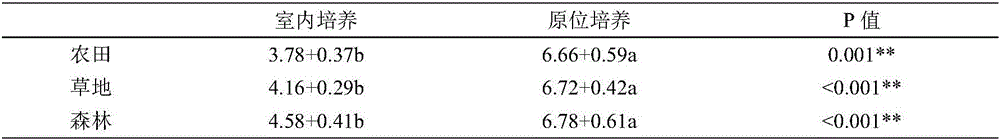
[0038] In the field or in the field, use a cube aluminum fresh-keeping box to collect undisturbed soil samples from top to bottom according to the soil profile, prevent crushing during transportation, and maintain the original structure of the soil; after natural air-drying at room temperature, break it into small soils of about 1cm along the natural cracks piece. When the soil moisture content reaches 8% to 10%, the dry sieve method is used to separate the aggregates of the soil samples according to the grades of >2mm, 0.25~2mm, 0.053~0.25mm, and <0.053mm; the dry sieve method will be used for The graded soil aggregates were spread on the slabs respectively to increase the contact area of distilled water and improve the speed and effect of infiltration. Spray with a watering can, the water volume was 50% of the field water holding capacity, and infiltrated with distilled water for 5 minutes. The agglomerates soaked in distilled water are put into a cloth bag with a pore siz...
Embodiment 2
[0041]In the field or in the field, use a cube aluminum fresh-keeping box to collect undisturbed soil samples from top to bottom according to the soil profile, prevent crushing during transportation, and maintain the original structure of the soil; after natural air-drying at room temperature, break it into small soils of about 1cm along the natural cracks piece. When the soil moisture content reaches 10%, use the wet sieving method to place the air-dried soil sample on the uppermost layer of a set of sieves with apertures of 2mm, 0.25mm and 0.053mm, and adjust the water level of the bucket below the set of sieves to the uppermost sieve The soil sample is just submerged, and then infiltrated with distilled water at room temperature for 5 minutes. The separation of aggregates is carried out by moving the sieve up and down 3 cm, and repeating 50 times within 2 minutes to obtain > 2 mm, 0.25 ~ 2 mm, 0.053 ~ 0.25 mm And <0.053mm four particle size components, which are macroaggreg...
Embodiment 3
[0043] When the soil water content reaches 50%, use the wet sieving method to place the air-dried soil sample on the uppermost layer of a set of sieves with apertures of 2mm, 0.25mm and 0.053mm, and adjust the water level of the bucket under the set of sieves to the uppermost sieve The soil sample is just submerged, and then infiltrated with distilled water at room temperature for 5 minutes. The separation of aggregates is carried out by moving the sieve up and down 3 cm, and repeating 50 times within 2 minutes to obtain > 2 mm, 0.25 ~ 2 mm, 0.053 ~ 0.25 mm And <0.053mm four particle size components, which are macroaggregates, intermediate agglomerates, microaggregates and powder-sticky agglomerates. The agglomerates soaked in distilled water are put into a cloth bag with a pore size of 300 meshes according to the size of the particles, and the bag containing the agglomerates is placed in a dry ice incubator for low temperature preservation. Bury it into the soil according to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com