A kind of preparation method of α-Fe2O3 magnetic nanorod
A magnetic nanorod, -fe2o3 technology, applied in the direction of iron oxide, iron oxide/iron hydroxide, etc., can solve the problems of restricting large-scale industrial production of magnetic nanorods, extremely harsh temperature and other conditions, and high cost of traditional processes. The structure is uniform and controllable, the process is simple and easy to control, and the effect of low equipment requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1: α-Fe 2 o 3 Preparation of Magnetic Nanorods
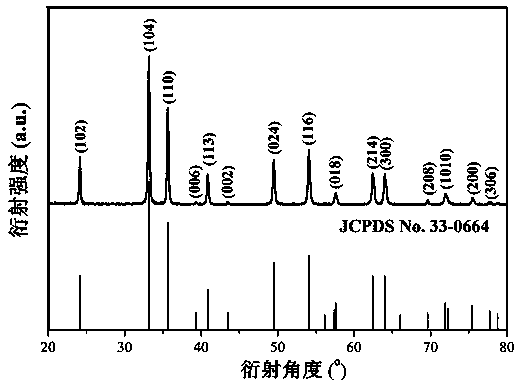
[0021] Prepare FeCl with a concentration of 1.6 mol / L 3 Solution, accurately transfer 50 mL to a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, according to urea and Fe 3+ Accurately weigh urea with a molar ratio of 4:1 and add it into a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, stir to dissolve, heat the solution to 85°C, and stir for 4 h. After centrifugation, the precipitate was washed 5 times with distilled water. After centrifugation, the precipitate was placed in a drying oven, and the precursor was obtained after drying. Grind the precursor, put it into a temperature-programmed resistance furnace for calcination at 400 °C for 4 h, and cool naturally to obtain α-Fe 2 o 3 magnetic nanorods.
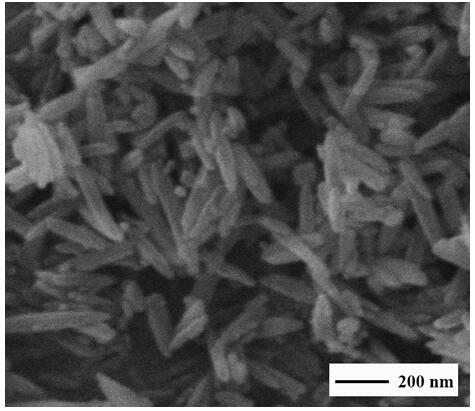
[0022] figure 1 α-Fe prepared for this example 2 o 3 The scanning electron micrograph of the magnetic nanorod can be seen from the electron micrograph that the prepared product is rod-shaped, with uniform appearance and good dispersion. Its rods hav...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Example 2: α-Fe 2 o 3 Preparation of Magnetic Nanorods
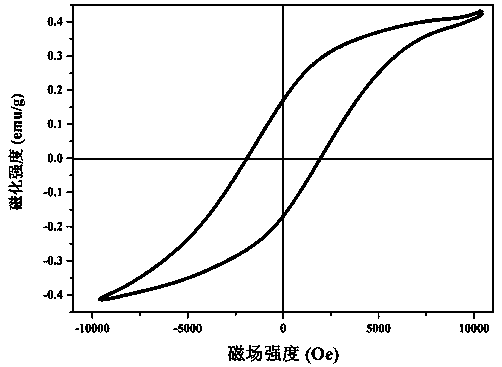
[0026] Fe(NO 3 ) 3 Solution, accurately transfer 50 mL to a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, according to urea and Fe 3+ The molar ratio of urea is 1:1, and the urea is accurately weighed and added to a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, stirred to dissolve, the solution is heated to 70°C, and stirred for 6 h. After centrifugation, the precipitate was washed 5 times with distilled water. After centrifugation, the precipitate was placed in a drying oven, and the precursor was obtained after drying. The precursor was ground, put into a temperature-programmed resistance furnace for calcination at 500 °C for 2 h, and cooled naturally to obtain α-Fe 2 o 3 Magnetic nanorods with a saturation magnetization of 0.45 emu / g.
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3: α-Fe 2 o 3 Preparation of Magnetic Nanorods
[0028] Prepare FeCl with a concentration of 0.5 mol / L 3 Solution, accurately transfer 50 mL to a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, according to urea and Fe 3+ Accurately weigh urea with a molar ratio of 3:1 and add it to a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, stir to dissolve, raise the temperature of the solution to 80°C, and stir for 3 h. After centrifugation, the precipitate was washed 5 times with distilled water. After centrifugation, the precipitate was placed in a drying oven, and the precursor was obtained after drying. Grind the precursor, put it into a temperature-programmed resistance furnace for calcination at 600 °C for 1 h, and cool naturally to obtain α-Fe 2 o 3 Magnetic nanorods with a saturation magnetization of 0.39 emu / g.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com