Method for reducing carbonyl into methylene at normal temperature and normal pressure
A methylene, normal pressure technology, used in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, preparation of amino compounds from amines, etc., can solve the problems of uneconomical environmental protection, easy generation of by-products, and high PMHS prices, and achieves a reduction in Cost, mild conditions, no pollution cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] In the flask, add 1mmol vanillin, 15mL water and 0.02g Pd / CN catalyst, remove the air in the reaction flask, and stir the reaction for 3h under a hydrogen balloon at normal temperature (25°C) and normal pressure to obtain vanillyl alcohol and 4-methylhexanol Genocinol. After the reaction, the catalyst was separated by centrifugation, and the reactants and hydrogenation products were qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed by gas chromatography (GC), and the conversion rate of vanillin and the selectivity of vanillyl alcohol and 4-methylguaiacol were calculated.
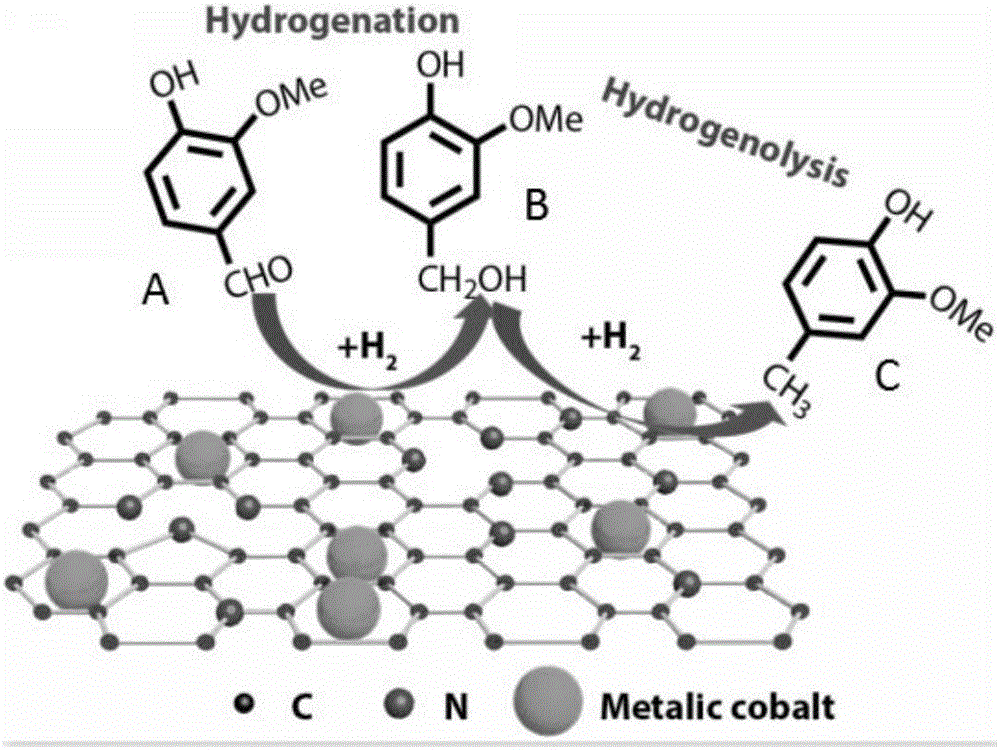
[0033] The schematic diagram of the hydrogenation reduction of vanillin is as follows: figure 1 as shown, figure 1 Among them, A is vanillin, B is vanillyl alcohol, and C is 4-methylguaiacol, from figure 1 It can be seen from the figure that the products of hydrogenation reduction of vanillin include both vanillyl alcohol and 4-methylguaiacol. In order to obtain 4-methylguaiacol with a higher yield, the 4-m...
Embodiment 2-5
[0036] Embodiment 2-5 and embodiment 1 step and operation are identical, only change the solvent that adds, obtain vanillyl alcohol and 4-methylguaiacol, the conversion rate of vanillyl alcohol and vanillyl alcohol and 4-methylguaiacol The selectivity is shown in Table 1:
[0037] Table 1. The results of using different solvents to catalyze the reduction of vanillin
[0038] Example solvent time (h) A conversion rate (%) B selectivity (%) C selectivity (%) 1 water 3 98.3 15.2 78.2 2 ethanol 3 98.7 0 93.9 3 Isopropanol 3 99.7 0 95.0 4 Tetrahydrofuran 3 100 0 >99 5 ethyl acetate 3 100 8.3 89.2
[0039] Experiment 1: Pd / CN catalyst reuse experiment
[0040] The Pd / CN catalyst among the embodiment 4 is separated and used continuously more than ten times by the method in the embodiment 4, and the conversion rate and the selectivity of each test reaction are respectively, and the results are shown in Table 2:...
Embodiment 6-27
[0045] The operations of Examples 6-27 are the same as those of Example 4, but the type and amount of carbonyl compound (substrate), the amount of Pd / CN catalyst, and the reaction time are changed.
[0046] Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the substrate and hydrogenation products were carried out by gas chromatography (GC), and the conversion rate of the substrate and the selectivity of the product were calculated.
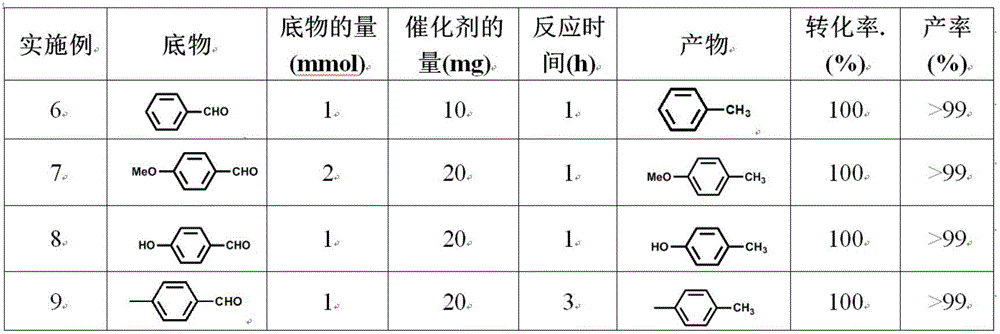
[0047] Table 3 The results of hydrogenation reduction of different substrates
[0048]
[0049]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com