Automatic irrigation control method based on water balance model
A technology of automatic irrigation and control methods, applied in botany equipment and methods, watering devices, climate change adaptation, etc., can solve the problems of inflexible changes, inflexible adjustments, feedback of water changes, etc., to increase control accuracy , fast calculation speed and simple model
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
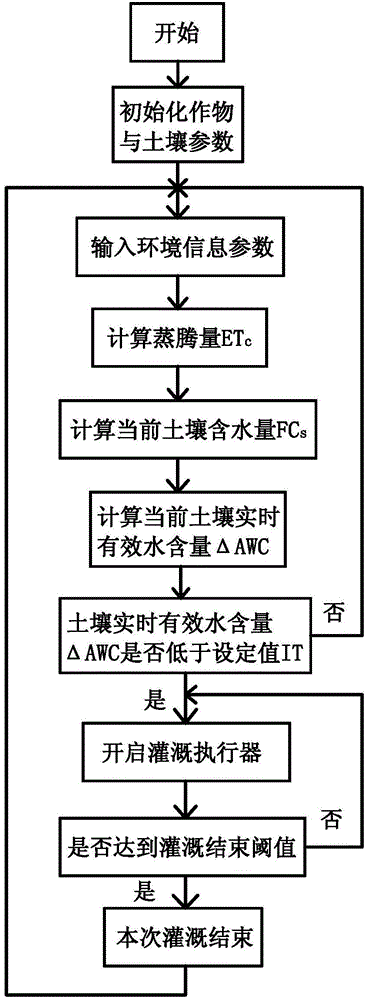
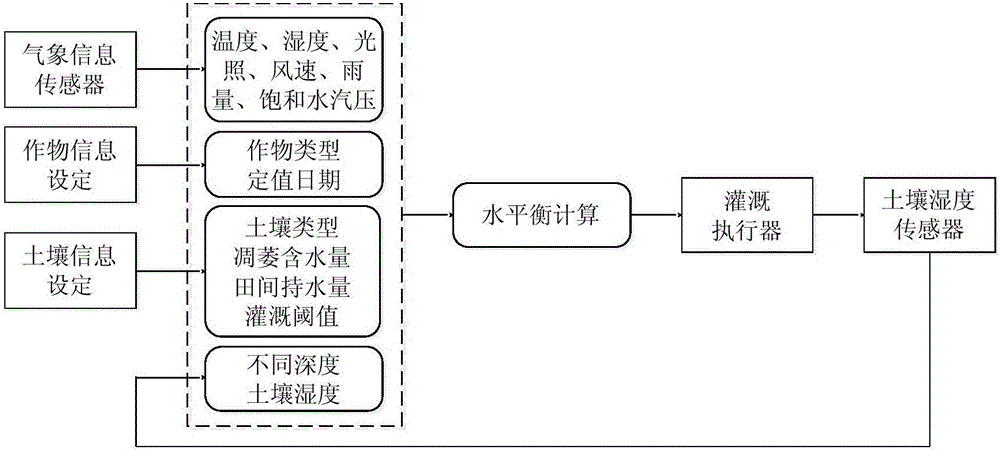
[0030] refer to Figure 1-2 , an automatic irrigation control method based on a water balance model, comprising the following steps:
[0031] A. Initialize the parameters, determine the planting crop category and planting date, and obtain the corresponding crop coefficient K c ; Determine the soil type, and obtain the corresponding wilting water content WP, field water capacity WHC and irrigation threshold IT;
[0032] B. Calculate the current soil moisture content FC through the detection value of the soil moisture sensor parameters s ;
[0033] C. Calculate the current soil effective water content AWC according to the wilting water content WP value corresponding to the soil type;
[0034] D. According to the air temperature, air relative humidity, light radiation intensity, wind speed, rainfall, saturated water vapor pressure, calculate the actual transpiration ET c ;
[0035] E. According to the last irrigation data, precipitation data, and the calculated current soil ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com