Method for preparing formaldehyde-free fiberboard using dialdehyde cellulose
A technology of dialdehyde cellulose and fiberboard, which is used in applications, household components, flat products, etc., can solve the problems of limited application and high production cost, and achieve the effects of moderate price, good physical properties and saving synthesis time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
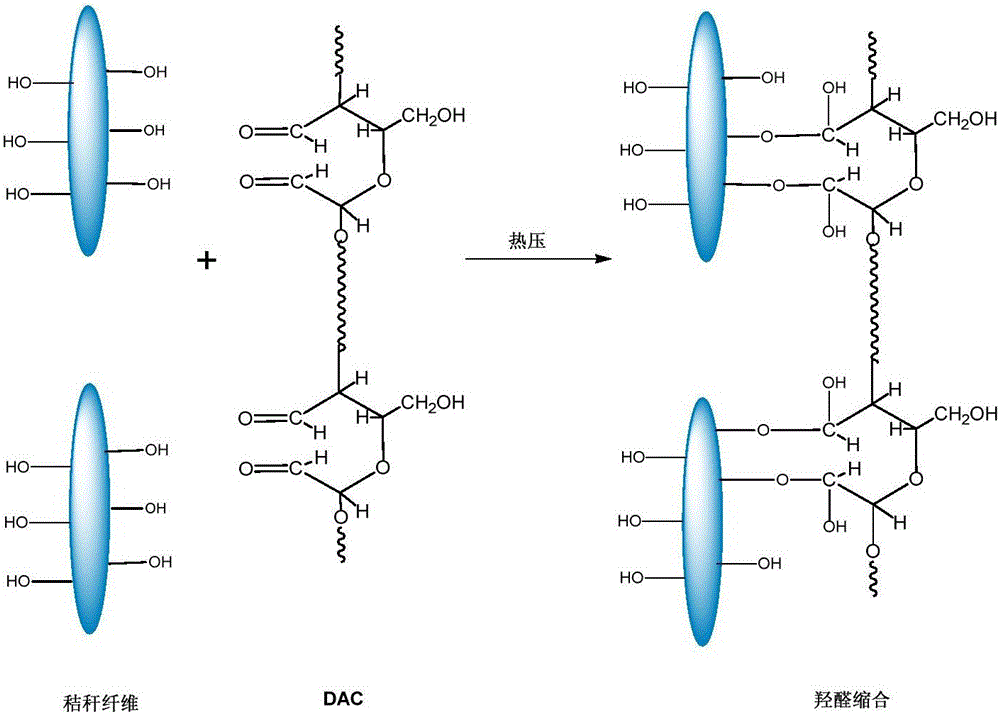
[0021] Formaldehyde-free fiberboard is synthesized from corn stover and dialdehyde cellulose as raw materials.
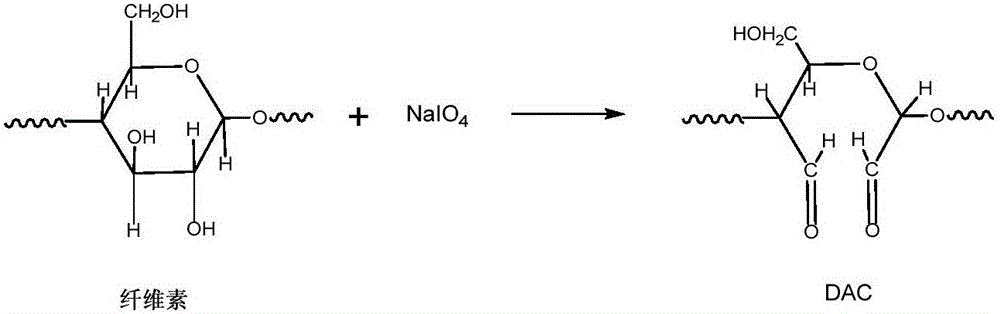
[0022] (1) Preparation of dialdehyde cellulose
[0023] Weigh 2g of absolutely dry bleached softwood pulp cellulose into a 250mL three-necked round bottom flask, add 100mLH 2 O, place the reactor in a constant temperature oil bath, then add 2.37g sodium periodate (analytical purity), and add 0.3mol / L HCl solution to adjust the pH to 2. In order to avoid the decomposition of sodium periodate, the reaction Enter nitrogen as a protective gas and perform shading treatment, and react for 5 hours at a temperature of 45°C. After the reaction is over, 110 mL of 0.1 mol / L ethylene glycol solution is added to react the excess sodium periodate. Vacuum filtration and drying to obtain dialdehyde cellulose.
[0024] (2) Straw pellets
[0025] A mechanical crushing method is used to crush the corn stalks to 75 micron size straw particles.
[0026] (3) Preparation of formaldehyde-free fib...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Formaldehyde-free fiberboard is synthesized from corn stover and dialdehyde cellulose as raw materials.
[0031] (1) Preparation of dialdehyde cellulose
[0032] Weigh 2g of absolutely dry bleached softwood pulp cellulose into a 250mL three-necked round bottom flask, add 100mLH 2 O, place the reactor in a constant temperature oil bath, then add 2.37g sodium periodate (analytical purity), and add 0.3mol / L HCl solution to adjust the pH to 2. In order to avoid the decomposition of sodium periodate, the reaction Enter nitrogen as a protective gas and perform shading treatment, and react for 5 hours at a temperature of 45°C. After the reaction is over, 110 mL of 0.1 mol / L ethylene glycol solution is added to react the excess sodium periodate. Vacuum filtration, drying to obtain dialdehyde cellulose.
[0033] (2) Straw pellets
[0034] A mechanical crushing method is used to crush the corn stalks to 75 micron size straw particles.
[0035] (3) Preparation of formaldehyde-free fiberb...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Formaldehyde-free fiberboard is synthesized from corn stover and dialdehyde cellulose as raw materials.
[0040] (1) Preparation of dialdehyde cellulose
[0041] Weigh 2g of absolutely dry bleached softwood pulp cellulose into a 250mL three-necked round bottom flask, add 100mLH 2 O, place the reactor in a constant temperature oil bath, then add 2.37g sodium periodate (analytical purity), and add 0.3mol / L HCl solution to adjust the pH to 2. In order to avoid the decomposition of sodium periodate, the reaction Enter nitrogen as a protective gas and perform shading treatment, and react for 5 hours at a temperature of 45°C. After the reaction is over, 110 mL of 0.1 mol / L ethylene glycol solution is added to react the excess sodium periodate. After vacuum filtration and drying, the dialdehyde cellulose is obtained.
[0042] (2) Straw pellets
[0043] A mechanical crushing method is used to crush the corn stalks to 70 micron size straw particles.
[0044] (3) Preparation of formalde...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Static bending strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com