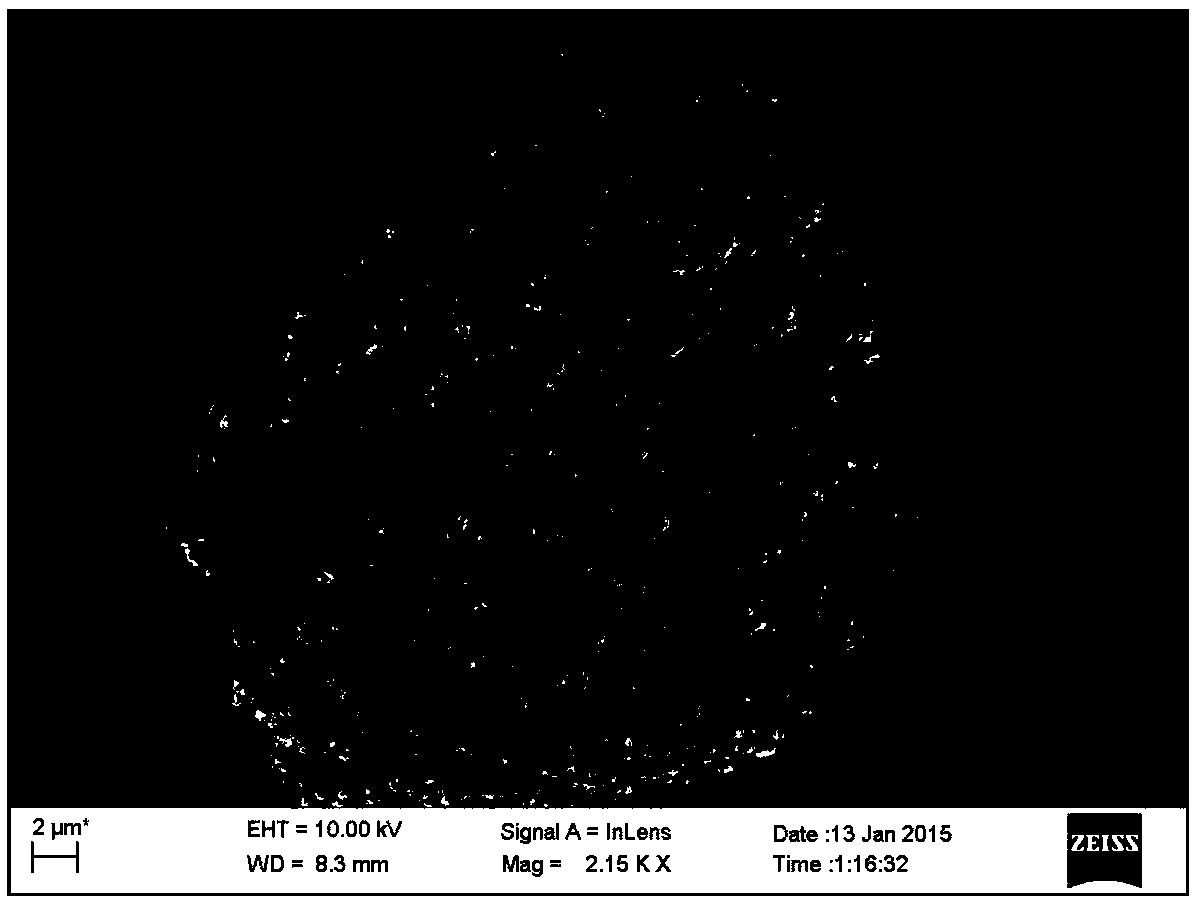
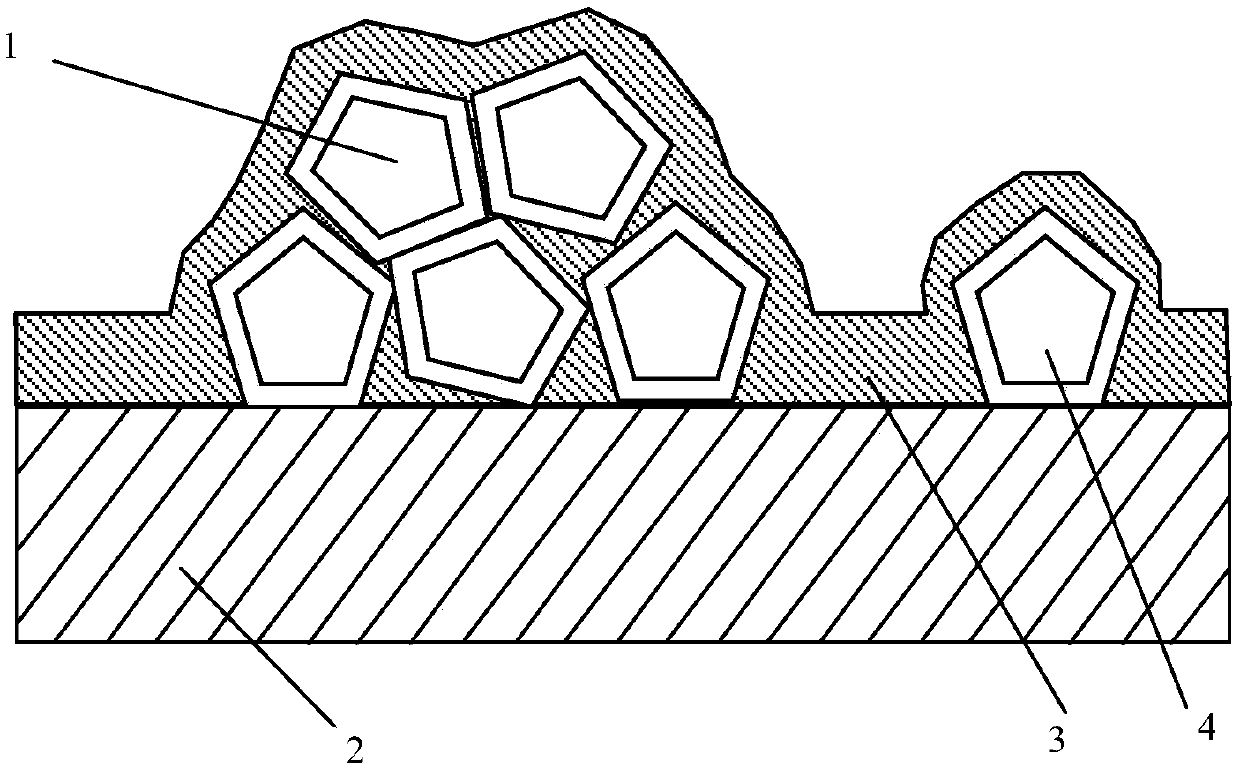
A method of making electroplated superabrasive cutting wire
A technology of superhard abrasives and cutting wires, applied in electrolytic coatings, coatings, etc., can solve the problems of large fluctuations in the diameter of cutting wires, increase costs, and be easily corroded, so as to improve cutting quality, reduce production costs, and improve The effect of production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Embodiment 1: the manufacture of electroplated superabrasive cutting wire with a diameter of 0.08 mm and a diamond particle size of 10 μm
[0044] The first step: the removal of oil and other solid impurities on the surface of diamond abrasive
[0045] First put the diamond abrasive into 20wt% NaOH solution to soak for degreasing, clean with water, then soak the diamond abrasive in 30% nitric acid solution to remove solid impurities on the surface, then rinse with water.
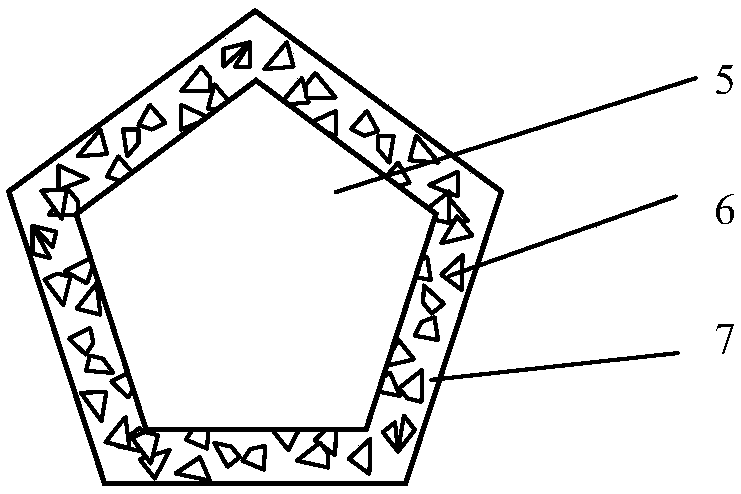
[0046] The second step: the diamond surface is chemically composite plated with a nickel-phosphorus alloy layer (7) containing solid particles (6)
[0047] The diamond abrasive treated in the first step is plated with a nickel-phosphorus alloy layer (7) containing solid particles (6) by chemical composite plating, and the diamond abrasive is chemically composite-plated with nickel-phosphorus alloy containing solid particles (6) After layer (7), the weight gain is 60%; the formula and process conditio...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2: the manufacture of the electroplated superabrasive cutting wire with a diameter of 0.18 mm and a diamond particle size of 30-40 μm
[0056] The first step: the removal of oil and other solid impurities on the surface of diamond abrasive
[0057] First put the diamond abrasive into 15wt% NaOH solution to soak for degreasing, clean with water, then soak the diamond abrasive in 35% nitric acid solution to remove solid impurities on the surface, then rinse with water.
[0058] The second step: the diamond surface is chemically composite plated with a nickel-phosphorus alloy layer (7) containing solid particles (6)
[0059] The diamond treated in the first step is coated with a nickel-phosphorus alloy layer (7) containing solid particles (6) by chemical composite plating, and the diamond abrasive is chemically composite-plated with a nickel-phosphorus alloy layer containing solid particles (6). (7) Post-weight gain of 35%; the formula and process conditions of...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Example 3: Manufacture of an electroplated superabrasive cutting wire with a baseline diameter of 0.37 mm and a particle size of cubic boron nitride of 50-60 μm
[0068] The first step: removal of oil and other solid impurities on the surface of cubic boron nitride abrasive
[0069] First put the cubic boron nitride abrasive into 10wt% NaOH solution to soak for degreasing, wash with water, then soak the cubic boron nitride abrasive in 35% nitric acid solution to remove solid impurities on the surface, and then rinse with water.
[0070] The second step: the surface of cubic boron nitride is chemically composite plated with a nickel-phosphorus alloy layer (7) containing solid particles (6)
[0071] The cubic boron nitride treated in the first step is plated with a nickel-phosphorus alloy layer (7) containing solid particles (6) by chemical composite plating, and the cubic boron nitride abrasive contains solid particles (6) through chemical composite plating. ) after the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com