Comparison identifying method for dendrobium huoshanense and dendrobium hercoglossum
A technology of Dendrobium huoshanense and Dendrobium dendrobii is applied in the field of comparison and identification of Dendrobium huoshanense and Dendrobium dendrobii, which can solve problems such as unfavorable on-site detection, long time consumption, and the use of large-scale instruments.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1, the preparation and use method of the kit for identifying Dendrobium Huoshanense
[0025] 1. Design and synthesis of primer pairs for identification of Dendrobium huoshanense
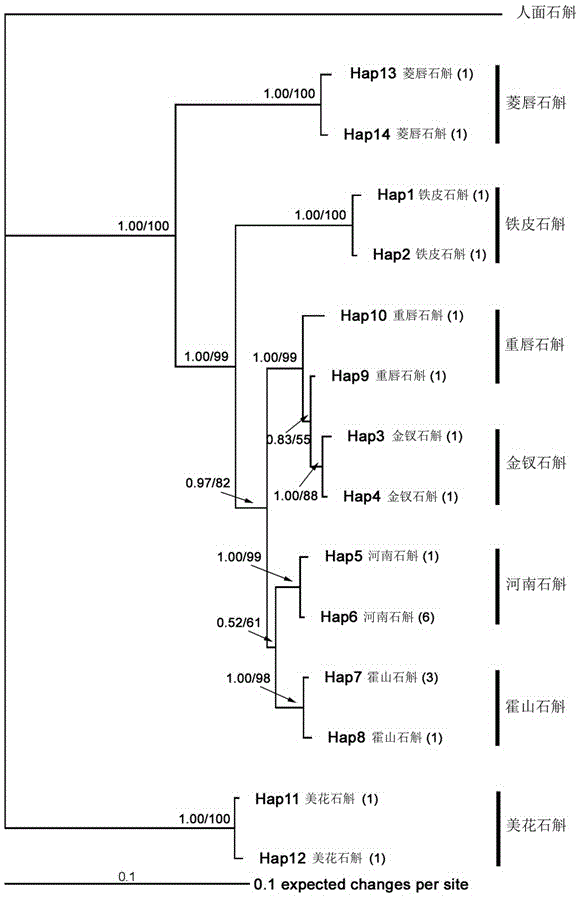
[0026] The ITS sequences of Dendrobium Huoshanense and its obfuscated products were obtained from GenBank or sequenced in this study, as shown in Table 1 below. Among them, the haplotype sequences (including Hap5, Hap6 and Hap7) obtained by sequencing in this study are shown in sequence 4 to sequence 6 in the sequence listing.
[0027] Table 1 ITS sequences of Dendrobium Huoshanense, Dendrobium heavy lip and some similar species
[0028] Numbering
sample name
Number of samples
Login ID
The serial number obtained in this study
1
Dendrobium officinale Dendrobium
catenatum
1
Hap1
KP743543
2
Dendrobium officinale Dendrobium
catenatum
1
Hap2
KF143439
3
Dendrob...
Embodiment 2
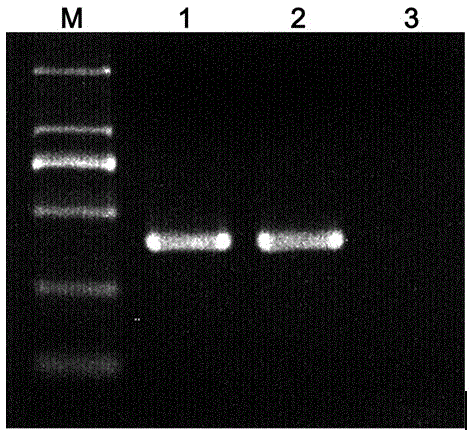
[0045] Embodiment 2, using the kit prepared in Example 1 to identify the specificity analysis of Dendrobium Huoshanense
[0046] Samples to be tested: Dendrobium Huoshanense (collected from Anhui) and Dendrobium double-lipped (collected from Guangxi). All of them conformed to the description of the identification characteristics in Flora of China and related literature. Through identification, the physical objects of each sample are consistent with the names, and the quality meets the standards.
[0047] 1. Extract genomic DNA from the sample to be tested
[0048] About 50 mg of dry samples were taken respectively (of course, 100 mg of fresh samples can also be used for genomic DNA extraction), and total DNA was extracted by CTAB method. details as follows:
[0049] Put the dry medicinal material without mildew in a pulverizer to grind and pulverize, and pass through a 40-mesh sieve. Transfer the powder to a 2.0 mL microcentrifuge tube and add 900 µL of sterilized CTAB ext...
Embodiment 3
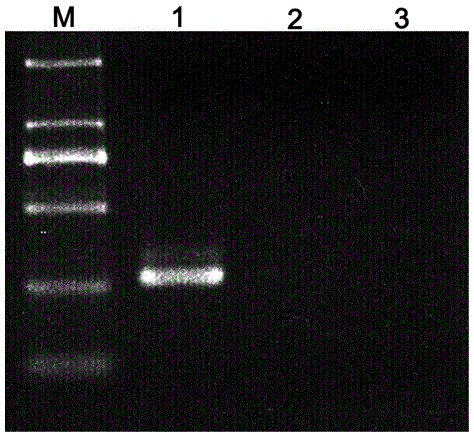
[0060] Embodiment 3, using the kit prepared in Example 1 to identify the sensitivity analysis of Dendrobium Huoshanense
[0061] Sample to be tested: Huoshan Dendrobium (collected in Anhui). Through the identification, the actual sample is consistent with the name, and the quality meets the standard.
[0062] 1. Extract genomic DNA from the sample to be tested
[0063] Take about 50 mg of dry samples (of course, 100 mg of fresh samples can also be used for genomic DNA extraction), and use CTAB method to extract total DNA. For specific operations, refer to Step 1 of Example 2.
[0064] 2. PCR amplification
[0065] The genomic DNA extracted from Dendrobium Huoshanense in Step 1 was serially diluted to obtain genomic DNA concentrations of 143 ng / μl, 71 ng / μl, 36 ng / μl, 18 ng / μl, 9 ng / μl, and 4 ng / μl, respectively. The serial dilutions of μl and 2 ng / μl were respectively used as templates, and the primer pair designed in Step 1 of Example 1 (upstream primer CP6s and downstrea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com