Method for producing ultralow-sulfur gasoline
An ultra-low sulfur gasoline technology, applied in the petroleum industry, hydrocarbon oil treatment, hydrotreating process, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing olefin saturation rate, reducing device energy consumption, and reducing waste lye discharge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
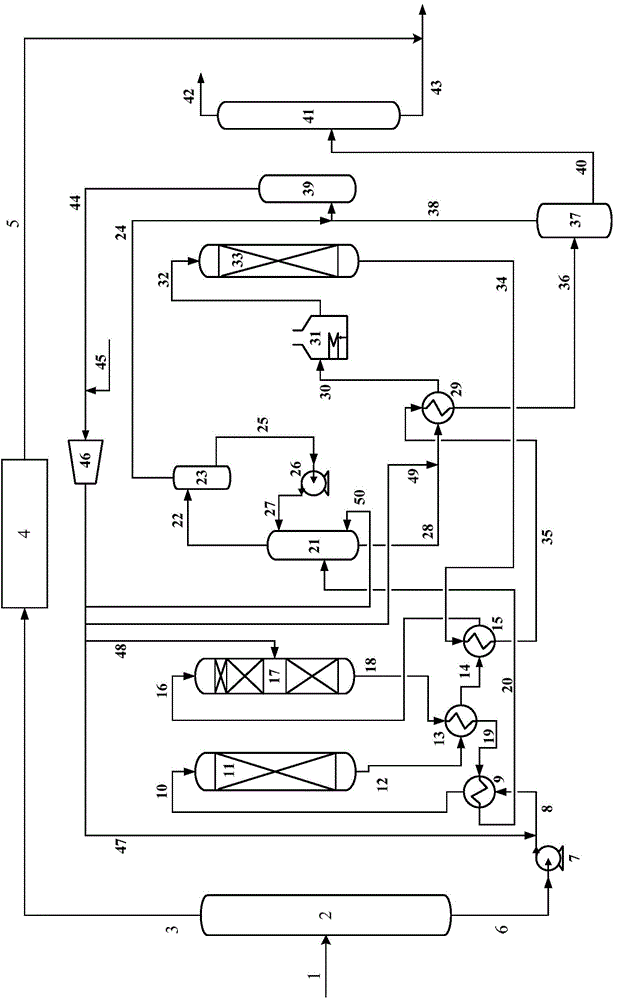
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
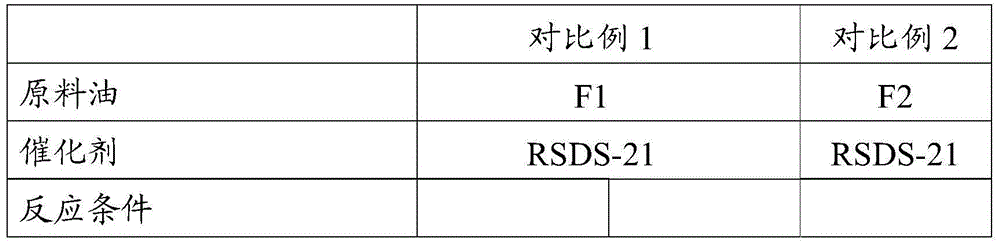
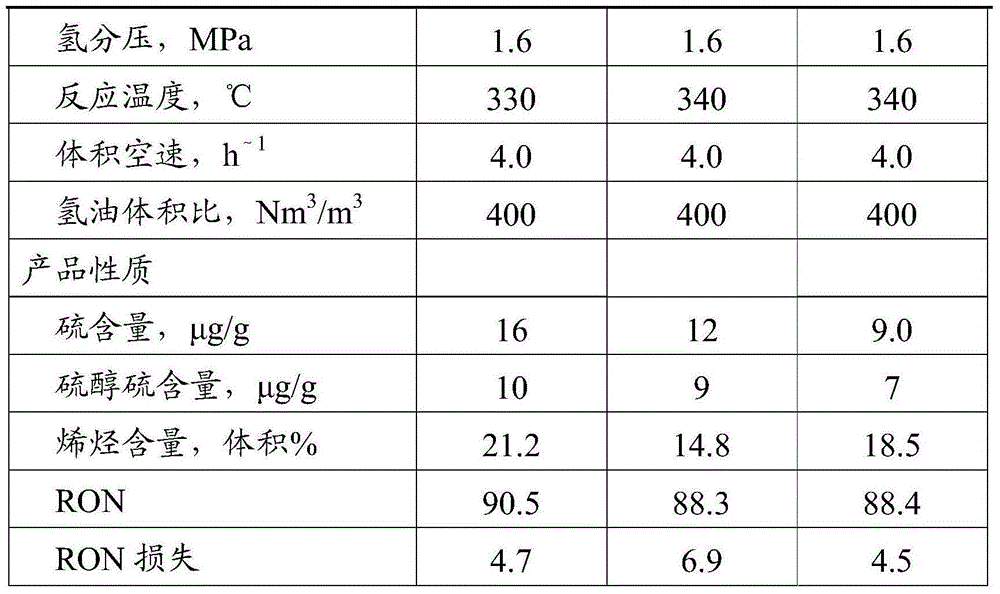
[0050] The same raw material oil F1 as in Comparative Example 1 was used. The feed oil F1 is first cut into light gasoline fraction and heavy gasoline fraction in fractionation unit, wherein the proportion of light gasoline fraction is 35% by weight, and the proportion of heavy gasoline fraction is 65% by weight. Alkaline extraction sweetening of light gasoline fraction. Heavy gasoline fractions undergo selective hydrodesulfurization. The first hydrogenation reactor is filled with fresh catalyst C1, the second hydrogenation reactor is filled with fresh catalyst C2, and the third reactor is filled with fresh catalyst C3. The catalyst in each reactor is sulfided. After the sulfidation is completed, the heavy fraction of the raw material oil F1 is mixed with hydrogen and enters the first and second hydrogenation reactors to contact with catalysts C1 and C2, respectively, to carry out selective hydrodediene reaction and selective hydrodesulfurization reaction; The effluent from...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The same raw material oil F2 as in Comparative Example 2 was used. The feed oil F2 is first cut into light gasoline fraction and heavy gasoline fraction in fractionation unit, wherein the proportion of light gasoline fraction is 30% by weight, and the proportion of heavy gasoline fraction is 70% by weight. Alkaline extraction sweetening of light gasoline fraction. Heavy gasoline fractions undergo selective hydrodesulfurization. Catalyst C1 is filled in the first hydrogenation reactor of the heavy gasoline hydrogenation unit; the catalyst combination C2 / C3 is filled in the second hydrogenation reactor, and the volume ratio of C2 and C3 in the reactor is C2:C3=80:20; The catalyst C3 is loaded in the third hydrogenation reactor. The catalyst in each reactor is sulfided. After the sulfidation is completed, the heavy fraction of the raw material F2 is mixed with hydrogen and enters the first and second hydrogenation reactors to contact with catalysts C1, C2 / C3, respective...
Embodiment 3
[0059] A kind of catalytic cracking gasoline is used as raw material oil F3. The feed oil F3 is first cut into light gasoline fraction and heavy gasoline fraction in fractionation unit, wherein the proportion of light gasoline fraction is 25% by weight, and the proportion of heavy gasoline fraction is 75% by weight. Alkaline extraction sweetening of light gasoline fraction. Heavy gasoline fractions undergo selective hydrodesulfurization. Catalyst C1 is filled in the first hydrogenation reactor of the heavy gasoline hydrogenation unit; the catalyst combination C2 / C3 is filled in the second hydrogenation reactor, and the volume ratio of C2 and C3 in the reactor is C2:C3=85:15; The catalyst combination C2 / C3 is loaded in the third hydrogenation reactor, and the volume ratio of C2 and C3 in the reactor is C2:C3=85:15. The catalyst in each reactor is sulfided. After the sulfidation is completed, the heavy fraction of the raw material F3 is mixed with hydrogen and enters the firs...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com