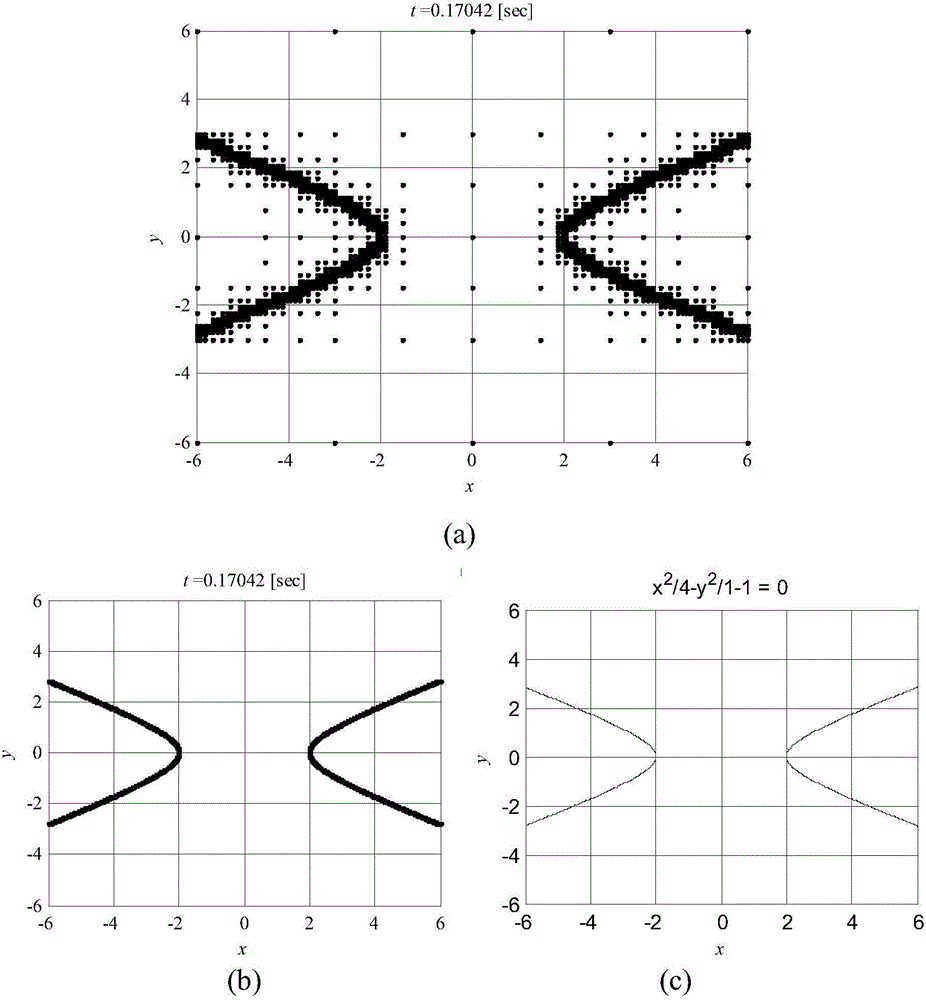
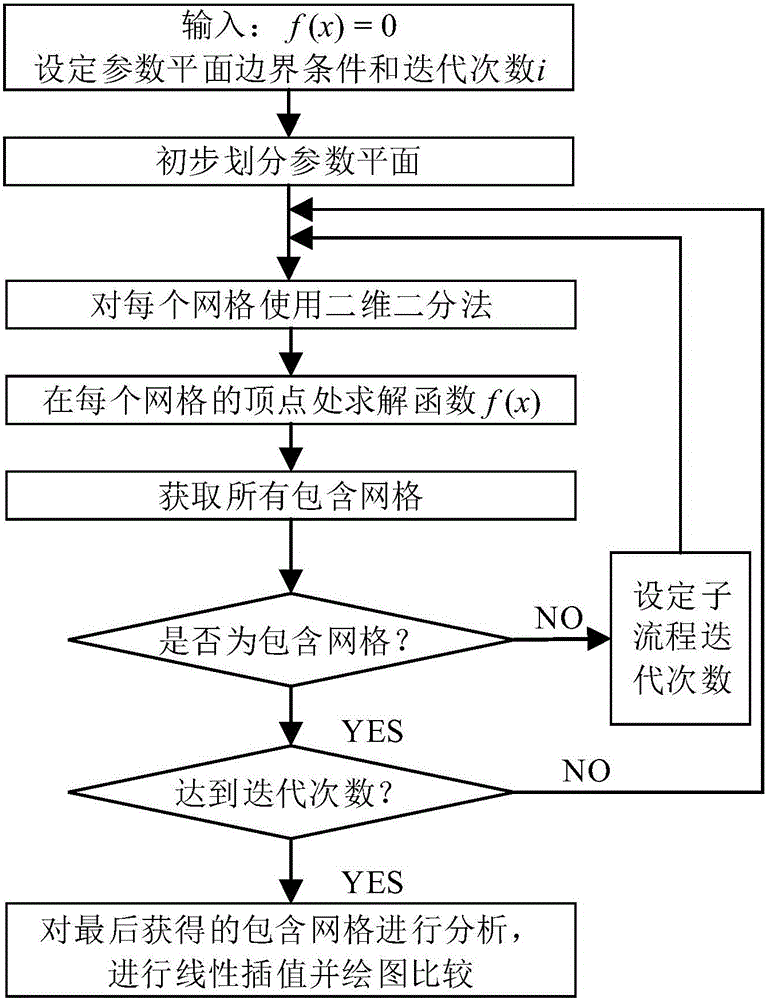
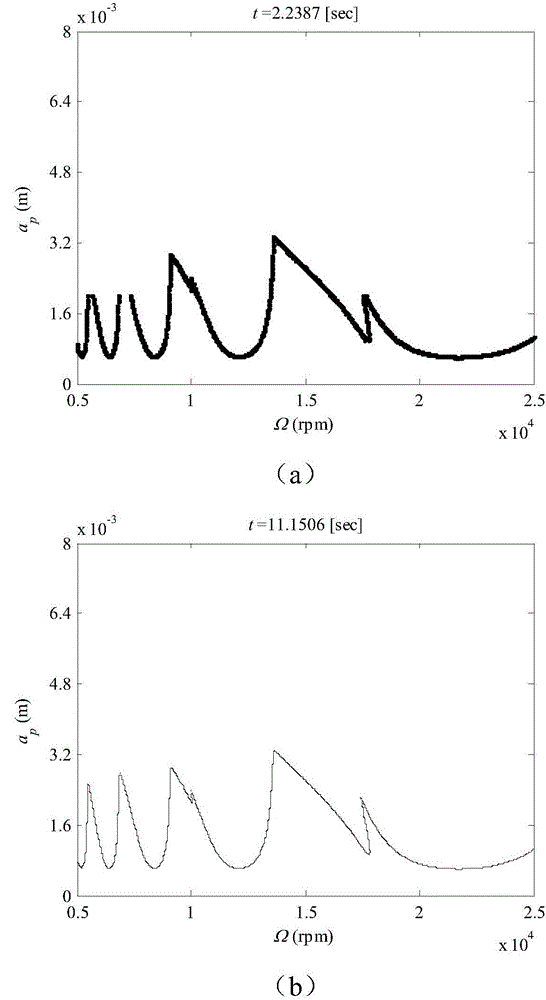
A dichotomy-based machine tool machining stability boundary rapid solving method
A stability and dichotomy technology, applied in the field of fast solution of machine tool machining stability boundary based on dichotomy, can solve problems such as difficult to meet actual engineering needs, numerical integration method calculation speed is not fast enough, calculation time is long, etc., to achieve process parameters High-speed and high-precision machining, moderate precision, and the effect of reducing calculation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] This embodiment is a single-degree-of-freedom system, and the milling stability is solved according to the method of the present invention, and its steps are:
[0066] (1) Set the parameter plane, the parameter plane is: the x-axis is the milling speed Ω (rpm), the upper and lower boundaries are 5000rpm-25000rpm, and the y-axis is the milling depth a p (m), the upper and lower boundaries are 0-0.008m; the function f(x) is the maximum value of the absolute value of the characteristic root of the judgment stability matrix minus 1; set the radial depth of cut a / D=0.50; set the number of iterations i=5. Other related parameters: number of milling cutter teeth N=2; tangential cutting force coefficient K t =6×10 8 (N / m 2 ); normal cutting force coefficient K n =2×10 8 (N / m 2 ); system natural frequency f n =922(Hz); relative damping ζ=0.011; model mass m t= 0.03993 (kg); in the numerical integration method, the initial discrete number n = 20; then, the entire paramete...
example 2
[0074] This embodiment is a two-degree-of-freedom system, and the milling stability is solved according to the method of the present invention, and its steps are:
[0075] (1) Set the parameter plane, the parameter plane is: the x-axis is the milling speed Ω (rpm), the upper and lower boundaries are 5000rpm-25000rpm; the y-axis is the milling depth a p (m), the upper and lower boundaries are 0-0.008m; the function f(x) is the maximum value of the absolute value of the characteristic root of the judgment stability matrix minus 1; set the radial depth of cut a / D=0.50; set the number of iterations i=4. Other parameters: number of milling cutter teeth N=2; tangential cutting force coefficient K t =6×108(N / m 2 ); normal cutting force coefficient K n =2×108(N / m 2 ); system natural frequency ω x = ω y =922(Hz); relative damping ζ x =ζ y =0.011; model mass m x = m y =0.03993(kg); the initial discrete number in the numerical integration method is n=15; then the entire paramet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com