Pulse sensor capable of calibrating static force and pulse collection device
An acquisition device and sensor technology, which is applied in the field of medical instruments, can solve the problems of sensor probe displacement, large temperature influence, and poor repeatability of static force, etc., and achieve accurate three-dimensional tactile information acquisition, accurate static force measurement, and dynamic force detection. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
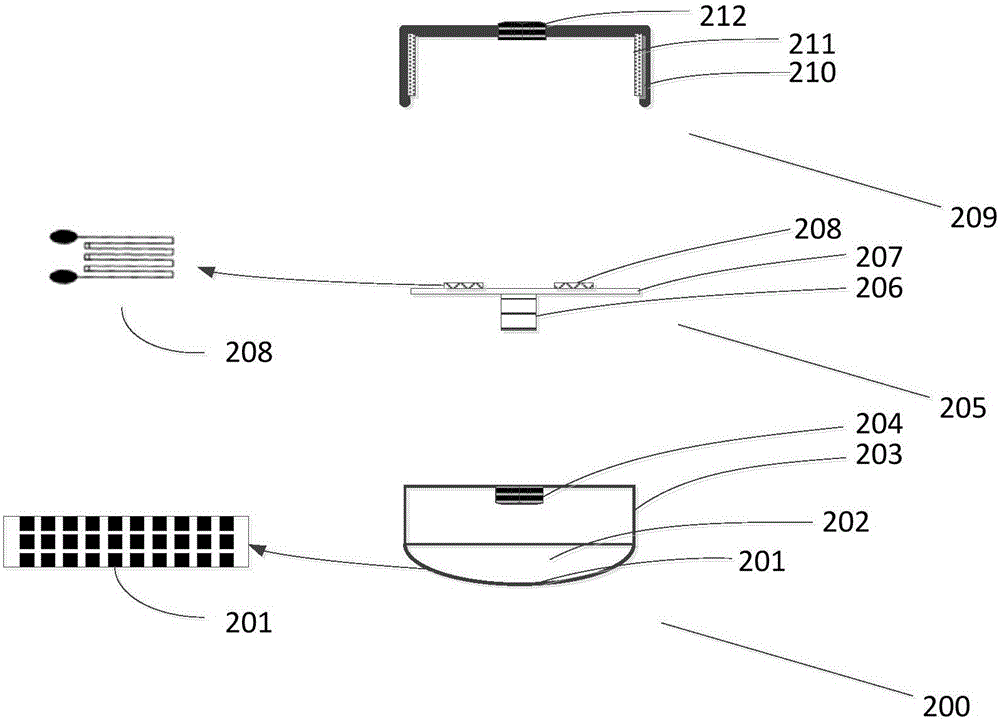
[0043] figure 2 It is a structural schematic diagram of a pulse sensor combined with a strain sensor and a flexible array sensor. Among them, the flexible array sensor is a dynamic force sensor, and the strain sensor is a static force sensor.
[0044] Specifically, the pulse condition sensor includes a flexible array sensor 200 , a strain sensor elastic body 205 and a strain sensor housing 209 . Wherein, the flexible array sensor 200 includes a flexible sensor film 201 , a soft filler 202 and a flexible array sensor housing 203 .
[0045] The flexible sensor film 201 is arranged at the bottom of the flexible array sensor housing 203, and a plurality of pressure-sensing contact points are distributed on the flexible sensor film 201. When in use, the flexible sensor film 201 is attached to the wrist of the human body to perform dynamic force and three-dimensional tactile information. Measurement. Implementations of the flexible sensor film 201 include PVDF films, piezoelectr...
Embodiment 2
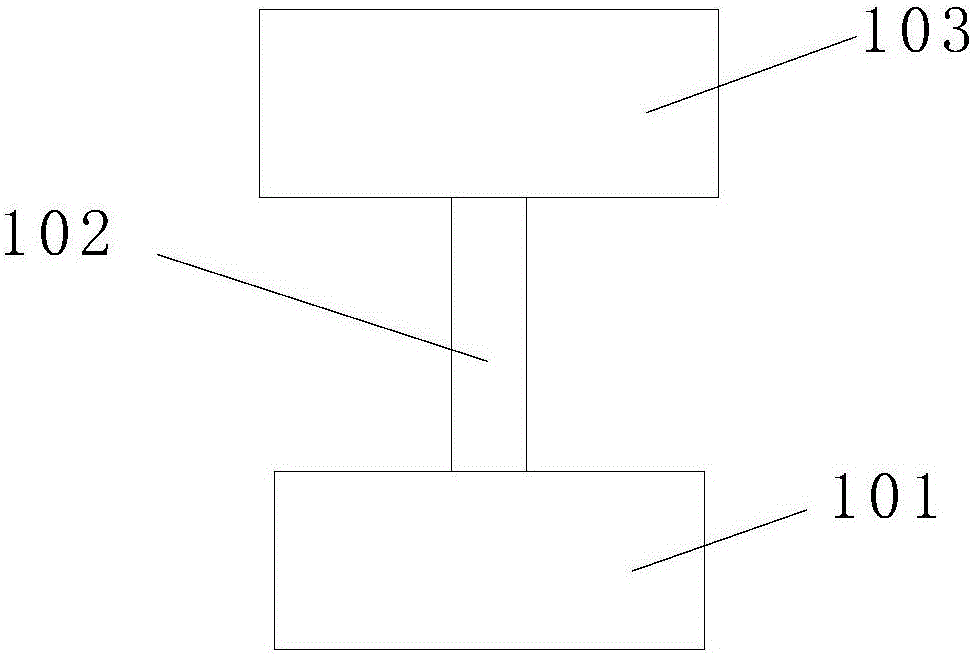
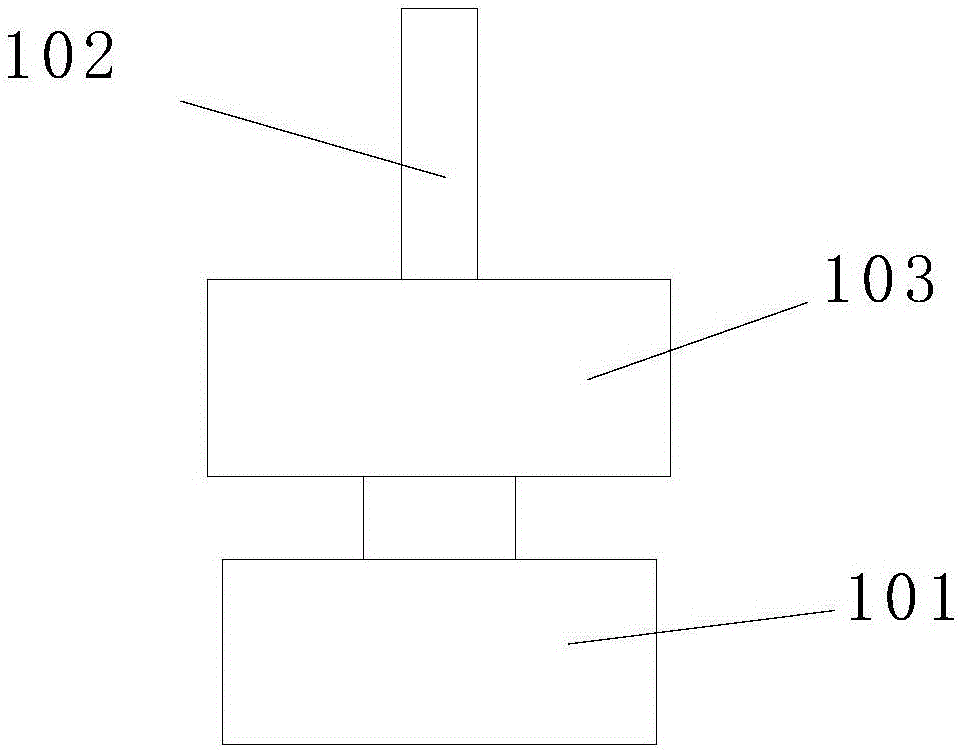
[0054] Figure 3a-3b These are two deformation structures based on Embodiment 1. A spring 102 is added to the pulse condition sensor shown in Embodiment 1, wherein the spring is a buffer assembly.
[0055] Spring 102 has two kinds of assembly methods: the first assembly method is as Figure 3a As shown, the two ends of the spring 102 are respectively screwed on the internal thread 204 at the top center of the flexible array sensor housing 203 and the external thread of the screw rod 206 to achieve elastic fixing of the flexible array sensor 200 and the elastic body 205 of the strain sensor. The second assembly method is as Figure 3b As shown, the screw 206 of the strain sensor elastic body 205 is screwed into the internal thread 204 provided on the top of the flexible array sensor housing 203 to realize the rigid fixation of the flexible array sensor 200 and the strain sensor elastic body 205; one end of the spring 102 It is screwed into the internal thread 212 of the strai...
Embodiment 3
[0059] This embodiment provides another way of implementing static force measurement in combination with strain gauge sensors and flexible array sensors: using existing industrial standard load cells or tension pressure sensors on the market for static force measurement, used to Replacing the strain sensor in Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 and combining it with the flexible array sensor in Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 can also achieve the effect of Embodiment 1, and the structural design is simpler.
[0060] Figure 4 The example in which the tension pressure sensor is an S-type tension pressure sensor 301 is given in , but those skilled in the art know that the strain gauge pressure sensor is not limited to this type, for example, it can also be a cantilever type, a spoke type, a plate ring type, Bellows type, bridge type, cylinder type and other styles.
[0061] There are threaded holes 302 on the top and bottom of the S-type tension pressure sensor 301 . The flexible arra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com