Probe for nucleic acid enriching capture and design method thereof
A probe and nucleic acid technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/testing, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to capture complementary strand nucleic acid libraries, mutation frequency deviation of sequencing results, capture copy number loss, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of improving specificity, increasing original copy number, and improving capture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
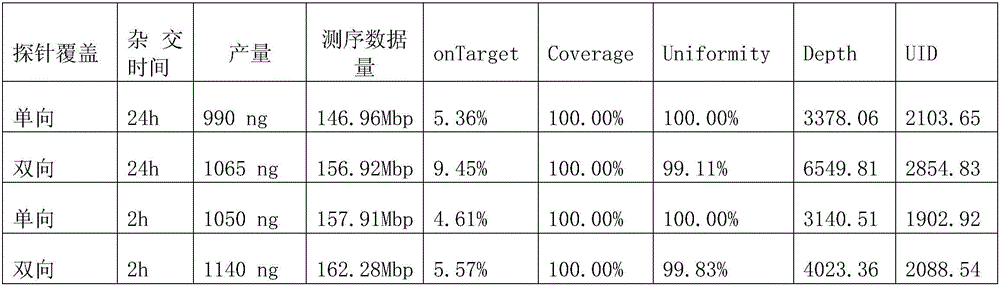
[0033] Example 1: The effect of bidirectional probes on the onTarget rate of different GC content fragments
[0034] Take 6 genome segments (Homo sapiens, Release 19(GRCh37.p13)
[0035]chr2:29446476-chr2:29446775; chr2:29447226-chr2:29447525;
[0036] chr2:29448065-chr2:29448364; chr6:117642641-chr6:117642940;
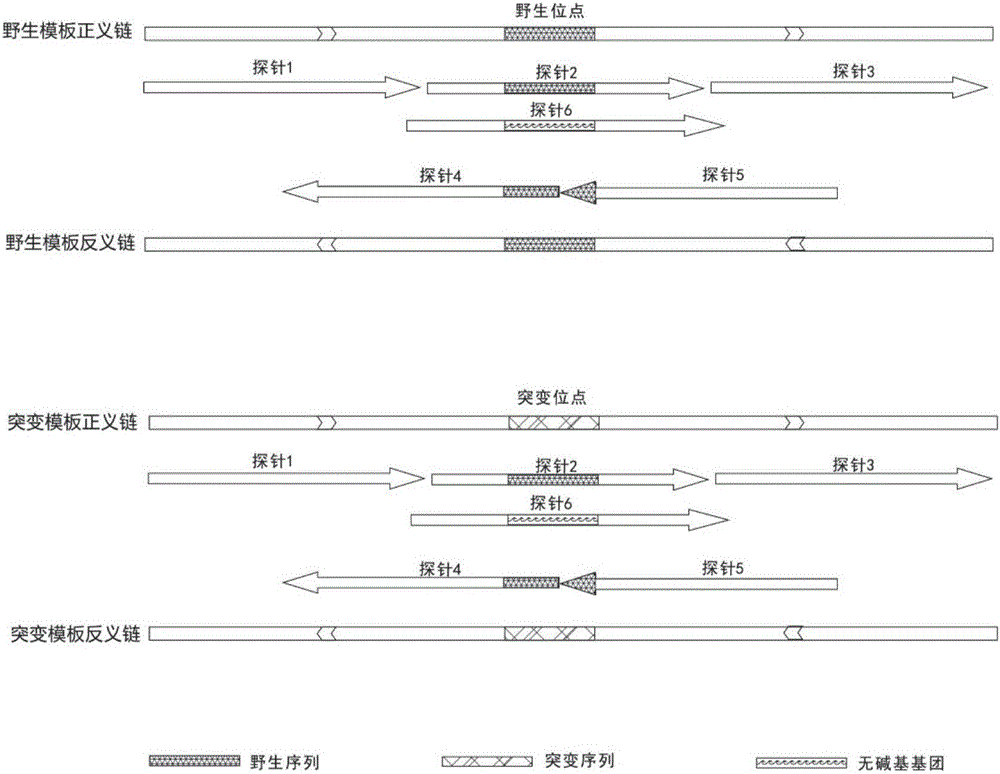
[0037] chr6:117645323-chr6:117645622; chr6:117641038-chr6:117641337), carry out probe design: unidirectional probe 3 times overlapping coverage, or bidirectional probe dislocation coverage; probe length is 59bp, probe 3' end Modified for Biotin. There are many specific probe sequences. Taking Homo sapiens, Release 19 (GRCh37.p13) chr2:29446476-chr2:29446775 segment as an example, 5 unidirectional probes are listed, which are SEQ ID NO: 1-5; 5 needles, which are SEQID NO:6-10. Take 30 ng of leukocyte DNA each, build a library with KAPA kit, and use hybridization reagents for 2h and 24h hybridization capture. The hybridization capture uses the SeqCap EZ Hybridizatio...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2, the impact of bidirectional probes on the onTarget rates of different chromosomes
[0043] Take 5 genome segments Homo sapiens, Release 19 (GRCh37.p13) chr2: 29446201-29448364, chr7: 55241635-55241748, chr7: 55242396-55242539, chr7: 55249029-552549107, chr7: 2792 probe as follows; Design: Non-overlapping coverage of unidirectional probes and coverage of bidirectional misplaced probes. The probe length is 35-80bp and the Tm of the probe is 72-78°C, and the 3' end of the probe is modified with Biotin. There are many specific probe sequences. Taking Homo sapiens, Release 19 (GRCh37.p13) chr2: 29446201-29448364 segment as an example, 5 unidirectional probes are listed, which are SEQ ID NO: 11-15; 5 bidirectional probes are listed The bar is SEQ ID NO:16-20, see Table 2. Take 30 ng of leukocyte DNA, build a library with KAPA kit, and use hybridization reagents to perform a hybridization capture for 2 hours. The hybridization capture uses the SeqCap EZ Hybridizat...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3, the influence of bidirectional probe on UID
[0048] Take multiple genome segments for probe design. Multiple genome segments include exon 31, intron 31, and exon 32 of the ROS1 gene and exon 19 of the EGFR gene, etc., and carry out the following scheme Unique probe design: 3-fold overlapping coverage of unidirectional probes, misplaced coverage of bidirectional probes, the length of the probes is 59bp, and the 3' end of the probes is modified with Biotin. After software analysis and test results, probes containing repetitive sequences are eliminated . There are many specific probe sequences, taking exon 19 of the EGFR gene as an example, Homo sapiens, Release 19 (GRCh37.p13) chr7: 55242415-55242513, listed 5 unidirectional probes that are finally applicable to the reference sequence, SEQ ID NO:21-25, enumerates 4 bidirectional probes that are finally applicable to the reference sequence, SEQ ID NO:26-29; taking exon 31, intron 31 and exon 32 of the ROS1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com