Electromechanical rotational damper with tension and compression stop
A technology of rotating shock absorbers and shock absorbers, applied in non-rotating vibration suppression, springs/shock absorbers, mechanical equipment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
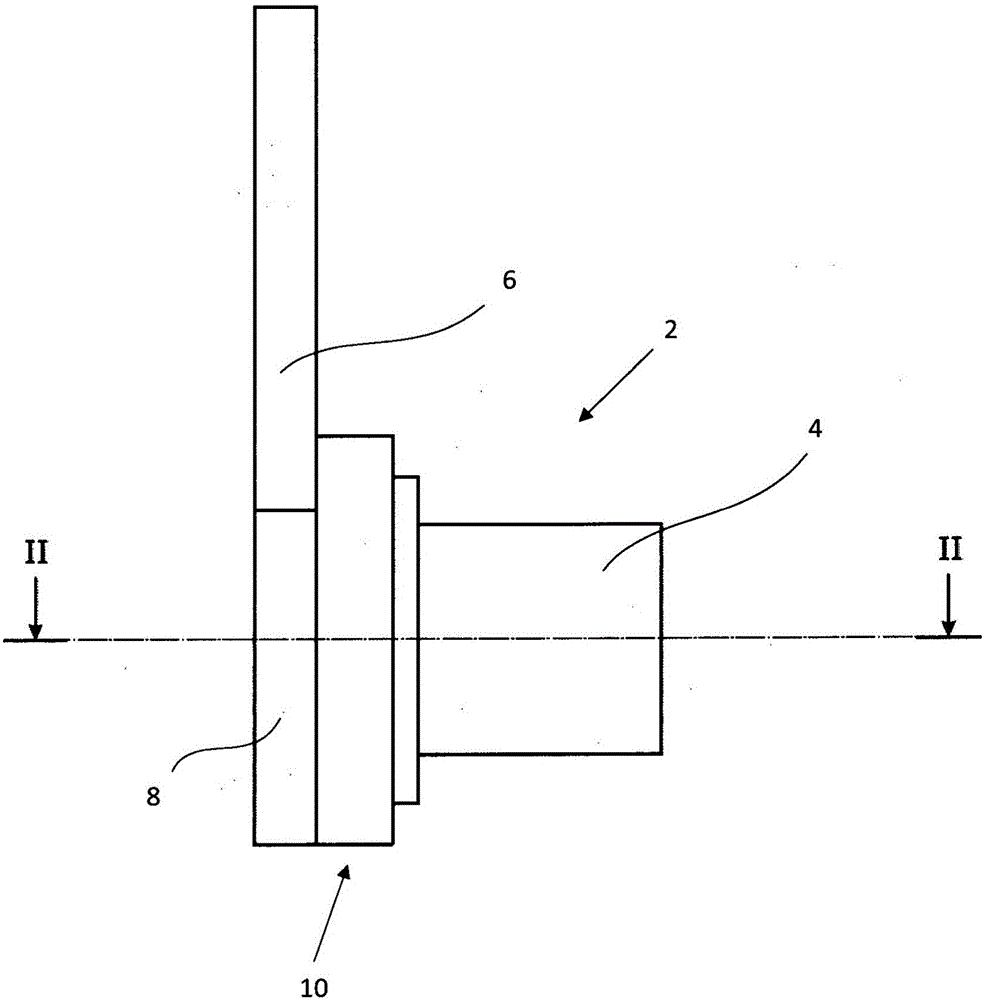
[0023] figure 1 A side view of a torsional vibration damper 2 is shown, which has a damper housing 4 fastened to a mass, the wheel suspension, by fasteners (not shown) or on the vehicle body. The articulated rod 6 is mounted pivotably relative to the shock absorber housing 4 and is connected to a second mass, ie the vehicle body or the wheel suspension. The articulated rod 6 is connected to a housing cover 8 , which is rotatably mounted on the shock absorber housing 4 . A harmonic drive 10 is arranged between the damper housing 4 and the housing cover 8 .
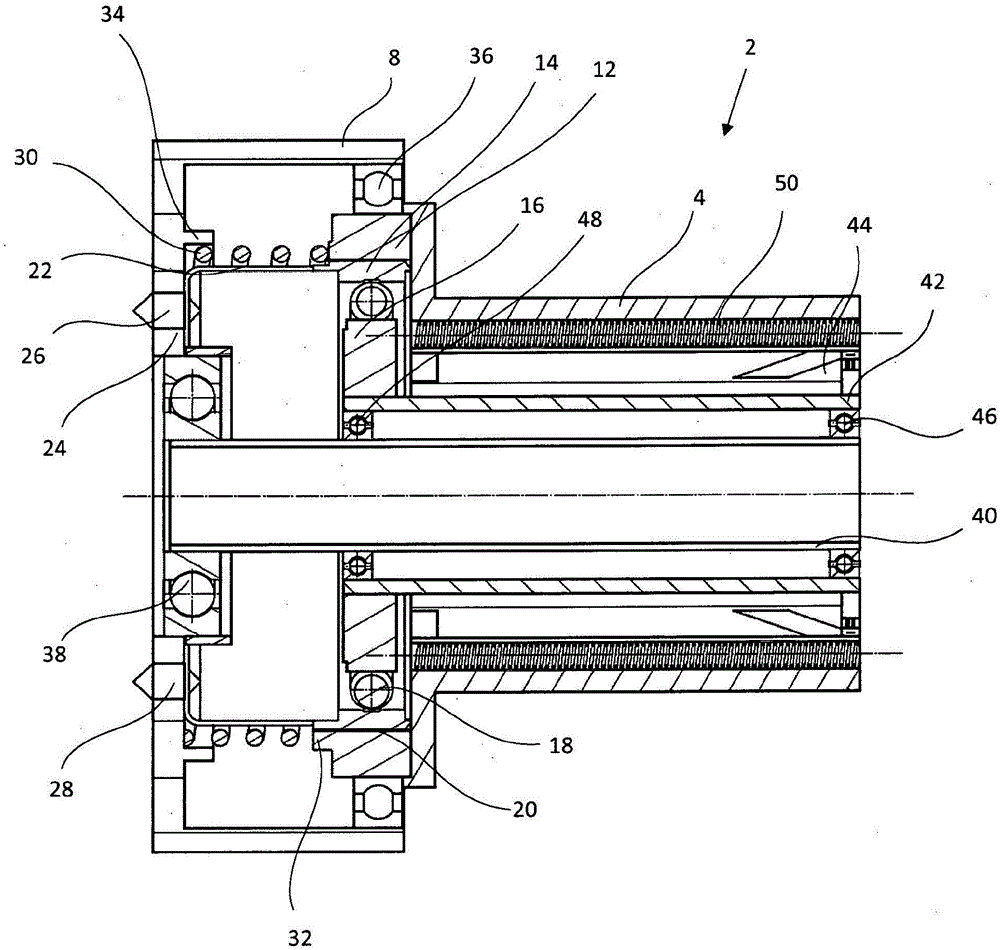
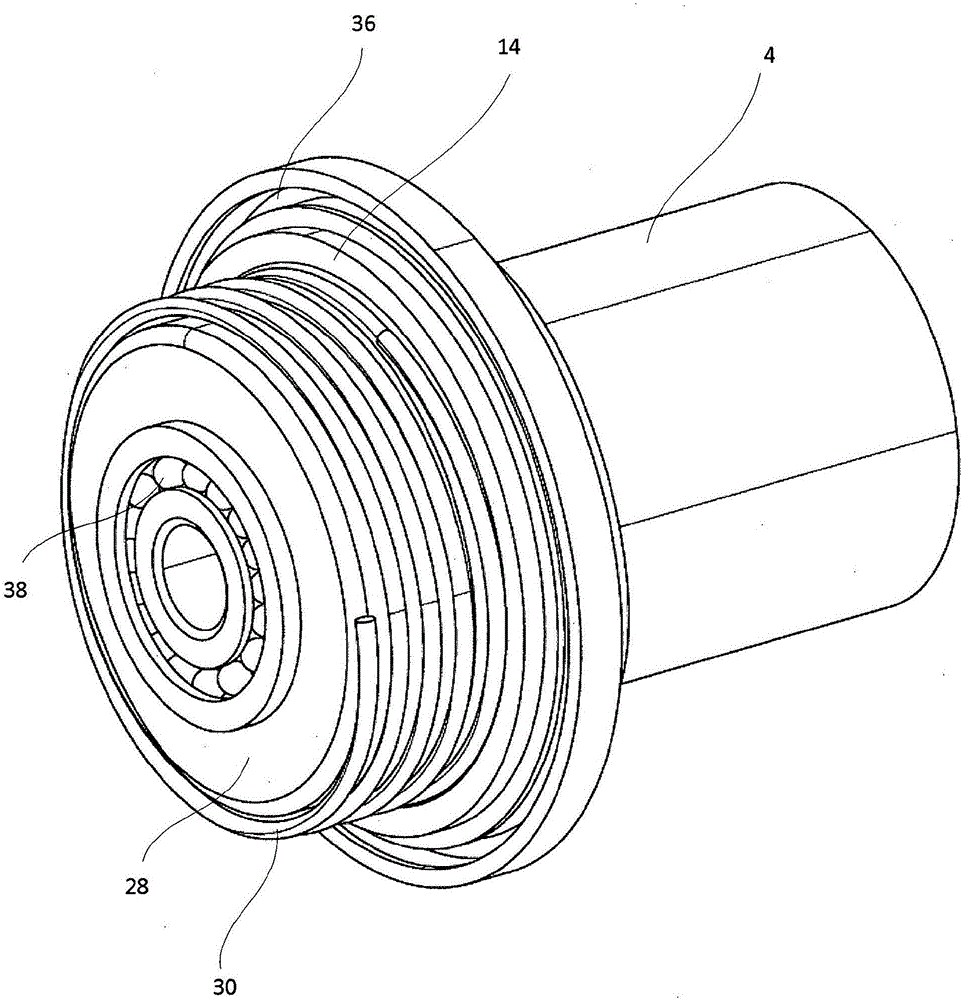
[0024] figure 2 showing along figure 1 The II-II line in the section cuts the sectional view of the rotary vibration absorber. The torsional vibration damper 2 here comprises a harmonic drive comprising a rigid unit 12 with internal toothing connected to the damper housing 4 and a rigid unit 12 with external toothing connected to the housing cover 8 . The connected flexible unit 14 is described below. The two units ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com