Process for producing thermal dye sublimation raw paper
A production process, thermal sublimation technology, applied in papermaking, paper machines, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve problems such as inability to meet the use requirements of thermal sublimation base paper, poor printing effect, lint and powder loss, etc., and achieve low cost and smooth surface Good degree of paper uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
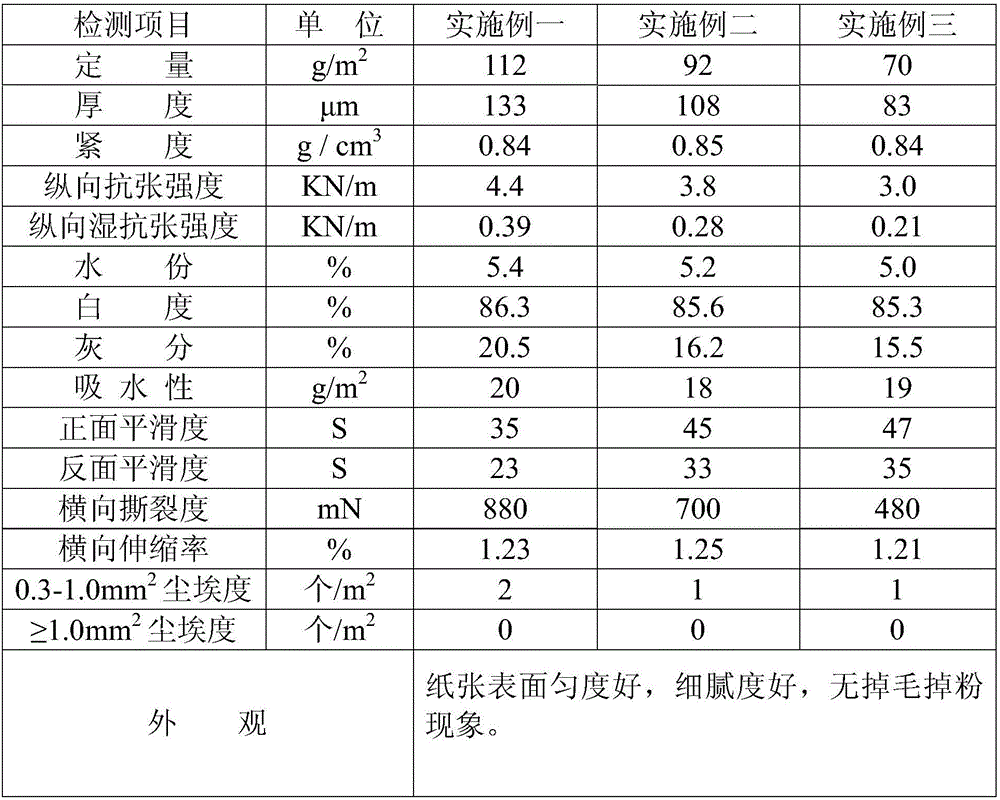
Embodiment 1
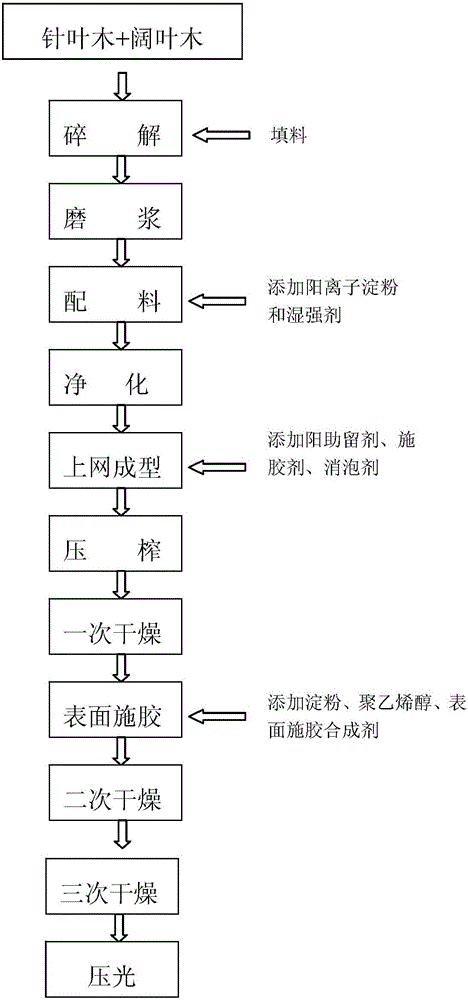
[0039] ① Disintegration: Add plant fiber into the pulper, and decompose it into the pulp tank through the pulper, and add fillers to the pulp tank at the same time, and control the dry pulp concentration of the pulp to 3.6%, of which coniferous wood accounts for 15% of the total mass of plant fibers, hardwood accounts for 85% of the total mass of plant fibers, and fillers account for 30% of the total mass of fillers and plant fibers.
[0040] ② Refining: Use a double-disc refiner to beat the pulp, the beating degree is controlled at 25°SR, and the wet weight is controlled at 4.5g.
[0041] ③ Ingredients: add cationic starch with an amount of 1.0% and a wet strength agent with an amount of 0.5% in the slurry after refining. As a specific implementation, the wet strength agent in this example adopts polyamide epoxy resin .
[0042] ④Dilution and purification: The slurry after batching is diluted to control the concentration of the feedstock, and the concentration of the feedsto...
Embodiment 2
[0048] ① Disintegration: Add plant fiber into the pulper, and decompose it into the pulp tank through the pulper, add fillers to the pulp tank at the same time, and control the dry pulp concentration of the pulp to 4%, of which coniferous wood accounts for 25% of the total mass of plant fibers, hardwood accounts for 75% of the total mass of plant fibers, and fillers account for 20% of the total mass of fillers and plant fibers.
[0049] ② Refining: Use a double-disc refiner to beat the pulp, the beating degree is controlled at 32°SR, and the wet weight is controlled at 5.5g.
[0050] ③Batching: Add cationic starch with an amount of 1.25% and a wet strength agent with an amount of 0.75% to the slurry after refining. As a specific implementation, the wet strength agent in this example adopts polyamide epoxy resin .
[0051] ④Dilution and purification: The slurry after batching is diluted to control the concentration of the feedstock, and the concentration of the feedstock is co...
Embodiment 3
[0057] ① Disintegration: Add plant fiber to the pulper, and decompose it into the pulp tank through the pulper, and add fillers to the pulp tank at the same time, and control the absolute dry pulp concentration of the pulp to 4.2%, of which coniferous wood accounts for 30% of the total mass of plant fibers, hardwood accounts for 70% of the total mass of plant fibers, and filler accounts for 15% of the total mass of fillers and plant fibers.
[0058] ② Refining: use a double-disc refiner to beat the pulp, the beating degree is controlled at 35°SR, and the wet weight is controlled at 6.5g.
[0059] ③Batching: Add cationic starch with an amount of 1.5% and a wet strength agent with an amount of 1.0% to the slurry after refining. As a specific implementation, the wet strength agent in this example adopts polyamide epoxy resin .
[0060] ④Dilution and purification: The slurry after batching is diluted to control the concentration of the feedstock, and the concentration of the feed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com