Method for preparing isomaltooligosaccharides from alpha-glucosidase through synchronous saccharification and glucoside conversion
A technology of isomaltose oligosaccharide and glucosidase, applied in the field of enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of low conversion rate and long production time, and achieve the effect of remarkable catalytic performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1: Obtaining of α-glucosidase coding gene fragment
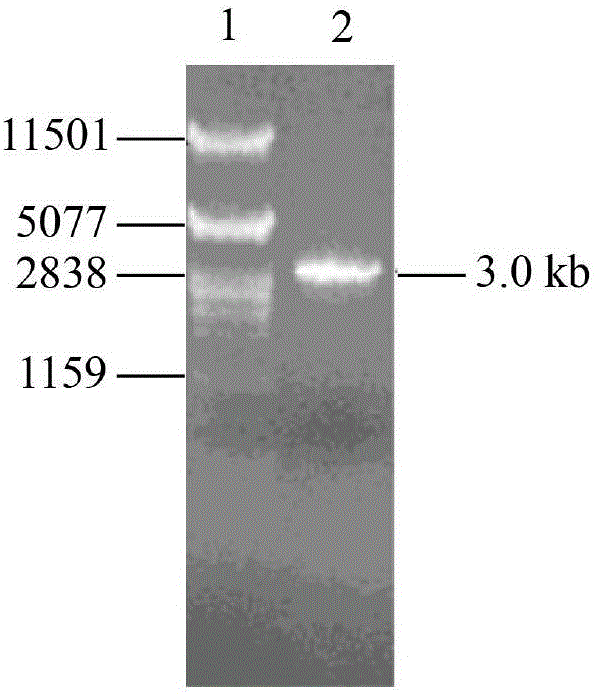
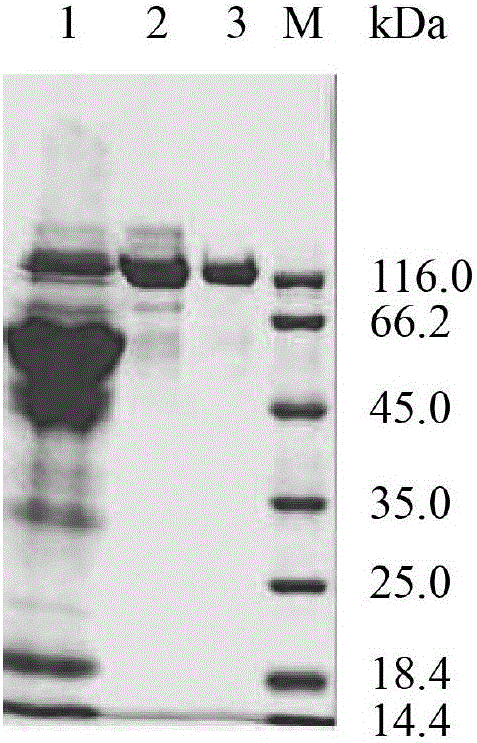
[0045] Total RNA of Aspergillus niger NRRL3135 was extracted with TRNzol total RNA extraction reagent. Using total RNA as a template, referring to the instructions of the RT-PCR kit, using oligo(dT) as a primer to reverse transcribe the first-strand cDNA, and then using the first-strand cDNA as a template, primers F1 (SEQ ID NO: 5) and R1 (SEQ ID NO: 6) carried out PCR amplification to produce Aspergillus niger α-glucosidase gene agD ( figure 1 ). The PCR product was ligated with the plasmid pMD19-T simple vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid pMD-agD, which was transformed into Escherichia coli JM109 competent cells. Positive transformants were screened, and their plasmids were extracted for enzyme digestion verification. The correct recombinant plasmid verified by enzyme digestion was then sequenced (sequence SEQ ID NO: 1, its amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO: 2).
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2: Utilize error-prone PCR method to construct α-glucosidase mutant library
[0047] Nucleotide mutations were introduced into the α-glucosidase gene agD by error-prone PCR in vitro. The reaction conditions for error-prone PCR are as follows:
[0048]
[0049] PCR amplification conditions: 94°C for 3 min; 30 cycles of 94°C for 1 min, 58°C for 1 min, and 72°C for 1.5 min; 72°C for 10 min. The primers used were primers F1 (SEQ ID NO:5) and R1 (SEQ ID NO:6).
[0050] The error-prone PCR amplification product (named after agDX) was purified by a DNA purification and recovery kit, digested with restriction endonucleases Xba I and Kpn I, and digested with the correspondingly digested plasmid pHY-WZX (Dandan Niu and Zhengxiang Wang. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol, 2007, 34:357-362) were connected to construct the recombinant plasmid pHY-WZX-agDX. Take 8 μL of recombinant plasmid pHY-WZX-agDX DNA and Bacillus licheniformis CBB3008 competent cells, mix evenly, trans...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3: Screening of thermostable mutant strains
[0053] Pick a single colony on the LB plate, use 96-well plate to culture with LB liquid based on 30-32°C for 55-70 hours, the liquid volume is 200-250 μL, and at the same time, use the initial recombinant bacteria B. licheniformis CBB3008 (pHY-WZX) For control.
[0054] Centrifuge the 96-well plate I to remove bacteria, and transfer 10 μL supernatant from each well to another 96-well plate II. And the 96-well plate was placed at 60°C for heat treatment for 60 minutes. Add 50 μL of 0.2% substrate o-methoxyphenyl-α-D-glucoside to each well, and incubate at 30° C. for 10 minutes. Add 80 μL of 2.5 mol / L NaOH solution to terminate the reaction (in the control group, the stop solution is added first, and then the substrate is added). Prepare diazonium salt solution at the same time: take 0.2g / L NaNO 2 100mL, then add 5mL of 3mol / L HCl to make the solution acidic, incubate at 30°C for 5min, add 10mL of 50g / L aniline, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com