An unsupported 3D printing method based on oblique layering
A three-dimensional printing, unsupported technology, applied in the direction of additive processing, etc., can solve the problems of poor surface quality between the support and the entity, lower printing efficiency, long post-processing time, etc., to save printing raw materials and eliminate the process of support removal , the effect of improving printing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
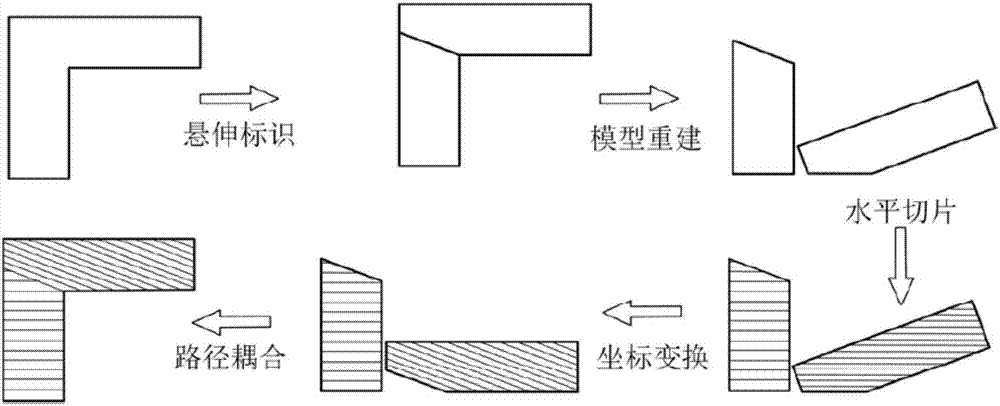
[0082] Here, a case part generated by three-dimensional design software is taken as an example to illustrate the trajectory code processing process and the final algorithm execution effect of the present invention.
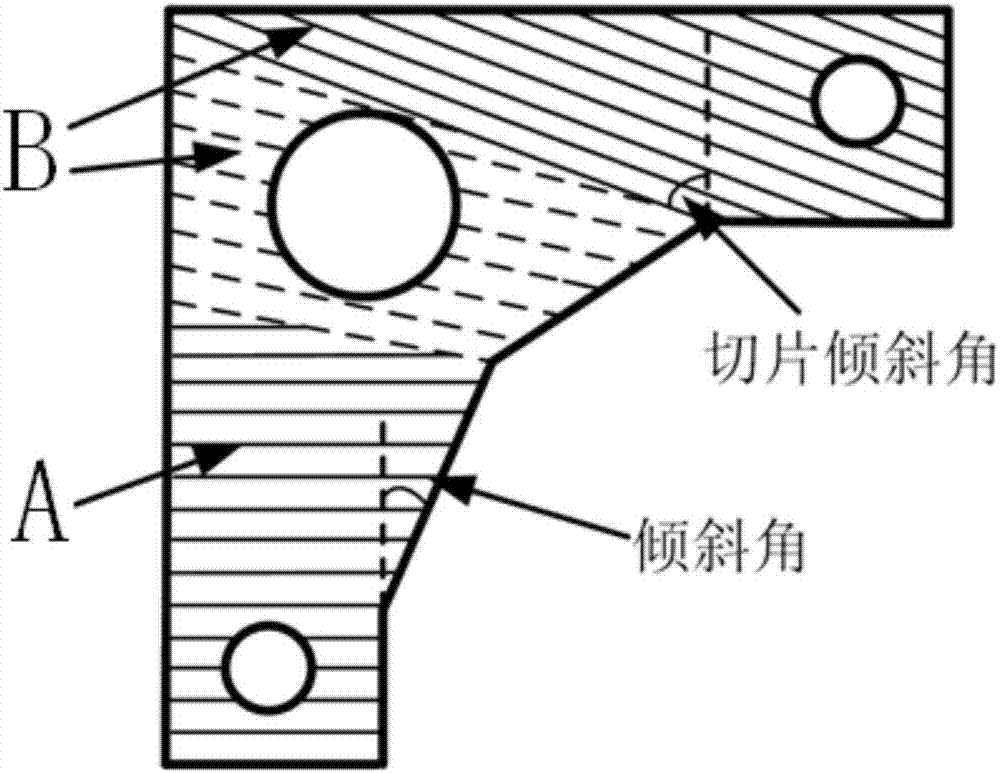
[0083] Such as Figure 8 As shown, the model has common design elements such as plane features, hole features, and shell features. Its size is 80mm*80mm*80mm. In order to demonstrate the actual oblique slice principle and visualization effect of the present invention, Figure 8 The layer height in is set to 5 times (0.5mm~1.5mm) in the actual algorithm. It can be clearly seen from the figure that the printed model is discretized into layers of slices. The model is divided into three parts using horizontal codes and inclined motion codes, and the slice inclination angle and layer height of the two parts of the inclined layered structure. There are also differences. Through calculation, the slice inclination angle is 55 degrees and 74 degrees, and the layer height is ...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Here, a common complex kettle model in daily life is taken as an example to illustrate the effect of the oblique slice track of the present invention in processing complex curved surfaces.
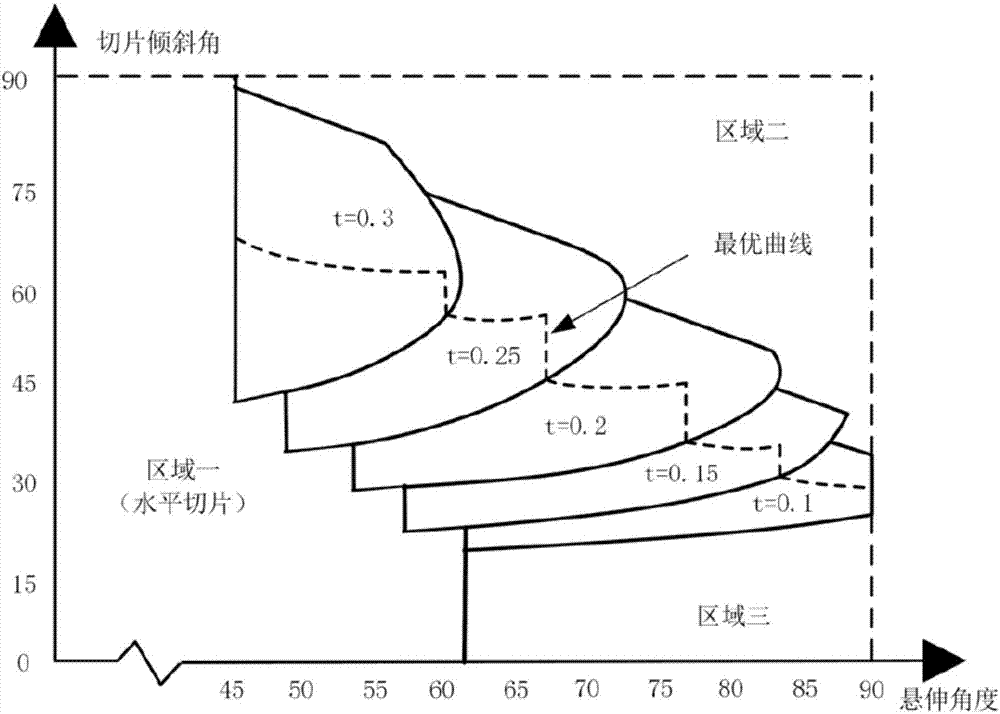
[0086] Such as Picture 9 As shown, the model display also uses the method of zooming up to 5 times to obtain a better visualization effect. The model can be roughly divided into four areas after surface identification. Among them, the inclination angles of areas 1, 3, and 4 are less than 60 degrees, and they are all marked as non-overhanging structures, and can be directly processed by horizontal slices to obtain the processing track, while area 2 has a larger overhanging surface, so the tilt in the present invention is adopted Slicing method. Area 1, Area 3, and Area 4 all use a layer height of 0.2mm, and the printing speed and filling rate are the same as in Example 1. Area 2 is used as the processing section of oblique layering, the layer height is 0.1mm, and the slice inclinatio...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Here, a typical cantilever beam model is taken as an example to illustrate the processing effect of the oblique slice track of the present invention on the limit overhang structure.
[0089] Such as Picture 10 As shown, the cantilever beam model includes three parts, a base for bonding the upper structure and the printer platform, a vertical beam and a suspension beam. The triangular base is designed with a larger area, mainly to improve the adhesion between the model and the printer platform, and to offset the overturning moment in the printing process. The main structure of the cantilever beam shown in area 3 is in a horizontal state and is in the limit printing position with an inclination angle of 90 degrees. When there is no supporting structure, due to the effect of gravity, the accumulation of materials cannot be achieved by horizontal layering. The slicing result shown in the figure is similar to that of Example 1. It consists of multiple oblique slices and horizo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com