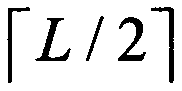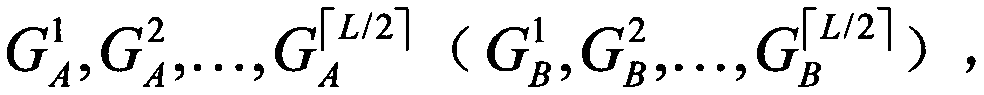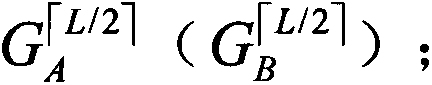Two-party quantum private comparison method based on five-quantum bit entangled state
An entangled state, five quantum technology, applied in the field of quantum cryptography, to achieve the effect of security performance guarantee
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0125] 1. Application examples of two-party quantum privacy comparison methods
[0126] here to with The method of the present invention is illustrated by way of example. Without loss of generality, suppose The ith five-qubit entangled state |Θ> prepared by TP is denoted as TP will particle with Send to Alice, particle with Send it to Bob. Then, Alice (Bob) on the particle with ( with ) to apply the Z base (Bell base) measurement to obtain the measurement result Without loss of generality, suppose for |00>(|Φ + >), then is 00. Then, Alice(Bob) calculates get Finally, Alice (Bob) announces to TP After hearing the announcement from Alice and Bob, TP reacts to the particle Apply Z base measurement to get the measurement result because at this time is |0>, then is 00. Then, TP calculates get and announce R to Alice and Bob i . Upon receipt of R from TP i After that, both Alice and Bob calculate get Once they found R i′ ≠0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com