Periodic metal contact gain-coupled distributed feedback semiconductor laser device
A technology of metal contact and gain coupling, applied in the structure of optical waveguide semiconductors, etc., can solve the problems of complex technology and difficult cost, and achieve the effects of simple manufacturing process, reduced manufacturing cost, and good side mode suppression ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
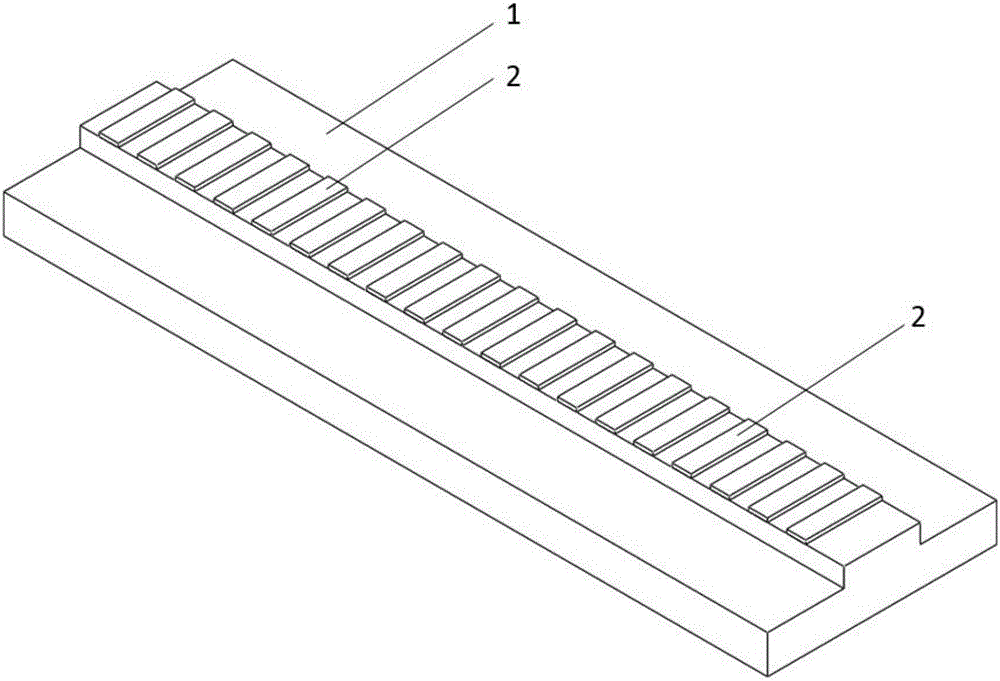
[0029] Such as figure 1 As shown, in this example,
[0030] On the designed and prepared GaAs-based semiconductor laser chip 1 with a wavelength of λ and an effective refractive index n in this wavelength band, a ridge-shaped mesa is prepared at one time by photolithography and etching. The width of the mesa is 100 μm and the height is 1.4 μm. . Deposit 200nm thick SiO 2 Insulation. Then, periodic electrode openings are prepared by overlaying. The opening period δ is: δ=Mλ / 2n, where M is a positive integer greater than 2. In this embodiment, when n=3.48, λ=980 nm, M=40, then δ=5.632 μm. The width of each electrode strip is 1.5 μm. Etching off SiO by means of ohmic contact 2 P-surface electrodes are evaporated on the electrode strips. Since only periodic electrodes have metal contacts, the preparation of periodic metal contacts 2 is completed. The required periodic metal contact gain coupling distribution feedback semiconductor laser single tube device is obtained throug...
Embodiment 2
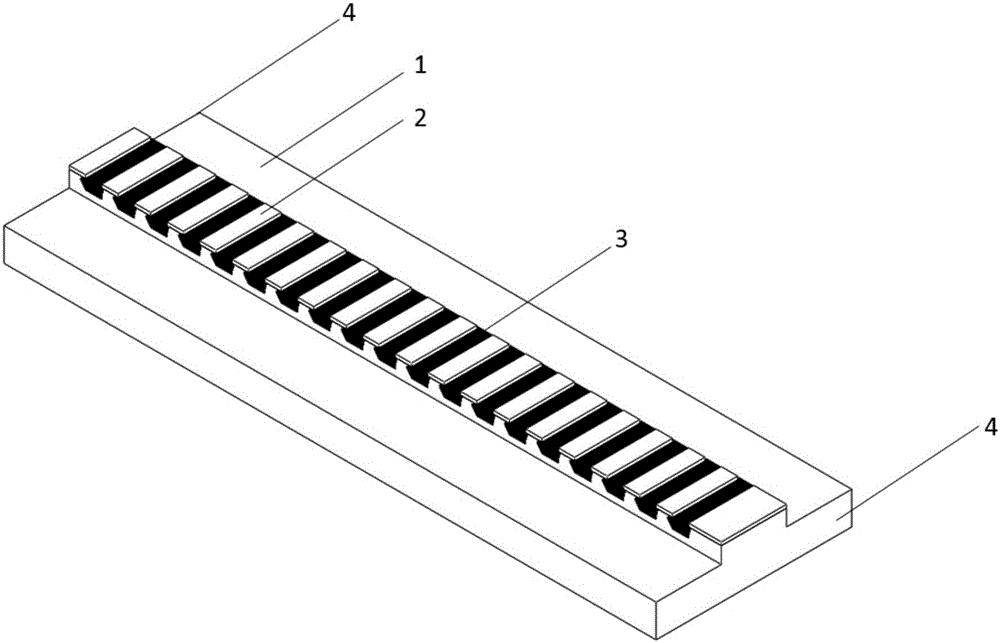
[0032] Such as figure 2 As shown, in this example,
[0033] In the already designed and prepared λ 1 and lambda2 All wavelengths have optical gain, and the effective refractive index in this band is n 1 and n 2 On the InP-based semiconductor laser chip 1, a ridge-shaped mesa was prepared at one time by photolithography and etching, with a mesa width of 4 μm and a height of 1.86 μm. The lateral current confinement region 3 is prepared by oxidation or carrier injection, and the electrode period δ is: δ=M i λ / 2n, i takes 1 or 2, M i is a positive integer greater than 2, and n is the effective refractive index of the semiconductor laser waveguide in this band. In this example, when n 1 =3.16,λ 1 =1550nm, take M 1 =80, then δ=19.62μm, there are n in this cycle 2 =3.15,λ 2 =1526nm, M 2 =81. The width of each electrode is 15 μm. Deposit 200nm thick SiO 2 Insulation. Periodic metal contacts 2 are fabricated by overlaying, etching and ohmic contact. The required period...
Embodiment 3
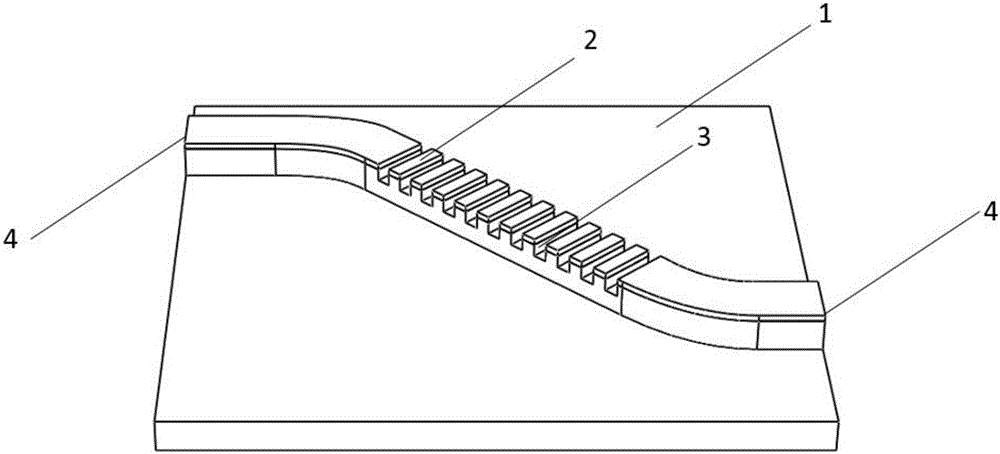
[0035] Such as image 3 As shown, in this example,
[0036] In the already designed and prepared λ 1 and lambda 2 All wavelengths have optical gain, and the effective refractive index in this band is n 1 and n 2 On the GaAs-based quantum dot semiconductor laser chip 1, a ridge-shaped mesa with a curved waveguide is etched at one time by photolithography and etching. The width of the mesa is 6 μm and the height is 1.4 μm. By bending the waveguide, the resonance direction of the periodic metal contact gain-coupling distributed feedback semiconductor laser is adjusted to the crystal orientation with high nonlinear coefficient. Optical grooves are prepared by overlaying and etching for the lateral current confinement region 3, and the electrode period δ is: δ=M i λ / 2n, i takes 1 or 2, M i is a positive integer greater than 2, and n is the effective refractive index of the semiconductor laser waveguide in this band. In this example, when n 1 =3.28,λ 1 = 1300nm, take M 1 =...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com