Method for measuring the cladding light ratio of double-clad fiber lasers
A technology of double-clad optical fiber and measurement method, which is applied in the direction of testing optical performance, etc., can solve the problems of limited measurement range, inability to detect the outer boundary of the cladding light field, blurred edges, etc., and achieves the effect of a large measurement range.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
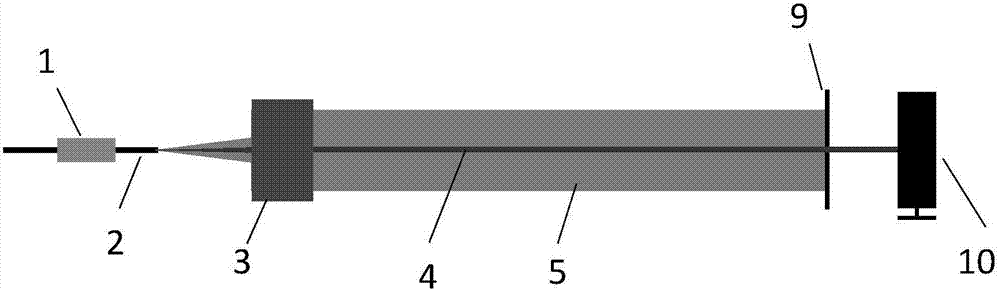
[0037] A method for measuring the cladding light ratio of a double-clad fiber laser of the present invention, such as figure 1 As shown, the method specifically includes the following steps:
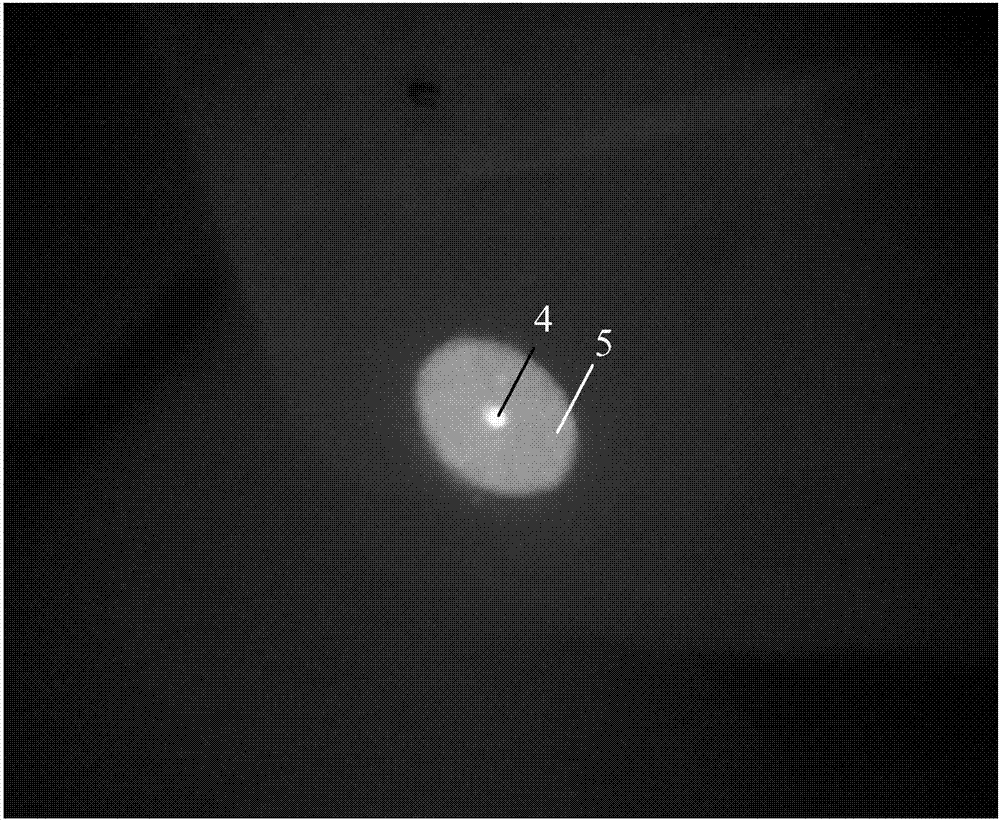
[0038] First, clamp the output fiber 2 of the double-clad fiber laser with the fiber holder 1, turn on the laser to emit light, adjust its output power to the level of watts, and adjust the position of the end face of the output fiber 2 so that it is located on the object plane of the lens group 3 . The lens group magnification that this embodiment adopts is 100 times, and object plane position is positioned at apart from lens group front surface 2cm place, image plane is positioned at apart from lens group rear surface 4m optical path place, the system aberration of lens group 3 to fiber core imaging is less than Or equal to 0.5 times the signal light wavelength. Further adjust the optical fiber holder 1, and repeatedly adjust the three-dimensional space position, pitch and swing of ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] In order to separate the core light, the cladding light of the signal light band, and the cladding light of the pump light band (ie, the remaining pump light) to obtain the ratio of the cladding light of the signal light band, Figure 4 The method for measuring the ratio of cladding light in the signal light band of the high-power double-clad fiber laser of the present invention is shown, comprising the following steps:
[0043] The lens group 3 used in this embodiment has a magnification of 100 times, the object plane is 2 cm from the front surface of the lens group 3, and the image plane is 4 m away from the rear surface of the lens group 3. First, clamp the output fiber 2 of the double-clad fiber laser with the fiber holder 1, turn on the laser to emit light, adjust its output power to the level of watts, and adjust the position of the end face of the output fiber 2 so that it is located on the object plane of the lens group 3 . The optical fiber holder 1 is further...
Embodiment 3
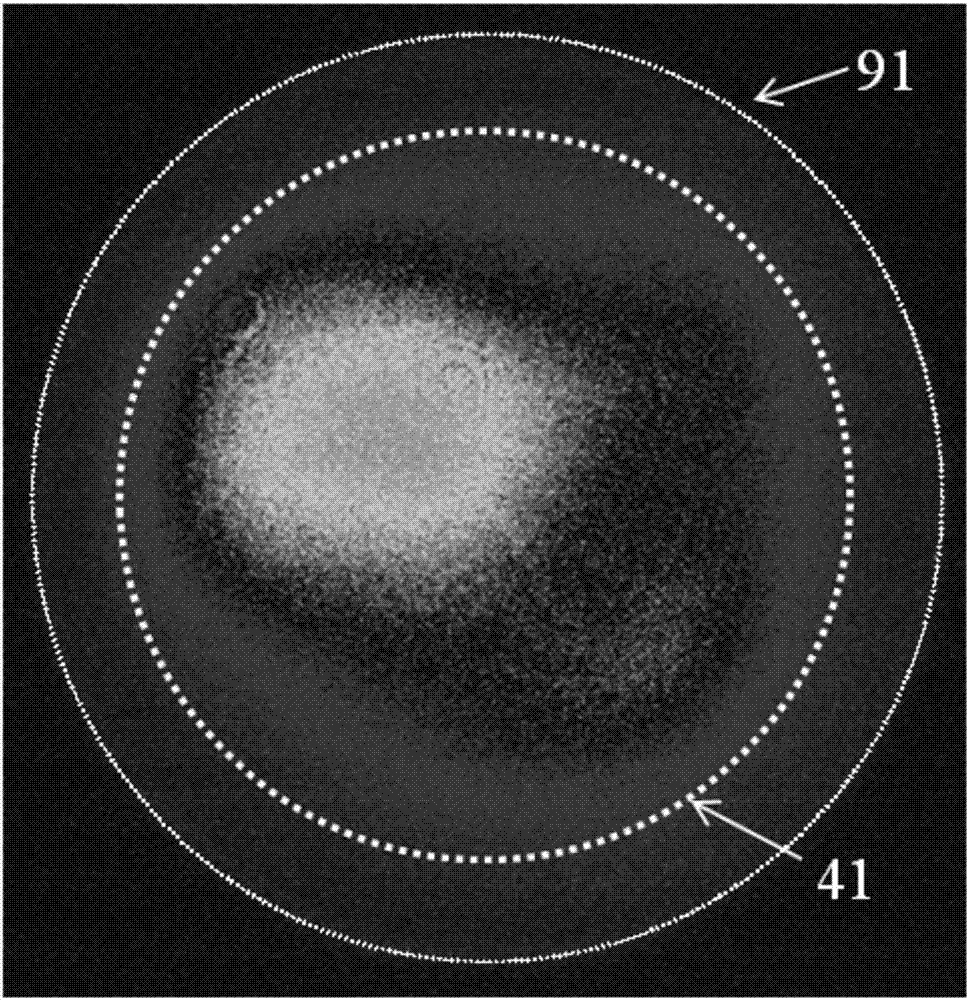
[0048] Figure 5 For adopting the method of the embodiment of the present invention 2 ( Figure 4 As shown in the principle), the test results of the cladding light ratio of the output optical signal light band of the high-power fiber laser show that the diameter of the core / cladding of the output fiber 2 is 20 / 400 μm, and the numerical aperture is 0.06 / 0.46 respectively. The abscissa is the pump power of the amplifier, the left ordinate is the ratio of cladding light in the signal light band to the signal light band of the output light, and the right ordinate represents the total output power (ie P 1 ). The black square curve represents the change of the total output power with the pump spectrum power of the amplifier, and the hollow diamond curve represents the cladding optical power P of the remaining pump light band 4 Variation with pump spectral power. Figure 5 The test results using different diaphragm apertures and the estimated results using cladding light filters ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com