Safety protection method for underground metal pipeline
A technology for safety protection and metal pipelines, applied in the field of pipeline safety, can solve problems such as loss of repair value, insufficient repair, failure to detect corrosion points in time, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
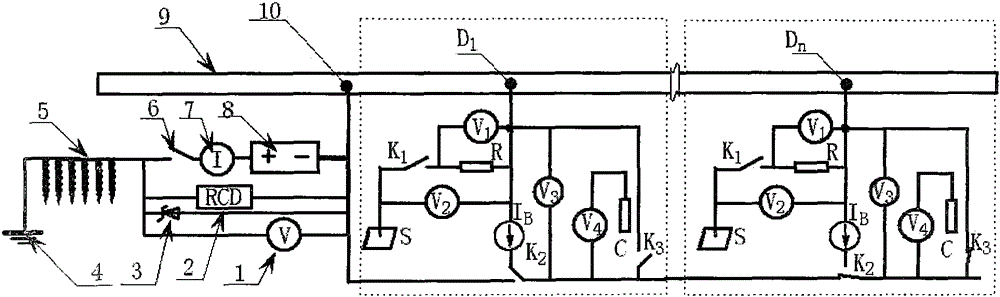
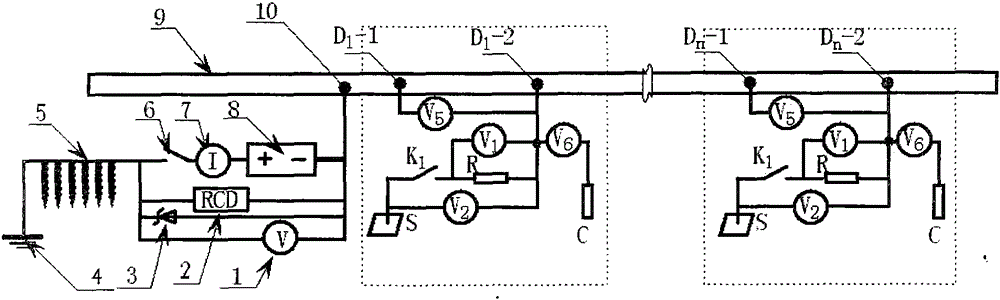
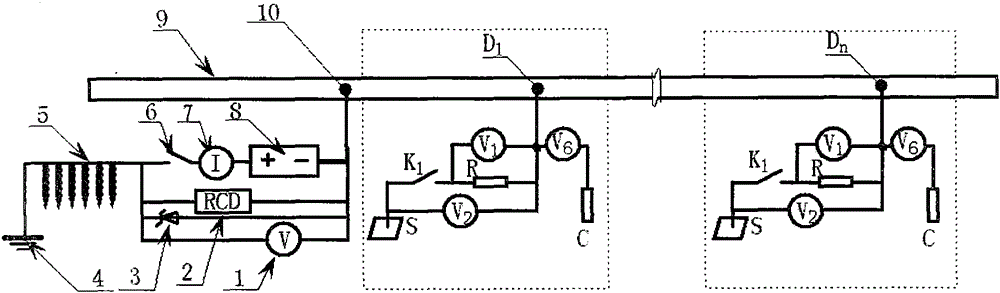
[0076] For a section of 10km long newly built pipeline, the implementation method is briefly described.
[0077] A section of 10km-long newly-built pipeline, external dimension: Φ273×6.5, material is X80, using the protection method of the present invention, after testing the earth potential along the pipeline route, the fluctuation value does not exceed 20mV, this section is determined to be a pipeline protection unit, and the insulation is used as The main method of pipeline protection, cathodic protection as an auxiliary method of protection.
[0078] Insulation protection part: All line pipes adopt normal temperature type (N) 3LPE reinforced anti-corrosion structure; pipe joints are made of radiation cross-linked polyethylene heat shrinkable tape with epoxy primer; pipe repairs are made of polyethylene repair sheets, heat shrinkable Belt; the hot-simmering elbow adopts a single-layer fusion-bonded epoxy powder coating + butyl rubber modified asphalt anti-corrosion primer +...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com