A Projective Reconstruction Method Based on Trajectory Basis
A trajectory-based and projective technology, applied in the field of computer vision research, can solve problems such as large errors, achieve the effects of small errors, increase computing speed, and reduce unknowns
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] This article uses the dance video sequence in the Cameron University laboratory and converts it into an image sequence for experiments. In order to reflect the movement situation, when selecting feature points, select the arm and lower leg parts that can reflect the movement situation.
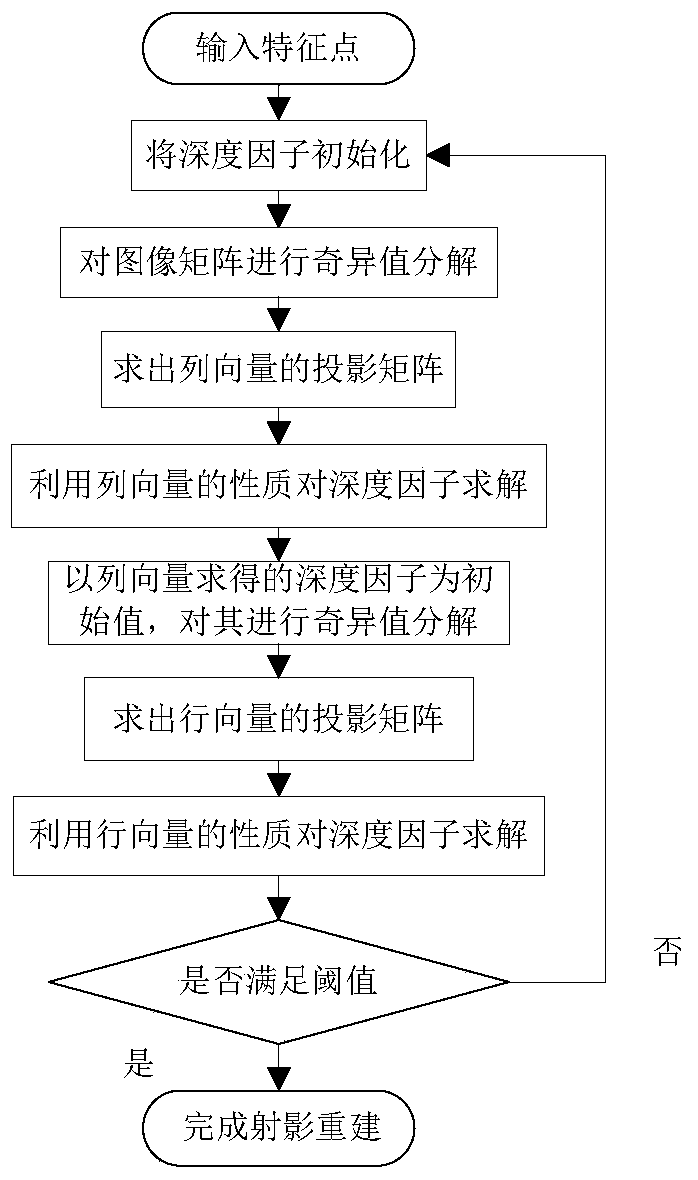
[0047] Carry out projective reconstruction according to the method of the present invention, the flow chart is as follows figure 1 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0048] (1) In the image sequence (such as figure 2 and 5 ) to extract the feature point data that can reflect the motion trajectory in each image, such as image 3 and 6 shown, specifically expressed as F and P are the number of images and the number of feature points, respectively;
[0049] (2) Solve the depth factor of the image according to the feature point data, and complete the projective reconstruction. The specific implementation steps are:
[0050] (2.1) Assuming that the camera model is a pers...
Embodiment 2
[0081] This embodiment is aimed at the reconstruction of image noise changes, the basic operation steps are the same as in Embodiment 1, and the number of images F=80 and the number of feature points P=100 are generated for experimentation, the number of iterations k is 30, and ξ is 10 -4 , and add Gaussian noise with zero mean and variance from 0 to 2 in the image, repeat the operation 60 times under the condition that the primitive r is 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10, and then calculate the average value, the experiment The result is as Figure 8 shown.
[0082] From Figure 8 It can be seen that v 3r+2 The value of increases linearly with the image noise, indicating that the method is more robust. At the same time, it can also be seen that the larger the number of primitives, the greater the v 3r+2 The smaller the value, the reason is that when the matrix is decomposed by singular value, the V values are arranged from large to small, so the corresponding value is smaller.
[008...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com