Application of CRISPR-Cas9 system based on new gRNA (guide ribonucleic acid) sequence in preparing drugs for treating hepatitis B
A DNA sequence and sequence technology, applied in gene therapy, DNA/RNA fragments, digestive system, etc., can solve the problems of not involving HBV DNA destruction and clearance, difficult to determine the course of treatment, and HBV drug resistance mutation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Design and synthesis of gRNA sequences targeting HBV conserved sequences of four different serotypes, and construction and screening of corresponding CRISPR-Cas9 systems
[0060] 1. Selection and design of specific gRNA
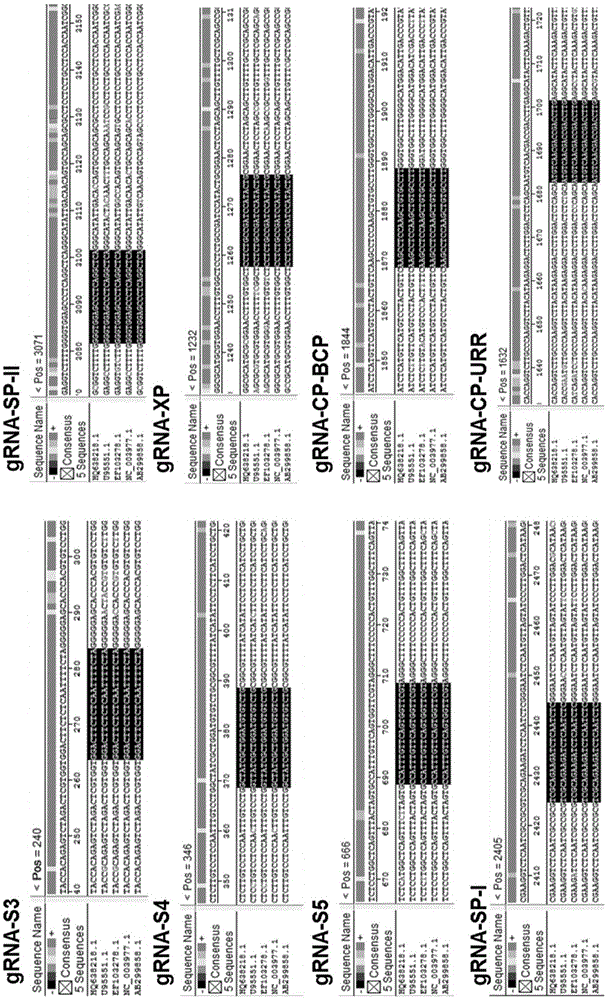
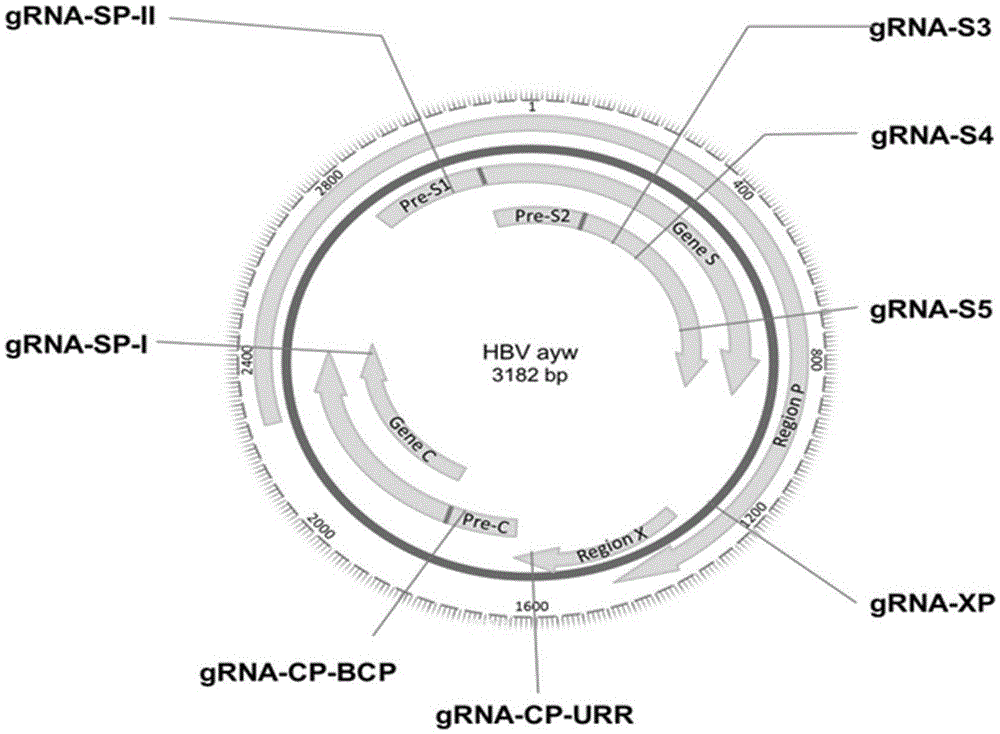
[0061] Taking the HBV sequence of adr serotype (GenebankID: AB299858) as the reference sequence, the CRISPR online design tool ( http: / / crispr.mit.edu / ) to find a target sequence with a higher score, the form of the target sequence is 5'-N(20)NGG-3' or 5'-CCNN(20)-3'. Then we compared the gene sequences of the main four different serotypes of HBV, including: adr (GenBankaccessionnumber.HQ638218), ayw (U95551), ayr (NC003977), adw (EF103278) and adr (AB299858), from Among the selected target sequences, 8 target sequences located in the conserved region of HBV were selected ( figure 1 , figure 2 ).
[0062] Table 1. Candidate gRNA sequences
[0063]
[0064]
[0065] 2. Synthesis of target sequence and construction of CRISPR-Cas9 system
...
Embodiment 2
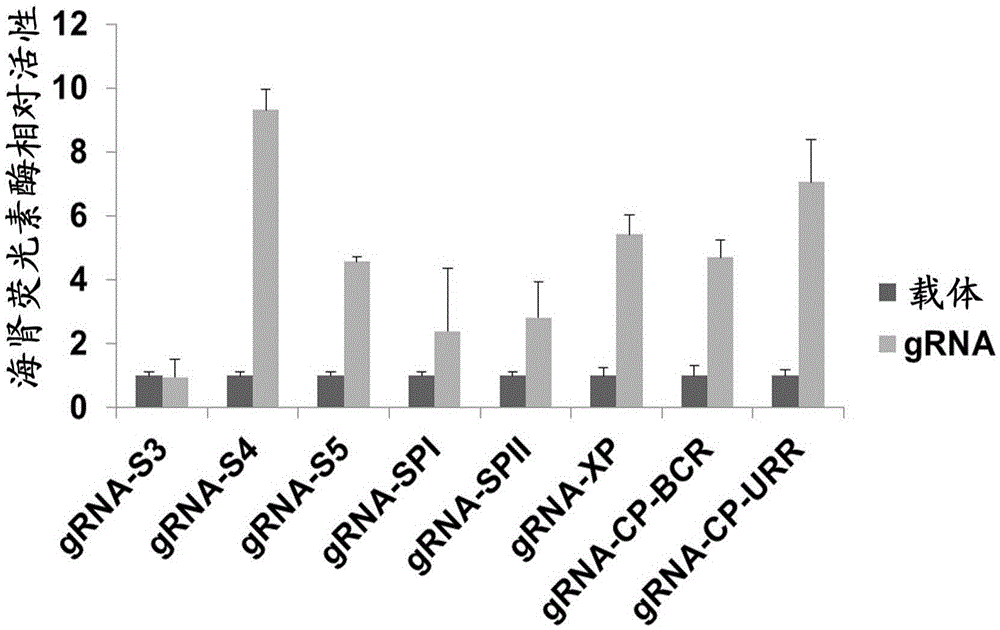
[0154] Example 2: Evaluation of the effect of gRNA-S4 target on inhibiting HBV replication
[0155] 1. Detection of HBV surface antigen, HBV DNA and HBV replication intermediates after transfection of gRNA-S4 into HBV stably transfected cells
[0156] a. Cells transfected with CRISPR-Cas9 system with S4 target and CRISPR-Cas9 system without target (control)
[0157] 1) Transfection is performed when the cells adhere to the wall and grow to about 90% of the cell culture dish with a diameter of 10 cm.
[0158] 2) Transfection system (per well):
[0159] Medium500μl+ LTX Reagent 22.5 μl
[0160]
[0161] 3) Mix the above two systems and incubate at room temperature for 30 minutes.
[0162] 4) Add the reaction system to a cell culture dish with a diameter of 10 cm, and add puro screening after 48 hours of culture to improve transfection efficiency
[0163] 5) Divide the screened two groups of cells into 2×10 cells per well 4 The cells were divided into three 24-well pl...
Embodiment 3
[0218] Example 3: Detection of HBV replication in HBV stably transfected cells after S4 site deletion
[0219] 1. Screening of S4 site mutation monoclonal cell lines
[0220] 1.1 Cell transfection with CRISPR-Cas9 system with S4 target and CRISPR-Cas9 system without target (control)
[0221] 1) Transfection is performed when the cells adhere to the wall and grow to about 90% of the cell culture dish with a diameter of 10 cm.
[0222] 2) Transfection system (per well):
[0223] Medium500μl+ LTX Reagent 22.5 μl
[0224]
[0225] 3) Mix the above two systems and incubate at room temperature for 30 minutes.
[0226] 4) Add the reaction system to a cell culture dish with a diameter of 10 cm, and add puro screening after 48 hours of culture to improve transfection efficiency
[0227] 5) Divide the screened two groups of cells into ten 96-well plates with 1 cell per well, subculture to 48-well plates, and extract the total DNA of cells in each well.
[0228] 6) Amplify wi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com