Primer for detecting main drug-resistant mutation sites of aids therapeutic nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor and application thereof
A technology of reverse transcriptase inhibition and drug-resistant mutation sites, which is applied in the field of medical detection, can solve the problems of long detection time and high cost, and achieve the effects of low cost, easy mastery and fast operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1: Construction of HIV-1 wild-type plasmid and mutant plasmid
[0037] (1) Ligate the reverse transcriptase gene sequence (1.1 kb in length, relative to HXB2 position: 2243-3304) identified by sequencing to the pUCm-19 vector, then transform, extract the plasmid DNA, and verify the plasmid connection by sequencing Correct, obtain the HIV-1 wild-type cloning plasmid and dilute to 0.01ng / uL.
[0038] (2) Through the method of artificial site-directed mutagenesis, the bases corresponding to the 41st, 65th, 70th, 184th, 210th, and 215th amino acids of the reverse transcription gene in the HIV-1 wild-type cloning plasmid were mutated to obtain M41L, D67N, and K65R , K70R, K70E, M184V, M184I, L210W, T215Y, T215F mutant plasmids, diluted to 0.01ng / uL.
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2: ASPCR method detects the specificity and sensitivity of M41L site
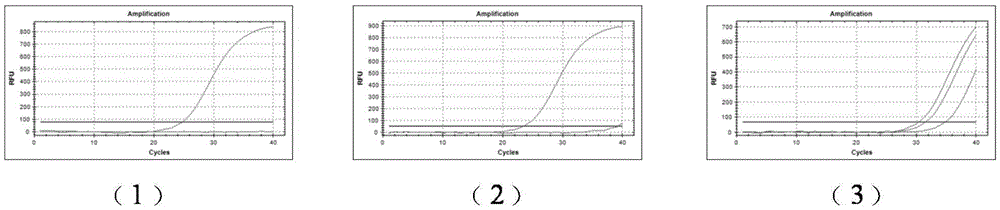
[0040] (1) Using the HIV-1 wild-type cloning plasmid and the M41L site mutant plasmid as templates, real-time PCR detection was performed using the M41L site wild-type amplification primers SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.21. The result is as figure 1 As shown in -(1), the amplification curve of the wild-type template showed an S-shaped growth, and the CT value of the number of cycles experienced by the fluorescence signal reaching the set threshold was 24.8. The mutant template had no amplification curve, and the fluorescence signal did not reach the set threshold. The threshold value is set, and there is no CT value. The difference between the two is obvious, and the amplification specificity is high.
[0041] (2) Using the HIV-1 wild-type cloning plasmid and the M41L site mutant plasmid as templates, the M41L site mutant amplification primers SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.21 were used for real-t...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3: ASPCR method detects the specificity and sensitivity of D67N site
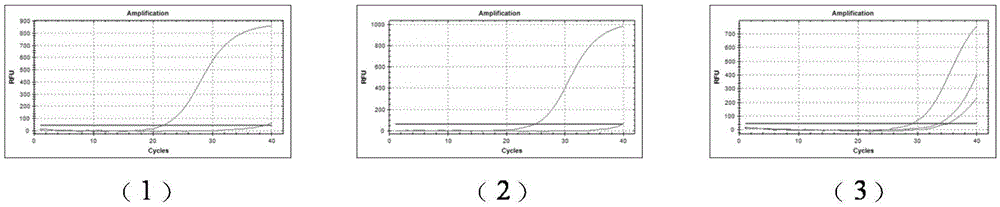
[0044] (1) Using the HIV-1 wild-type cloning plasmid and the D67N site mutant plasmid as templates, real-time PCR detection was performed using the D67N site wild-type amplification primers SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.21. The result is as figure 2 - As shown in (1), the primer pair specifically amplifies the HIV-1 wild-type sequence.
[0045] (2) Using the HIV-1 wild-type cloning plasmid and the D67N site mutant plasmid as templates, real-time PCR detection was performed using the D67N site mutant amplification primers SEQ ID NO.4 and SEQ ID NO.21. The result is as figure 2 -As shown in (2), the primer pair specifically amplifies the D67N site mutant sequence.
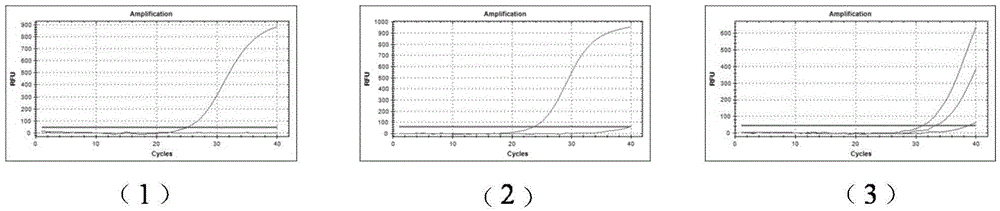
[0046] (3) Using the 1%-10% mutation samples of the D67N site as a template, real-time PCR detection was performed using the D67N site mutant amplification primers SEQ ID NO.4 and SEQ ID NO.21. The result is as figure 2 -As s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com