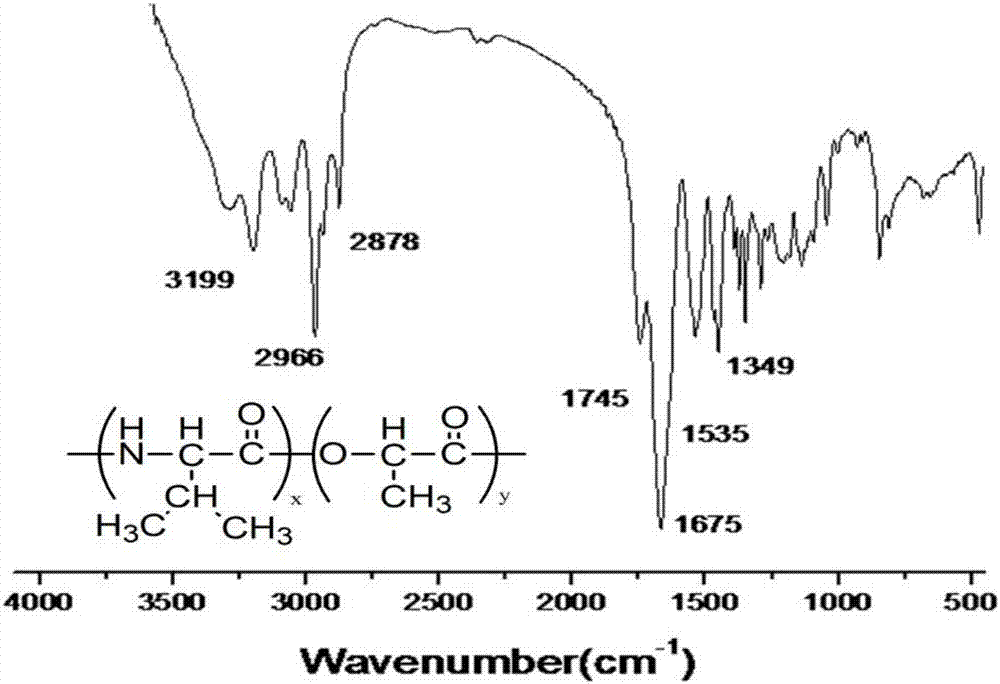
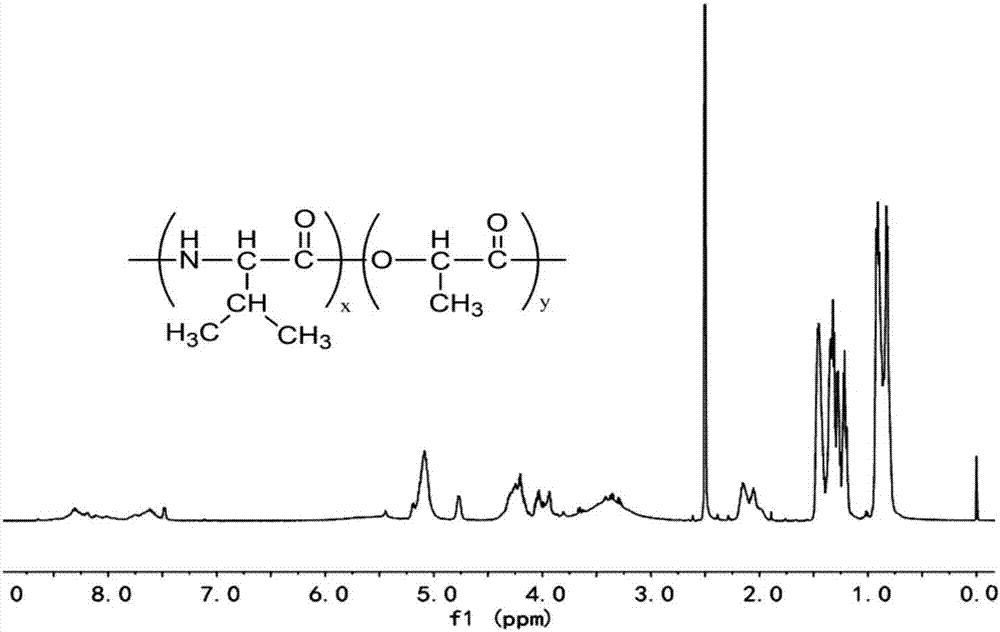
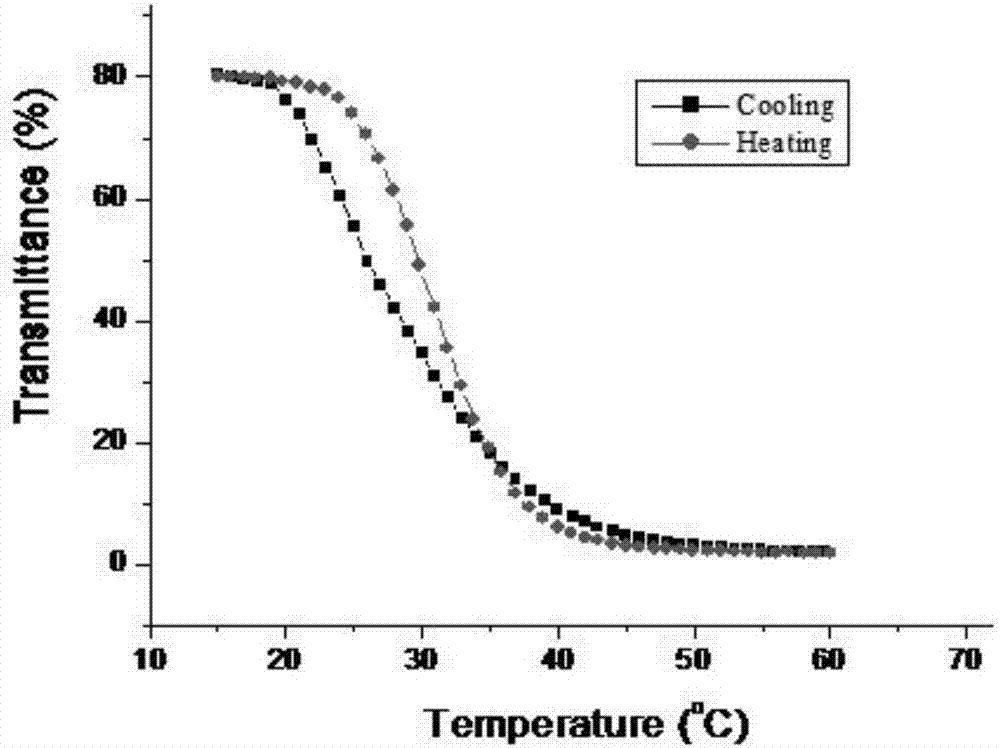
Thermosensitive poly(lactic acid-valine) material and preparation method thereof
A valine and temperature-sensitive technology, which is applied in the field of temperature-sensitive poly(lactic-valine) materials and their preparation, can solve the problem of not being able to have both biocompatibility, biodegradability and temperature-sensitive properties, single, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of excellent biodegradability and excellent biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] (1) Dehydration stage
[0042] In a microwave reactor (such as CEM microwave synthesizer, DISCOVER SP), put 5.0 g of lactic acid in a 100 mL long-necked flask, and put a magnetic stirring bar. React at a vacuum of 0.06 MPa and a temperature of 120° C. for 30 minutes to remove free water in the reaction solution. Then, add 0.6% SnCl in the reaction flask 2 and p-toluenesulfonic acid as a reaction catalyst, reacted for 45 minutes at a vacuum of 0.08MPa and a temperature of 160°C, SnCl 2 And the addition of p-toluenesulfonic acid is 0.6%, calculated with the mass of lactic acid.
[0043] (2) Polymerization stage
[0044] 6.0 g of valine was added, and the reaction was continued at a vacuum of 0.08 MPa and a temperature of 170° C. for 30 minutes.
[0045] (3) Insulation stage
[0046] The reaction was maintained for 60 minutes at a vacuum of 0.08 MPa and a temperature of 160°C. After the reaction temperature dropped to 50°C, fully dissolve it with 6mL of anhydrous met...
Embodiment 2
[0053] (1) Dehydration stage
[0054] In a microwave reactor (such as CEM microwave synthesizer, DISCOVER SP), put 5.0 g of lactic acid in a 100 mL long-necked flask, and put a magnetic stirring bar. React at a vacuum of 0.04 MPa and a temperature of 110° C. for 35 minutes to remove free water in the reaction solution. Then, add 0.6% SnCl in the reaction flask 2 With p-toluenesulfonic acid as a reaction catalyst, the vacuum was 0.06MPa, and the temperature was 158°C for 50 minutes.
[0055] (2) Polymerization stage
[0056] 6.0 g of valine was added, and the reaction was continued at a vacuum of 0.06 MPa and a temperature of 165° C. for 40 minutes.
[0057] (3) Insulation stage
[0058] The reaction was maintained for 70 minutes at a vacuum of 0.06 MPa and a temperature of 158°C. After the reaction temperature drops to 40°C, fully dissolve it with 6mL of anhydrous methanol, and then add it dropwise into 160mL of diethyl ether under stirring, a yellowish precipitate precip...
Embodiment 3
[0063] (1) Dehydration stage
[0064] In a microwave reactor (such as CEM microwave synthesizer, DISCOVER SP), put 5.0 g of lactic acid in a 100 mL long-necked flask, and put a magnetic stirring bar. React for 40 minutes at a vacuum of 0.05 MPa and a temperature of 130° C. to remove free water in the reaction solution. Then, add 0.6% SnCl in the reaction flask 2 and p-toluenesulfonic acid as a reaction catalyst, and reacted for 58 minutes at a vacuum of 0.07 MPa and a temperature of 168°C.
[0065] (2) Polymerization stage
[0066] 6.0 g of valine was added, and the reaction was continued at a vacuum of 0.07 MPa and a temperature of 172° C. for 50 minutes.
[0067] (3) Insulation stage
[0068] The reaction was maintained for 65 minutes at a vacuum of 0.07 MPa and a temperature of 164°C. After the reaction temperature drops to 45°C, fully dissolve it with 6mL of anhydrous methanol, and then add it dropwise into 160mL of diethyl ether under stirring, and a yellowish precip...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com