Apparatus for obtaining high-quality optical images in a magnetic resonance imaging system
A nuclear magnetic resonance imaging and optical sensing technology, applied in the field of medical imaging, can solve problems such as interfering with the workflow, and achieve the effect of low heat dissipation and drift prevention
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
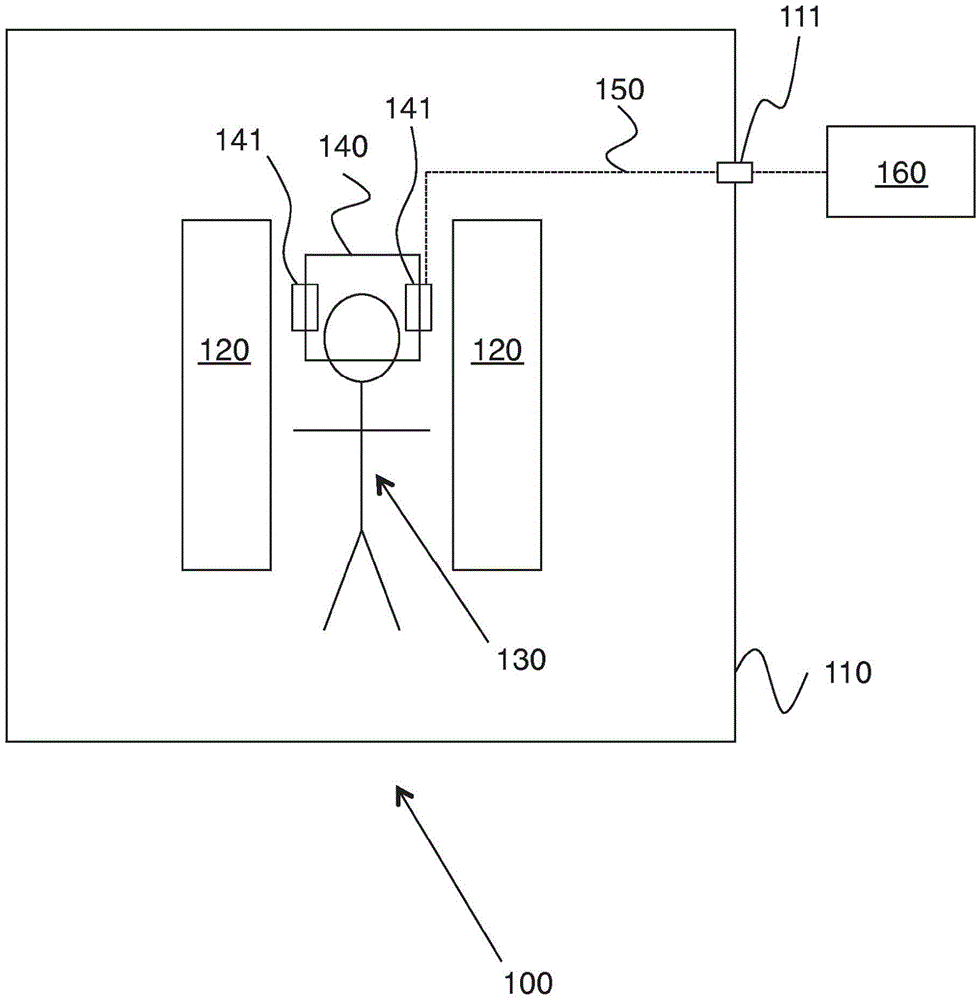
[0022] figure 1 An exemplary device based on the above principles is shown. Apparatus 100 includes a Faraday cage 110 that surrounds an MRI machine 120 within which a person (or animal) 130 is placed. The human head or animal is partially surrounded by an imaging coil 140 comprising one or more integrated cameras 141 . The only data communication with camera 141 is via optical fiber 150 , which passes through the Faraday cage to processing device 160 via waveguide 111 .
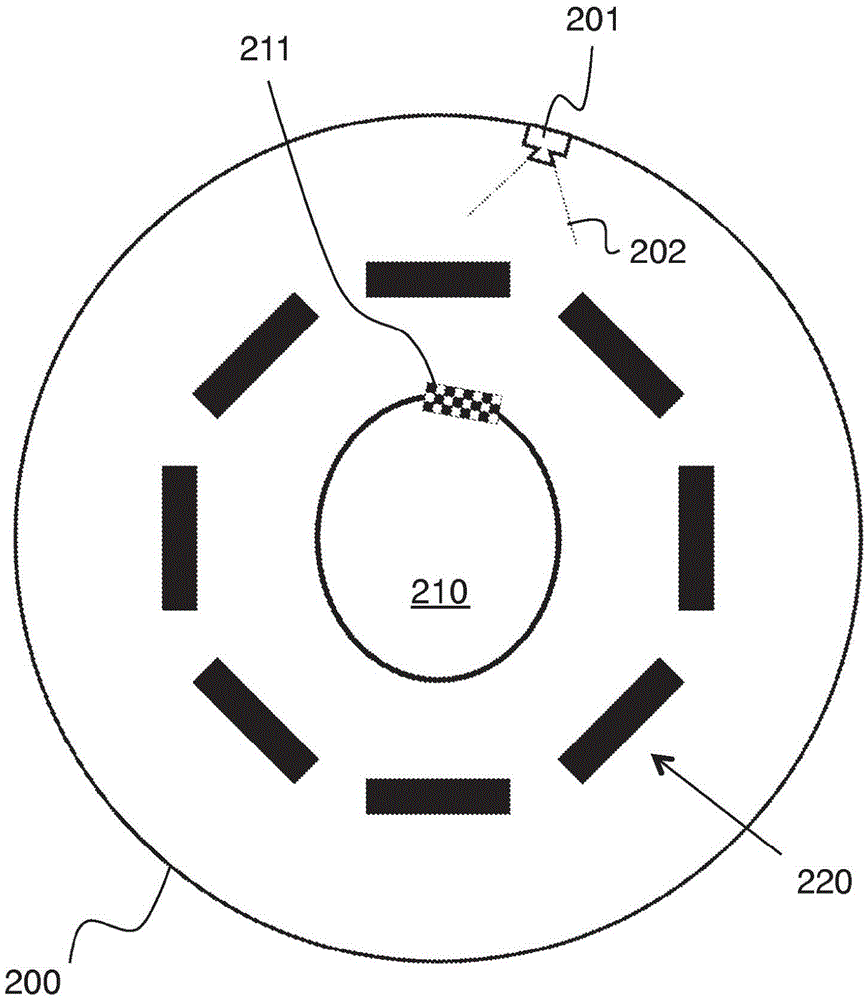
[0023] In order to better understand the present invention, it is helpful to consider the disadvantages of hole-mounted cameras. Figure 2A An MRI scanner bore 200 is shown surrounding a patient's head 210 with attached tracking markers 211 . As can be seen from the diagram, aperture mounted camera 201 suffers from the drawback that its field of view 202 will be significantly blocked by head coil 220 .
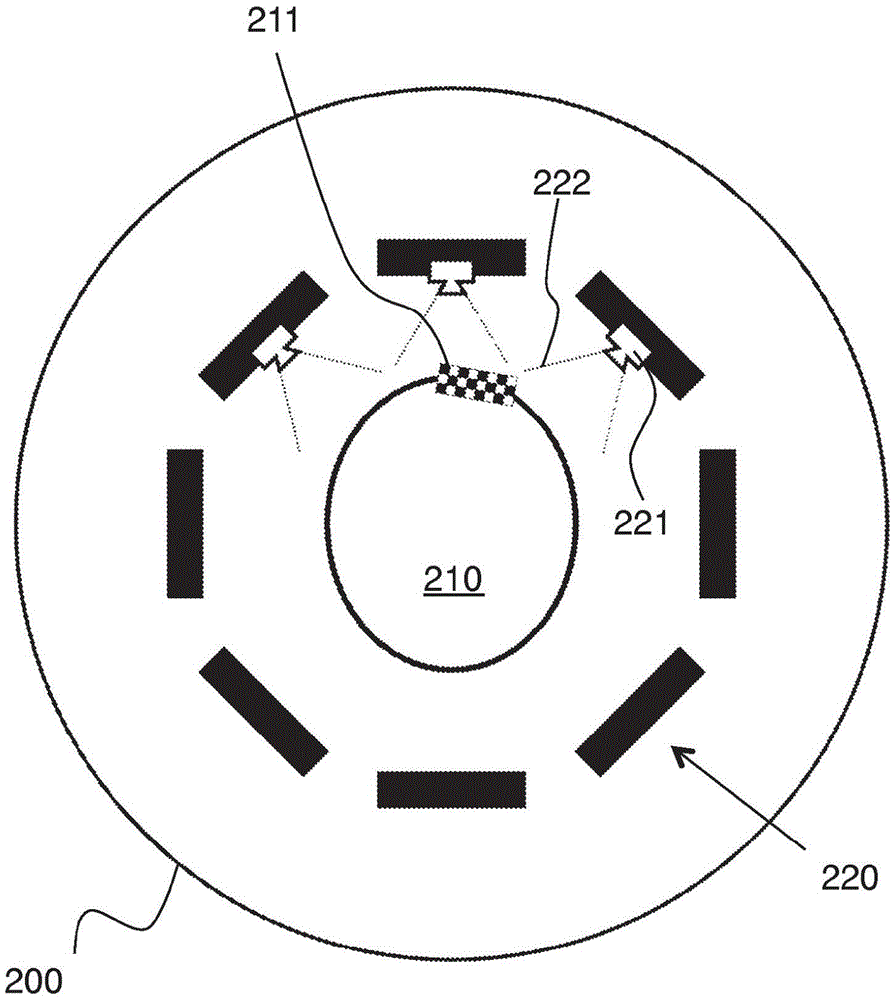
[0024] Figure 2B A similar arrangement is shown, except that a camera 221 is positioned on (or prefe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com