Method for improving sugar yield of lignocellulosic biomass after enzymolysis
A technology of lignocellulose and cellulase, applied in the direction of fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of purification and recycling, high cost of solvent, etc., and achieve the effect of convenient operation, low cost of solvent and high sugar yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
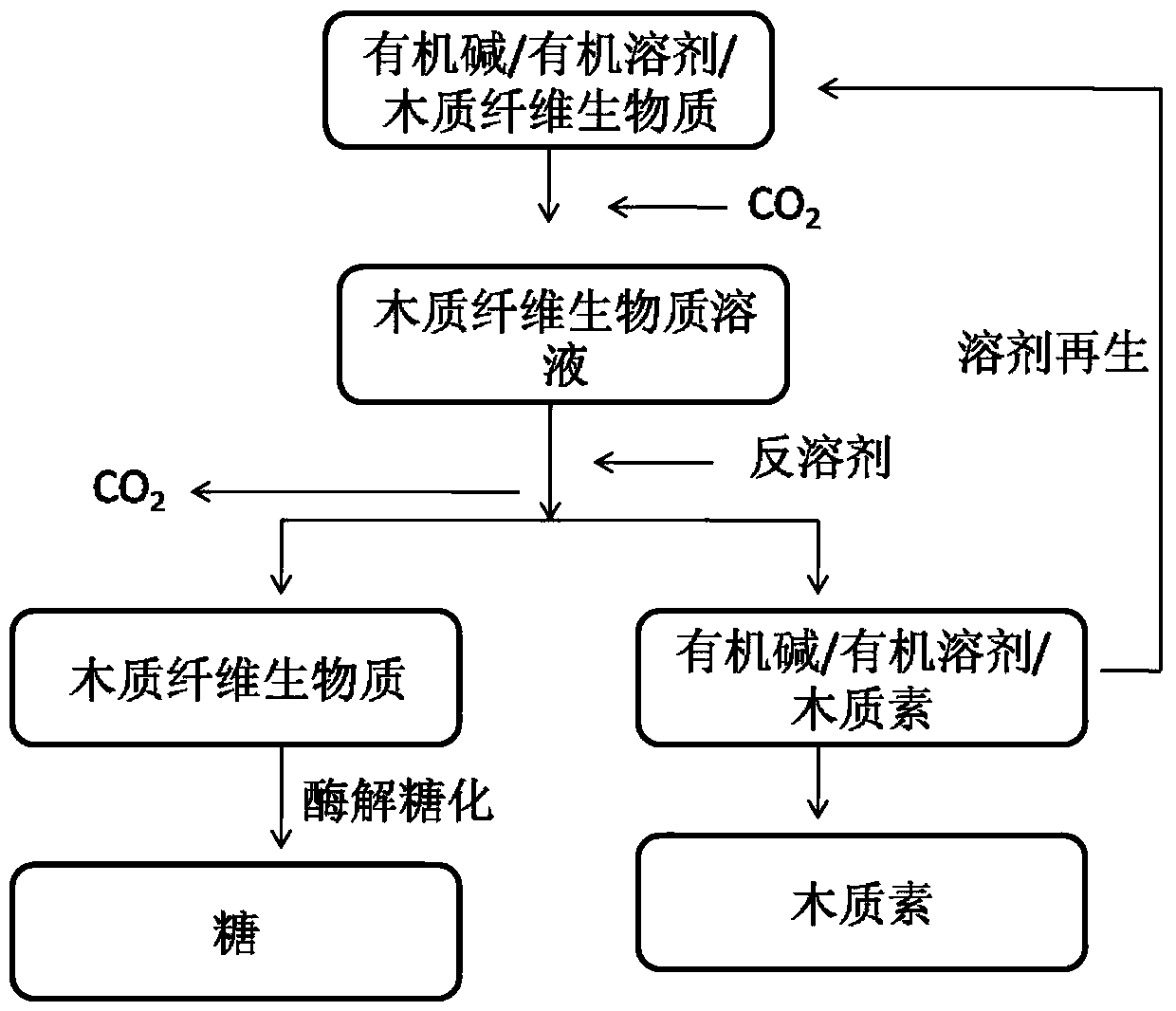
[0048] A method for improving the sugar production rate of lignocellulosic biomass enzymatic hydrolysis, characterized in that: it is carried out according to the following steps:
[0049] 1) Using lignocellulosic biomass as raw material;
[0050] 2) mixing lignocellulosic biomass, an organic base and an organic solvent;
[0051] 3) Fill the mixed system with a certain pressure of CO 2 , react at a certain temperature for a certain time;
[0052] 4) Release CO 2 , adding an anti-solvent to the system, the biomass is regenerated with the anti-solvent of cellulose, and then filtered and separated to obtain the pretreated lignocellulosic material;
[0053] 5) Taking a certain amount of regenerated lignocellulosic biomass, adding a buffer solution, cellulase and xylanase to carry out enzymatic hydrolysis to obtain a sugar solution.
[0054] See attached for details figure 1 .
Embodiment 2
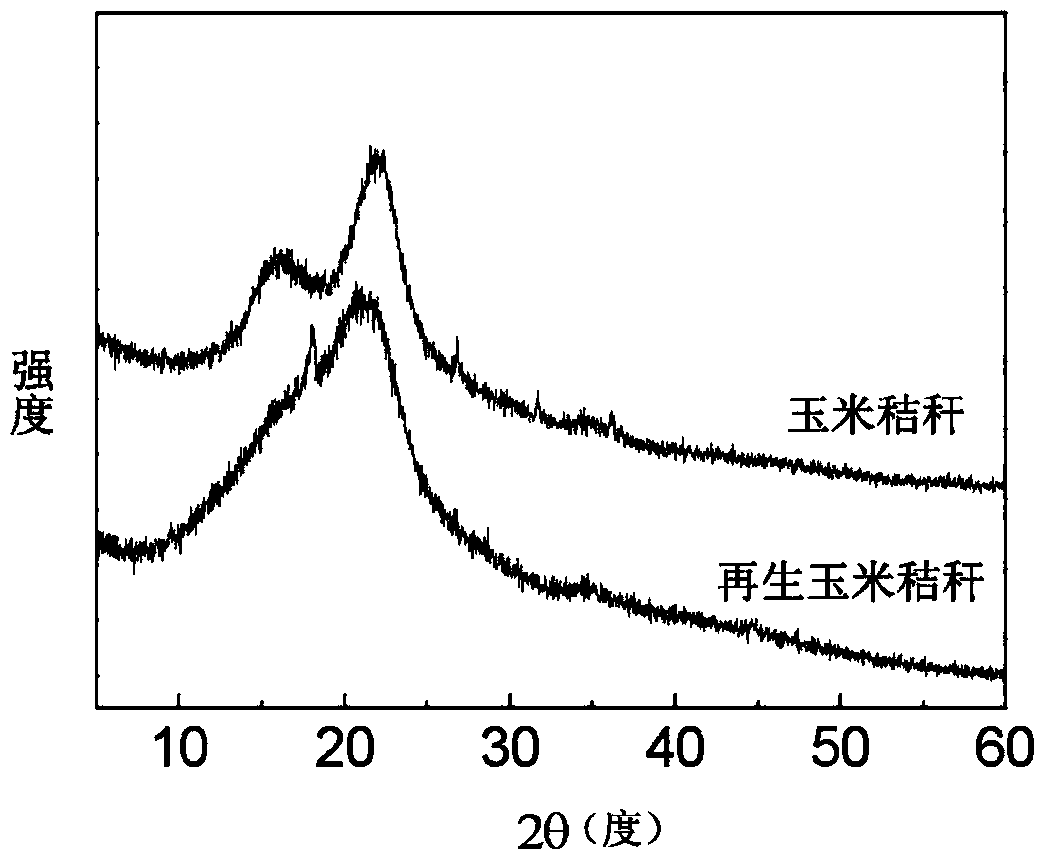
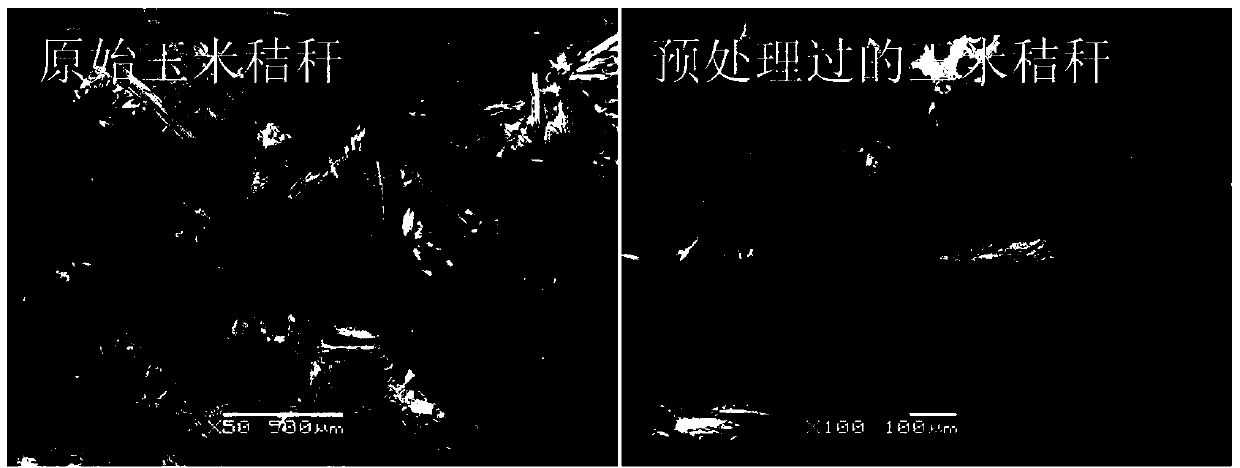
[0056] Add corn stalk lignocellulose (2.0 grams, physical size: 1 mm, moisture content2 , maintain the pressure at 0.5MPa, heat to 100°C, and dissolve for 60 minutes. cool down, releasing CO 2 , Open the reaction kettle, add 100 ml of anhydrous methanol to the system under agitation to regenerate the dissolved cellulose, filter, and collect the filtrate. Then, the filter residue was washed with 2*100 ml of anhydrous methanol, each time for 1 h, to completely remove the solvent, and then dried to obtain dissolved and pretreated lignocellulose. Filtrate, collect filter residue, and freeze-dry to obtain regenerated cellulose. Using regenerated cellulose as raw material, add acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution, the solid-liquid ratio is 1:10, the addition amount of Trichoderma viride is 15 FPU / g, and the ratio of 0.01 g / g substrate is added to xylanase. Shaking table speed: 100 rpm, enzymolysis conditions are pH 4.5, temperature 50°C, and enzymolysis time is 24 hours. Gl...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Wheatgrass lignocellulose (2.0 g, physical size: 0.1 mm, water content 2 , maintain the pressure at 2MPa, heat to 80°C, and dissolve for 180 minutes. cool down, releasing CO 2 , open the reaction kettle, and add 100 milliliters of absolute ethanol to the system under stirring conditions to regenerate the dissolved lignocellulose, filter, and collect the filtrate. Then the filter residue was washed with 2*100 ml of absolute ethanol for 1 hour each time to completely remove the solvent, and then dried to obtain dissolved and pretreated lignocellulose. Filtrate, collect filter residue, and freeze-dry to obtain regenerated cellulose. Using regenerated lignocellulose as raw material, add citric acid-sodium citrate buffer solution, the solid-liquid ratio is 1:20, the addition amount of Trichoderma reesei is 20 FPU / g, and the ratio of 0.03 g / g substrate is added to xylanase . Shaking table speed: 200 rev / min, enzymolysis condition is pH5.5, temperature 50°C, enzymolysis tim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com