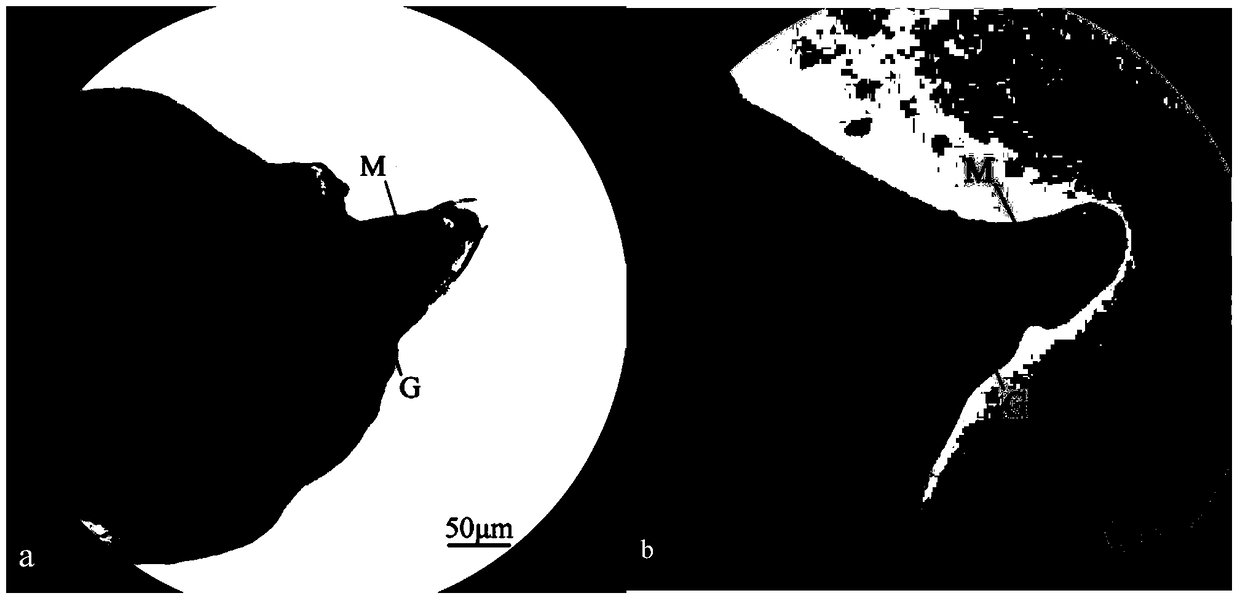
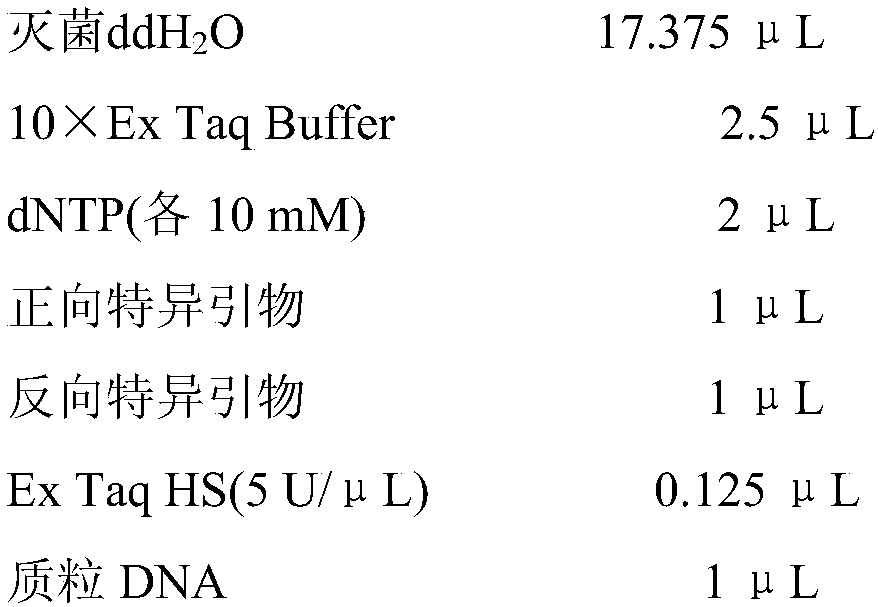
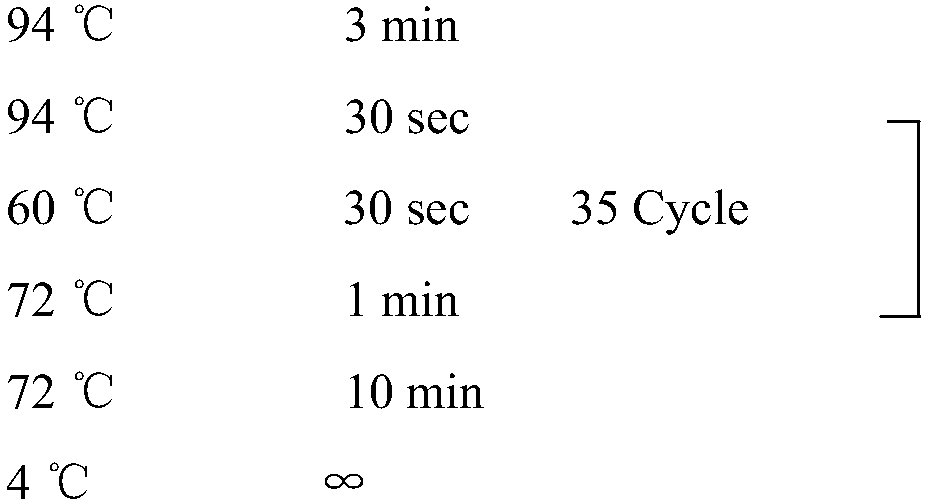In situ hybridization technique and application of esophageal gland gene of root-knot nematode
A technology of root-knot nematode and in situ hybridization, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of crop production loss, long survival time, difficult control, etc., and achieve good insects without deformation, Reduce the movement of insects and avoid deformation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Embodiment 1 The technology of the present invention detects the expression site of the MiPDCD6 gene in the esophageal gland of Meloidogyne gnats;
[0064] 1. Reagent purchase and configuration
[0065] (1). Purchase of main reagents:
[0066] Hybridization solution: purchased from Beijing Dingguo Biotechnology Co., Ltd.;
[0067] Anti-Digoxigenin-AP: purchased from Guangzhou Juyan Biotechnology Co., Ltd.;
[0068] 10×Blocking solution: purchased from Guangzhou Juyan Biotechnology Co., Ltd.;
[0069] ScriptMAX TM Thermo T7Transcription Kit: purchased from Toyobo (Shanghai) Biotechnology Co., Ltd.;
[0070] DNase I reagent: Beijing Tiangen Biotechnology Co., Ltd.;
[0071] (2). Main solution configuration:
[0072] 10×M9Buffer: Weigh 30.24g Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O, 6.0g KH 2 PO 4 , 10g NaCl, 0.5g MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, dilute to 200mL with distilled water, and autoclave;
[0073] Maleic Acid Buffer (Maleic Acid Buffer): Weigh 11.067g maleic acid and 8.766g NaCl and diss...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com