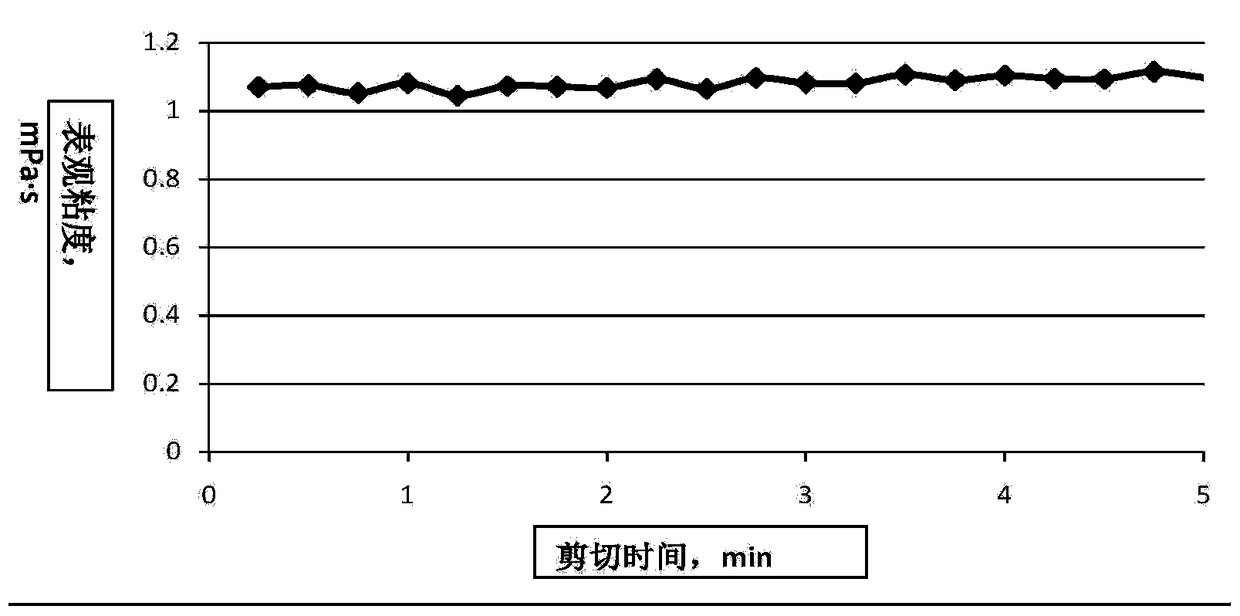
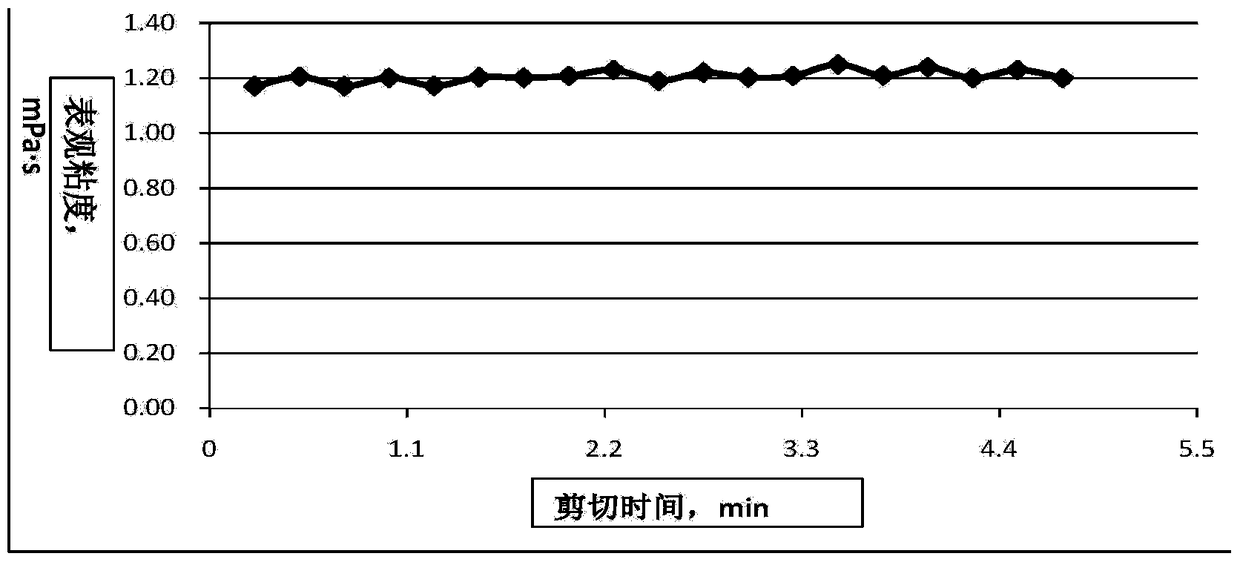
A kind of viscosity reducer of polyacrylamide polymer
A polyacrylamide and polymer technology, which is applied in the field of oil and gas exploration and development, can solve problems such as affecting the construction process and single well production, long ammonium persulfate gel breaking time, corrosion of production pipe strings, etc. Wide range of use conditions and short viscosity reduction time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] A viscosity reducer for polyacrylamide polymers, which consists of the following components by mass fraction: 2.2% salinity modifier, 0.5% viscosity modifier citric acid, 0.1% fluorocarbon surfactant, organic phosphate Corrosion inhibitor KD-GH022%, cleaning agent FeCl 3 1%, the balance is water, and the sum of each component is 100%. Wherein, the salinity regulator is composed of the following components by mass fraction: 45.5% KCl, 45.5% NaCl, 4.5% MgCl 2 and 4.5% CaCl 2 .
[0035] The preparation method of the viscosity reducer of the above-mentioned polyacrylamide polymer comprises the following steps: according to the above ratio, measure water and pour it into the stirring container, adjust the speed of the stirrer until the vortex formed by the liquid can see the central axis of the stirrer blade Up to the top, add salinity regulator into the water, stir well until it is completely dissolved, then add fluorocarbon surfactant and citric acid, stir for 4-5min, ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] A viscosity reducer for polyacrylamide polymers, which consists of the following components in terms of mass fraction: 30% salinity modifier, 0.1% viscosity modifier citric acid, 0.5% fluorocarbon surfactant, organic phosphate Corrosion inhibitor KD-GH020.5%, cleaning agent FeCl 3 0.1%, the balance is water, and the sum of each component is 100%. Wherein, the salinity regulator is composed of the following components by mass fraction: 33.3% KCl, 33.3% NaCl, 16.7% MgCl 2 and 16.7% CaCl 2 .
[0039] The preparation method of the viscosity reducer of the above-mentioned polyacrylamide polymer comprises the following steps: according to the above ratio, measure water and pour it into the stirring container, adjust the speed of the stirrer until the vortex formed by the liquid can see the central axis of the stirrer blade Up to the top, add salinity regulator into the water, stir well until it is completely dissolved, then add fluorocarbon surfactant and citric acid, sti...
Embodiment 3
[0042] A viscosity reducer for polyacrylamide polymers, which consists of the following components in terms of mass fraction: 16% salinity modifier, 0.5% viscosity modifier citric acid, 0.2% fluorocarbon surfactant, organic phosphate Corrosion inhibitor KD-GH021.5%, cleaning agent FeCl 3 0.4%, the balance is water, and the sum of each component is 100%. Wherein, the salinity regulator is composed of the following components by mass fraction: 31.3% KCl, 31.3% NaCl, 18.8% MgCl 2 and 18.8% CaCl 2 .
[0043] The preparation method of the viscosity reducer of the above-mentioned polyacrylamide polymer comprises the following steps: according to the above ratio, measure water and pour it into the stirring container, adjust the speed of the stirrer until the vortex formed by the liquid can see the central axis of the stirrer blade Up to the top, add salinity regulator into the water, stir well until it is completely dissolved, then add fluorocarbon surfactant and citric acid, sti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shear viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shear viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com