Compact and stable high-peak-power optical fiber output laser
A high-peak, laser technology, applied in the direction of lasers, laser components, phonon exciters, etc., can solve the problems of reduced spatial optical coupling efficiency, low output energy, poor laser stability, etc., to reduce the risk of fiber damage, The effect of increasing peak power and improving stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] The present invention will be further described through the embodiments below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, so as to better understand the present invention.
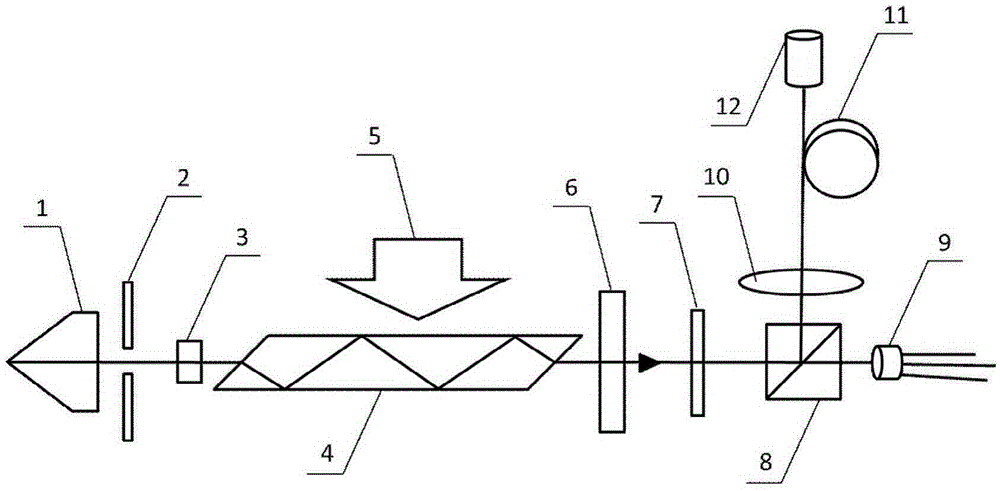
[0020] like figure 1 As shown, a compact and stable high peak power fiber output laser, including a resonant cavity, a half-wave plate (7), a polarization beam splitter (8) and a photodetector (9), are arranged in sequence along the optical path direction, and it is characterized in that, The resonant cavity includes a Paul prism (1), a passive Q-switching crystal (3), a laser crystal (4) and an output mirror (6) arranged in sequence; A coupling lens (10), an optical fiber (11) and a collimator lens group (12) are provided in sequence.
[0021] like figure 2 As shown, the Paul prism 1 includes two inclined planes a and b perpendicular to each other, a and b intersect on the line l, the midpoint of l is M, the Paul prism 1 also includes a longitudinal plane c, and the longitudinal plane c is a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com