Surface acoustic wave resonator type impedance sensor and surface acoustic wave resonator type impedance detection system
A surface acoustic wave and impedance detection technology, which is applied in impedance networks, uses electromagnetic/magnetic devices to transmit sensing components, electrical components, etc. The effect of improving the degree and reducing the package structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
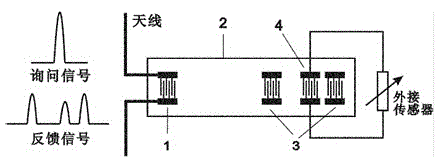
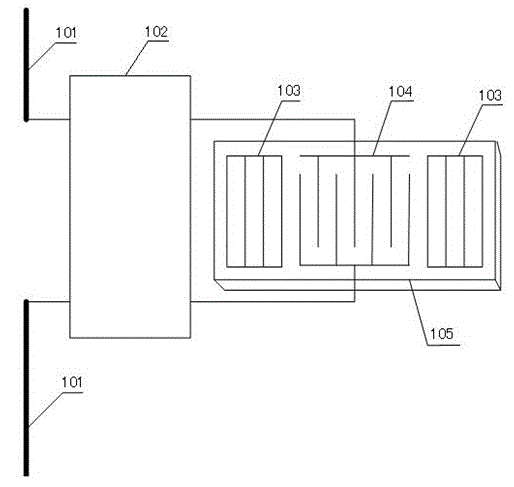
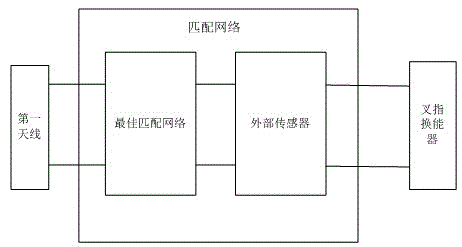
[0026] Embodiment one, see figure 2 As shown, the present embodiment provides a surface acoustic wave resonator type impedance sensor, including a first antenna 101, a matching network 102, a reflection grid 103, and an interdigital transducer 104, at least the reflection grid 103, and an interdigital transducer The energy device 104 is arranged on the piezoelectric substrate 105, see image 3 As shown, the matching network 102 includes an optimal matching network composed of at least one capacitor and at least one inductor. The optimal matching network is also connected in parallel with an external sensor, and the external sensor is a capacitive or inductive sensor. The working principle of the surface acoustic wave resonator type impedance sensor of this embodiment is: the external sensor is a capacitive or inductive sensor, and the capacitive or inductive sensor is to convert the measured mechanical quantity, such as displacement, pressure, etc. For sensors with changing ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment 2, this embodiment provides a schematic circuit diagram of a surface acoustic wave resonator type impedance sensor, see Figure 4 As shown, the optimal matching network is composed of the first capacitor C1 and the first inductor L1 connected in series, and the external sensors are connected in parallel at both ends of the series circuit composed of the optimal matching network.
[0029] where the external sensor can be as Figure 4 As shown, it is connected to the matching network through the outside of the wire, and it can also be connected as Figure 5 The integration shown in the matching network, the use of external or internal integration depends on the specific situation. For a relatively safe environment such as tire pressure detection, the external sensor can be integrated into the matching network. The product The high level of integration is conducive to reducing the packaging structure and reducing the overall volume of the sensor. For the detec...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Embodiment 3. This embodiment provides a schematic circuit diagram of a surface acoustic wave resonator-type impedance sensor. Since the external sensor is capacitive or inductive, no matter how it is connected to the matching network, it will Will change the reactance value of the matching network. This embodiment gives another way of incorporation, see Figure 6 As shown, the external sensor can also only be connected in parallel with the first inductor L1 to change the reactance value of the matching network. Of course, there are other combinations, which all belong to the protection scope of the present invention, and no examples will be given here.
[0031] The equivalent capacitive reactance of the matching network is C′, the equivalent inductive reactance L′, and the calculation method of the impedance value Zeq2 of the matching network is:
[0032] (1)
[0033] (2)
[0034] The general near-resonator equivalent circuit model of a resonator is as Figure 7...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com