Method for efficiently removing epibiotic microorganisms on surfaces of large seaweed
A technology of microorganisms and seaweeds, applied in the direction of fungi and bacteria, can solve the problems of killing endophytic microorganisms, affecting the diversity composition of endosymbiotic microorganisms, killing, etc., and achieves the effects of efficient removal, easy mass production, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1: The quartz sand method thoroughly removes the epiphytic microorganisms of the large green alga Enteromorpha (U.prolifera)
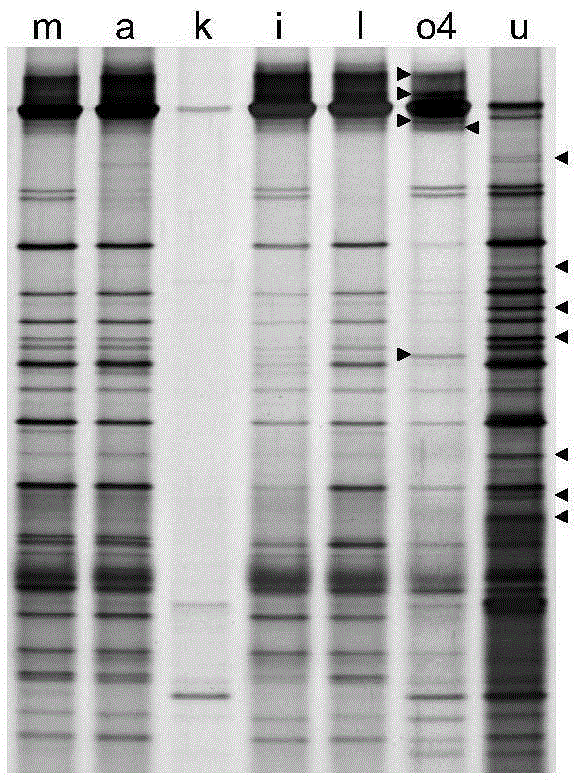
[0024] Enteromorpha is a single-layer tubular algal body, which is relatively fragile. In addition to the quartz sand method of the present invention, a total of 12 methods of enzymatic method, chemical method and physical method were compared for the removal effect of fresh Enteromorpha epiphytic microorganisms. Scanning electron microscopy was used to determine whether the epiphytic microorganisms of Enteromorpha were removed, and the effects of various methods on the endophytic microorganisms of Enteromorpha were detected by deformable gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE).
[0025] Test 7 kinds of enzymatic methods altogether, at first prepare the lysozyme of 2mg / ml, papain, helicase, cellulase, lysozyme+papain+helicase (every kind of enzyme concentration is 2mg / ml) and proteinase K, more Enzyme cleaners were purchased from finishe...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment 2: The quartz sand method thoroughly removes the epiphytic microorganisms of the large green alga Enteromorpha flatus (U.compressa)
[0032] Take about 0.03g of Enteromorpha algae and 0.3g of the above-mentioned quartz sand with a particle size range of 125-250μm and mix them in a 1.5ml Eppendorf centrifuge tube, add 1ml of sterilized seawater, and shake at 3200rpm for 2×15min to obtain the epiphytic The ideal result that the microorganisms have been completely eliminated without affecting the algal cells ( figure 1 , r).
Embodiment 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: Quartz sand method thoroughly removes the epiphytic microorganisms of large-scale green algae Enteromorpha (U.linza)
[0034] Take about 0.03g of Enteromorpha algae and 0.3g of the above-mentioned quartz sand with a particle size range of 125-250μm and mix them in a 1.5ml Eppendorf centrifuge tube, add 1ml of sterilized seawater, shake at 3200rpm for 2×15min, and obtain the attached The ideal result that the living microorganisms have been completely removed and has no effect on the algal cells ( figure 1 , s).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com