Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for efficiently co-fermenting glucose and xylose and application of recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
A Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and co-fermentation technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of natural Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolizing xylose, etc., and achieve the effect of optimizing fermentation ability and improving xylose fermentation ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
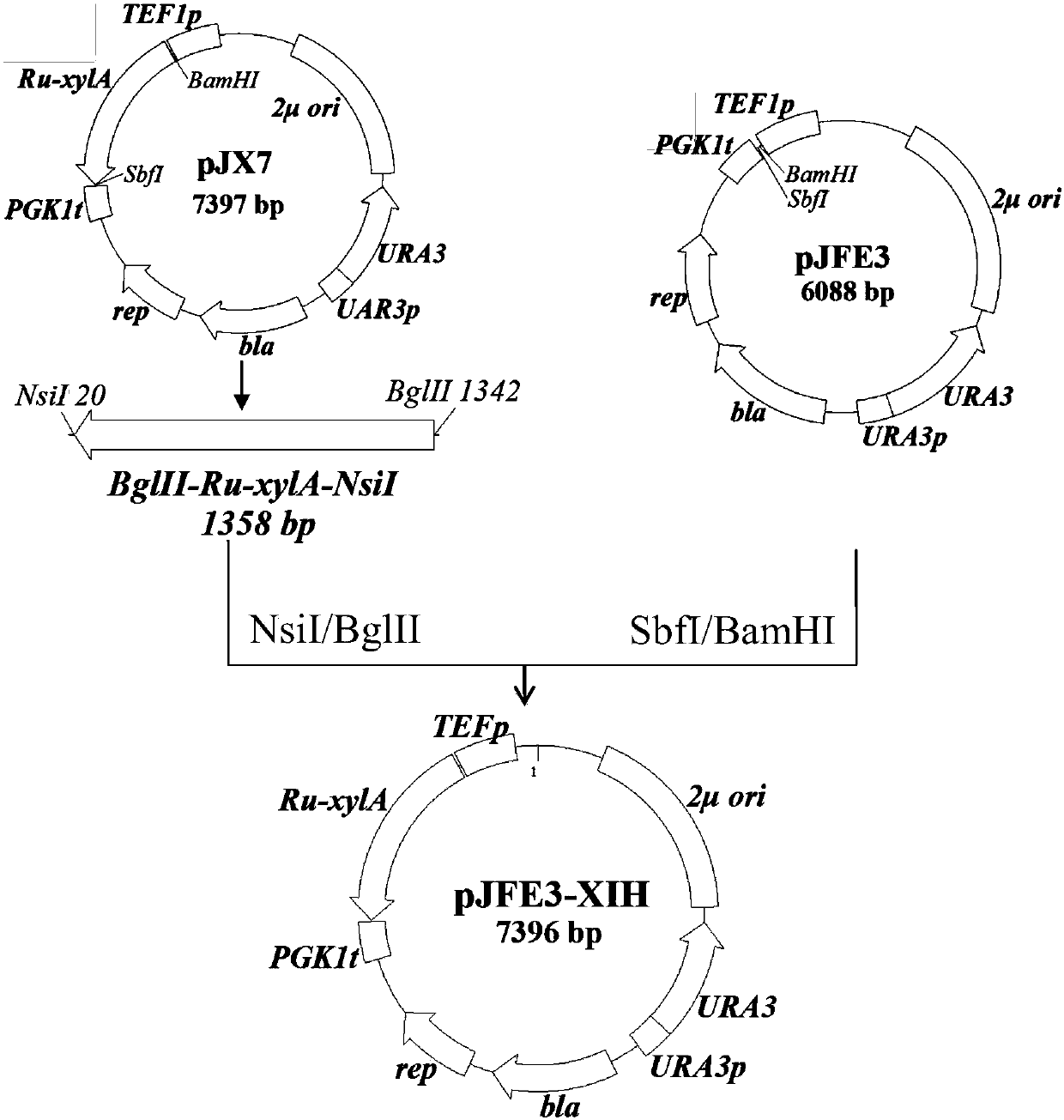
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Embodiment 1 culture medium, enzyme and reagent and relevant microorganism and molecular biology technique
[0053] (1) culture medium
[0054] LB medium used for Escherichia coli culture: 10gL -1 Peptone, 5gL -1 Yeast extract, 10gL -1 NaCl; add 20gL of solid medium -1 Agar powder; sterilization conditions: 115°C, 30min; when in use, add ampicillin (Amp) to 100μgmL -1 Used to screen E.coli transformants.
[0055] YEP medium used for Saccharomyces cerevisiae culture: 20gL -1 Peptone, 10gL -1 Yeast powder; add 20gL of solid medium -1 Agar powder; Sterilization conditions: 115°C, 30min. When using, add different concentrations of glucose or xylose as carbon source to make YEPD or YEPX medium respectively, or add glucose and xylose as carbon source to make mixed sugar medium, which is used for strain growth and fermentation performance detection. Add 400-800 μg mL if necessary -1 G418 or 200 μg mL -1 HygromycinB was used for screening and culturing of correspond...
Embodiment 2
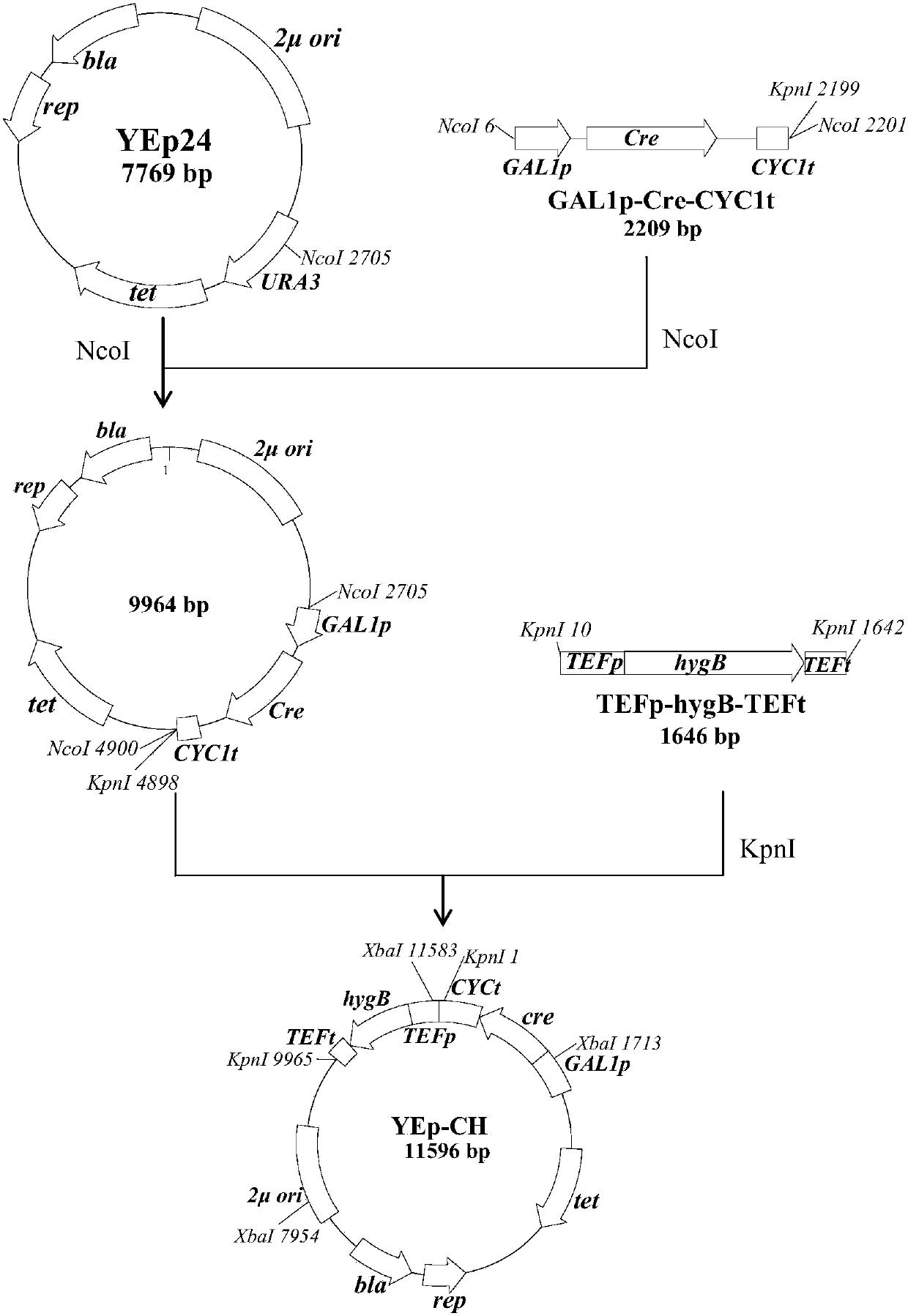
[0066] Construction of embodiment 2 plasmid YEp-CH
[0067] (1) Ordinary PCR amplification of DNA fragments
[0068] The following fragments were amplified by PCR: fragment GAL1p-Cre-CYC1t (Cre enzyme gene under the control of GAL1 promoter and CYC1 terminator), TEF1 promoter, TEF1 terminator, hygromycin B resistance gene (hygB).
[0069]Using the plasmid pSH47 as a template, use primers 1 and 2 to amplify the fragment GAL1p-Cre-CYC1t; using the plasmid pUG6 as a template, use primers 3 and 4 to amplify the TEF1 promoter; using the plasmid pUG6 as a template, use primers 5 and 6 Amplify the TEF1 terminator; use the plasmid pUCATPH (Luetal., 1994) as a template, and use primer 7 and primer 8 to amplify fragment hygB.
[0070] (2) fusion PCR amplified DNA fragment
[0071] Amplify the fragment TEF1p-hygB-TEF1t by fusion PCR: the DNA fragment TEF1 promoter obtained in step (1), the TEF1 terminator and the fragment hygB are simultaneously used as templates for PCR, and PCR ampli...
Embodiment 3
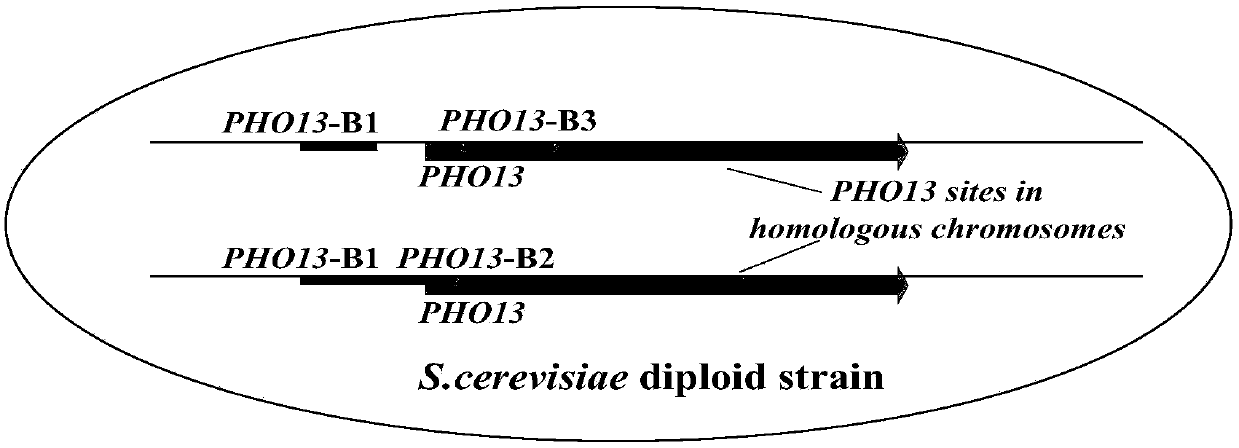
[0077] Example 3 Removal of screening marker genes by Cre-loxP recombination
[0078] The plasmid Yep-CH obtained in Example 2 was transferred into a recombinant yeast strain containing a selection marker gene (with loxP sites at both ends), and transformants were selected on a YEPD plate containing hygromycin B.
[0079] Cultivate the obtained transformant overnight in liquid YEPD medium containing hygromycin B, then collect the cells by centrifugation and wash twice with sterile water, resuspend the cells in galactose medium, culture with shaking at 30°C for two hours to induce Cre recombination Enzyme expression, then streak the bacterial solution on the YEPD plate, culture at 30°C for two days to isolate a single colony, drop the single colony on the YEPD plate without G418 and the YEPD plate containing G418, and select no G418 resistance after culturing at 30°C for two days The colonies obtained by PCR verified that the Cre-loxP recombination occurred correctly.
[0080]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com