A strain of pseudoantaba scsio S3 and its application
A technology of SCSIOS3 and Pseudo-Anabaena, applied in the direction of microorganisms, fermentation, bacteria, etc., to achieve good nitrogen fixation activity, broad application prospects, and high-value effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1: Isolation, purification and identification of Pseudoantabaena sp. SCSIO S3
[0020] 1. Separation and purification of Pseudanabaena sp. SCSIO S3
[0021] Collect the seaweed Thalias algae collected from Xincun Bay, Lingshui, Hainan Province, China, add seawater to scrub, and filter to obtain the cyanobacteria liquid. Pick cyanobacteria hyphae and culture them in marine cyanobacteria medium ATCC Medium 957, nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria medium ATC Medium 819, marine nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria medium ATCC Medium 1077 and BG-11Medium, and the continuous light intensity is 150μE / m 2 / s, the light cycle is 12:12h (light: dark cycle), the temperature is 23-27°C, in the light incubator (the model is LRH-250-GH microcomputer-controlled light incubator), every two weeks into fresh medium until the microscopic examination shows a single mycelium. The cyanobacteria SCSIO S3 was obtained by separation and purification.
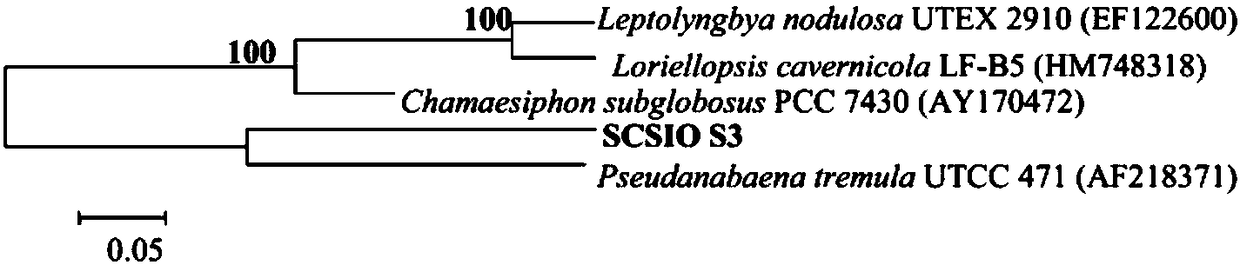
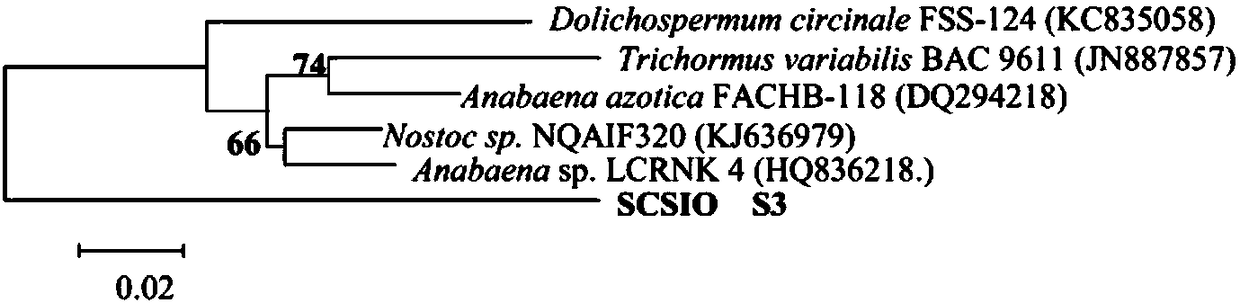
[0022] 2. Identification of Pseudanabaena sp...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The mensuration of embodiment 2 cyanobacteria indole acetic acid production
[0037] The salkowski colorimetric method was used to determine the ability of the isolate to produce plant growth hormone substances, and the standard curve was prepared using pure 3-IAA (3-indole acetic acid). Inoculate the cyanobacteria SCSIO S3 in 100mL selective liquid nitrogen-free liquid modified medium (formula is the same as in Example 1), and the continuous light intensity is 150 μE / m 2 / s, the light cycle is 12:12h (light: dark cycle), the temperature is 25-28°C, cultivate for 120h, take 5mL of the cyanobacteria culture supernatant every 24h, centrifuge at 10000r / min for 10min, take the supernatant and add colorimetric The solution was left to stand in the dark for 0.5h, taken out, and measured immediately with a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 530nm (Glickmann and DessauxY.A).
[0038] Indole acetic acid content in the sample (μg / mg) = (A × V1) / (W × V2) × 1000
[0039] In t...
Embodiment 3
[0044] 16SRNA and nitrogen fixation gene amplification of the strain of embodiment 3
[0045] Select the pure bacterial strain cyanobacteria SCSIO S3 that the separation and purification of embodiment 1 obtains to carry out DNA extraction and purification, the extraction and purification of DNA in this embodiment, its operation method refers to Dong Xiuzhu "Common Bacteria System Identification Manual" P 409 . 16S 27F / 1492R of nitrogen-fixing bacteria (Weisenburg et al., 1991, 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study., Journal of bacteria, 1991173 (2): 697-703 and nifH gene general primer PolF / PolR (refer to Poly et al., 2001, Comparison of nif (Gene Pools in Soils and Soil Microenvironments with Contrasting Properties, Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2001, 67 (5): 2255-2262) PCR amplification: PCR reaction system as shown in Table 1.
[0046] Table 1 PCR reaction system
[0047]
[0048] The PCR reaction conditions were: pre-denaturation at 95°C for...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com