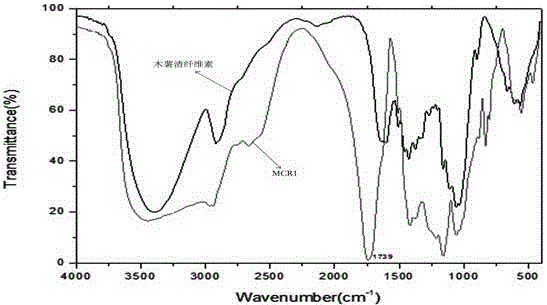
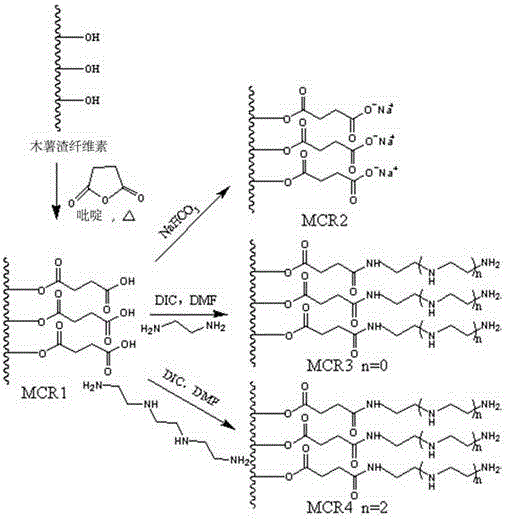
Method and application for extracting cellulose from manioc waste
A cassava residue and cellulose technology is applied in the direction of using microorganism/enzyme cellulose treatment, fiber raw material treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing pollution, improving adsorption effect, and improving economic and environmental value.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Using waste cassava residues as raw materials, cassava residue cellulose and heavy metal adsorption materials were prepared according to the following method:
[0053] 1. Extraction of cassava residue cellulose
[0054] Raw material pretreatment: wash cassava dregs with distilled water several times to remove impurities and soluble substances, then put them in a constant temperature drying oven at 80°C for 8 hours, crush them through a 40-mesh sieve, and store them in a desiccator for later use .
[0055] Weigh 10.00g of pretreated cassava residues, add 60ml of distilled water and boil for 5 minutes to fully gelatinize the starch in the cassava residues, add 100ml of 0.8wt% α-amylase solution, at 60°C, pH6.0 and 105W ultrasonic, Enzymolysis for 45min, inactivate enzyme (100°C, 5min), centrifuge (4000r / min, 20min), discard the supernatant, add 100ml of 5% NaOH solution, alkaline hydrolyze at 70°C for 90min, wash, and naturally Settle, discard the supernatant, filter, d...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Using waste cassava residues as raw materials, cassava residue cellulose and heavy metal adsorption materials were prepared according to the following method:
[0066] 1. Extraction of cassava residue cellulose
[0067] Raw material pretreatment: wash cassava dregs with distilled water several times to remove impurities and soluble substances, then put them in a constant temperature drying oven at 80°C for 8 hours, crush them through a 40-mesh sieve, and store them in a desiccator for later use .
[0068] Weigh 10.00g of pretreated cassava residue, add 40ml of distilled water and boil for 10min to fully gelatinize the starch in the cassava residue, add 100ml of 1.0wt% α-amylase solution, at 50°C, pH7.0 and 150W ultrasonic, Enzyme hydrolysis for 30min, inactivate enzyme (100°C, 5min), centrifuge (4000r / min, 20min), discard the supernatant, add 80ml volume 7% NaOH solution, alkali hydrolyze at 80°C for 60min, wash, naturally Settle, discard the supernatant, filter, dry ...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Using waste cassava residues as raw materials, cassava residue cellulose and heavy metal adsorption materials were prepared according to the following method:
[0073] 1. Extraction of cassava residue cellulose
[0074] Raw material pretreatment: wash cassava dregs with distilled water several times to remove impurities and soluble substances, then put them into a constant temperature drying oven at 70°C for 8 hours, crush them through a 40-mesh sieve, and store them in a desiccator for later use .
[0075] Weigh 10.00g of the pretreated cassava residue, add 60ml of distilled water and boil for 5min to fully gelatinize the starch in the cassava residue, add 100ml of 0.2wt% α-amylase solution, at 55°C, pH5.5 and 90W ultrasonic, Enzyme hydrolyze for 90min, inactivate enzyme (100°C, 5min), centrifuge (4000r / min, 20min), discard supernatant, add 120ml volume 3% NaOH solution, alkali hydrolyze at 75°C for 105min, wash, naturally Settle, discard the supernatant, filter, dry...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com