Microbial complex flora for eliminating sulfide in sediments
A compound flora and sulfide technology, applied in the methods of using microorganisms, microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of elimination, narrow ecological niche of pure bacteria, low biomass, etc., and achieve the maintenance of structure and composition. Reduce the effect of the adaptation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1: Screening, identification and genetic stability of microbial complexes for sulfide elimination in sediments
[0026] (1) Screening of microbial complex flora for sulfide elimination in sediments
[0027] 1) Collect the surface sediments within 10cm of depth in offshore aquaculture areas, and inoculate at a volume percentage of 10% to make a bacterial suspension:
[0028] In an Erlenmeyer flask, inoculate sterilized old seawater with a volume percentage of 10% of the collected surface sediment within a depth of 10 cm in an offshore culture area. Seal the Erlenmeyer flask with aluminum foil and place it on a constant temperature shaker at 30°C and shake at 120r / min for 30min to fully release the bacteria in the sediment. After shaking, let it stand for 30 minutes until the sediment re-precipitates, and the supernatant is the bacterial suspension;
[0029] 2) Inoculate the bacterial suspension in the above step 1) with an inoculum size of 10% by volume percent...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Embodiment 2: This study microbial compound bacterial agent is to the removal effect of sulfide
[0054] 1) Quickly thaw the microbial complex flora stored at -80°C in step 6) of the screening of microbial complex flora for sulfide elimination in sediments determined in Example 1 in a 30°C water bath;
[0055] 2) Inoculate the microbial complex flora after thawing in step 1) in an inoculum size of 10% by volume percentage in an inorganic salt medium with an initial concentration of sulfide of 1000 mg / l, in an anaerobic bottle at 30° C. , 150r / min constant temperature shaking culture. Among them, the inorganic salt medium is: K 2 HPO 4 : 1.2g / l, KH 2 PO 4 : 1.2g / l, NH 4 Cl: 0.4g / l, MgCl 2 : 0.2g / l, ferric citrate: 0.01g / l, NaHCO 3 : 2g / l, Na 2 S 2 o 3 ·5H 2 O: 3.875g / l, prepared with sterilized aged sea water.
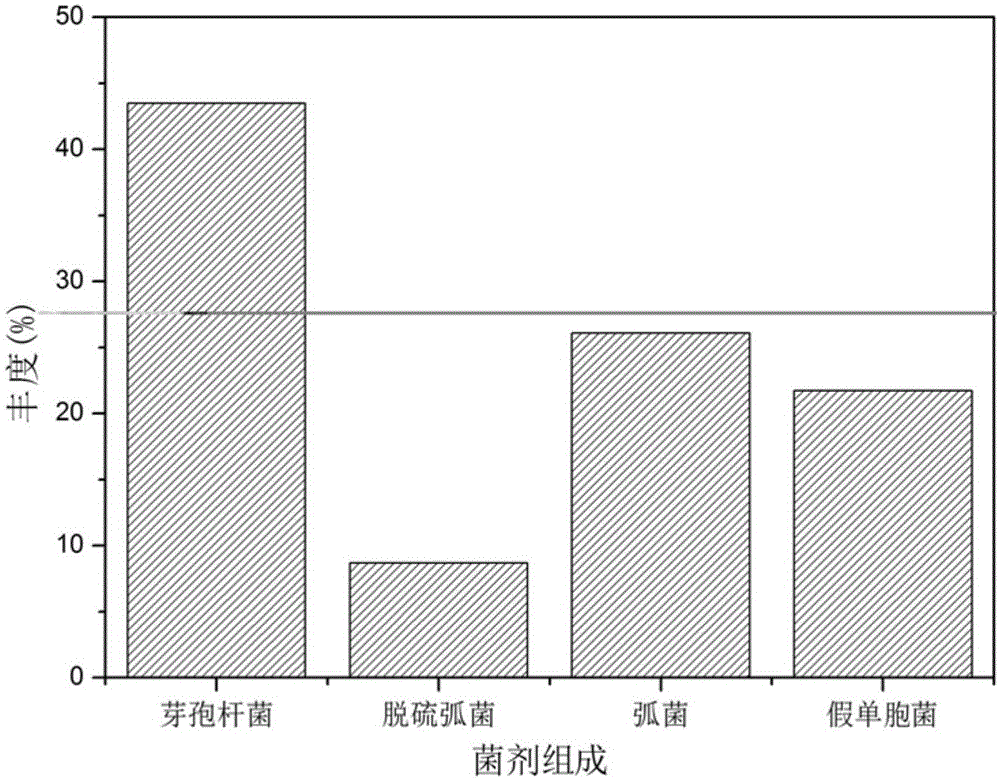
[0056] At the same time, the microorganisms identified in Example 1 were selected for specific strains (Vibrio mimeticus, Desulfovibrio, Pseudomonas ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com