Method for forming Y-shaped gate metal dielectric hole through auxiliary of photoresist
An auxiliary medium and photoresist technology, applied in electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of small size and reduced gate parasitic capacitance, and achieve a reduction in gate parasitic capacitance and significant reduction in gate parasitic capacitance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037] The method for forming a Y-shaped gate metal dielectric cavity assisted by photoresist includes the following five steps:
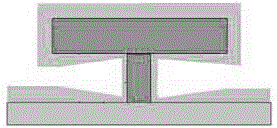
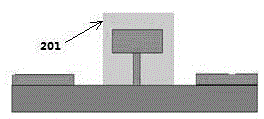
[0038] 1) After gate metallization, apply photoresist, carry out pattern photolithography and development, and form as shown in Figure 2-a, Figure 2-b The auxiliary photoresist pattern shown forms a cover 201 for the gate metal strip.
[0039] 2) Low temperature growth of SiN medium 200nm, as shown in Figure 3-a, Figure 3-b As shown; the growth temperature of the medium should be low (using ICP-PECVD, 60°C), otherwise the photoresist will be deformed or even flow due to heat; the thickness of the medium should not be too small, otherwise it will be easily broken in the subsequent decoating process.
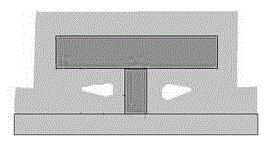
[0040] 3) Photolithography forms photoresist mask patterns (for dielectric etching) (401, 402) as shown in Figure 4-a and 4-b; perform SiN dielectric etching, after dielectric etching, the lower layer assists The photoresist is exposed at both end...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com