Dimer of rivastigmine, caffeic acid and ferulic acid, preparation method and pharmaceutical composition thereof
A technology for preparing medicines and compositions, applied in the field of derivatives of Ming, can solve problems such as unclear central action
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
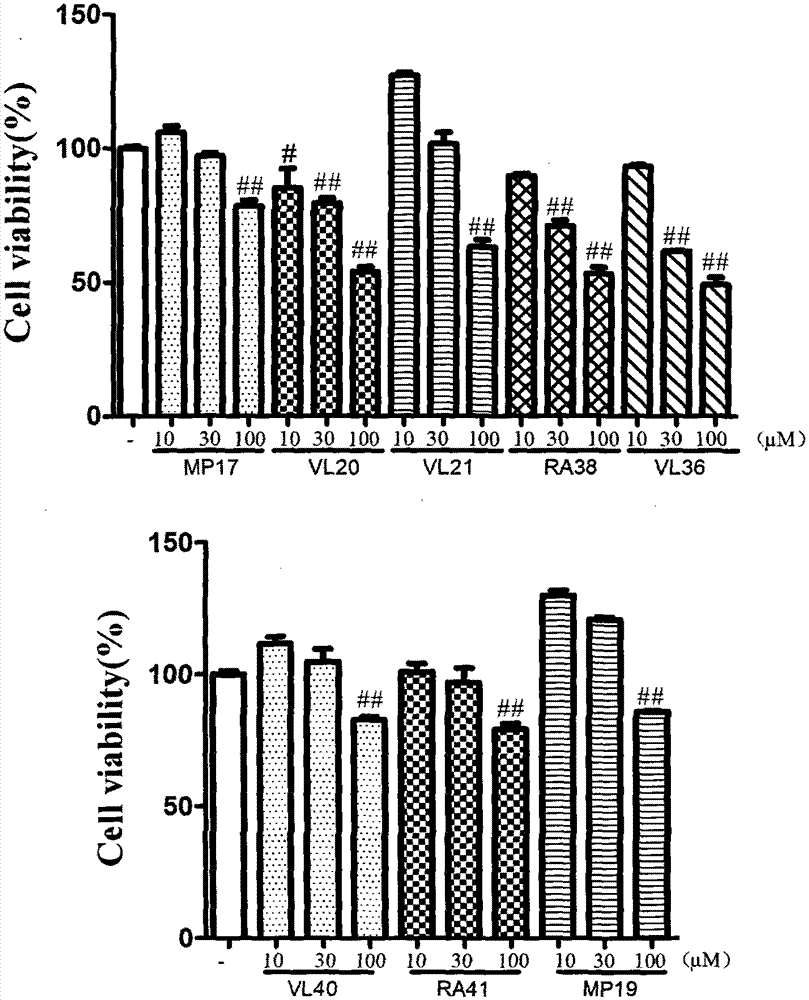
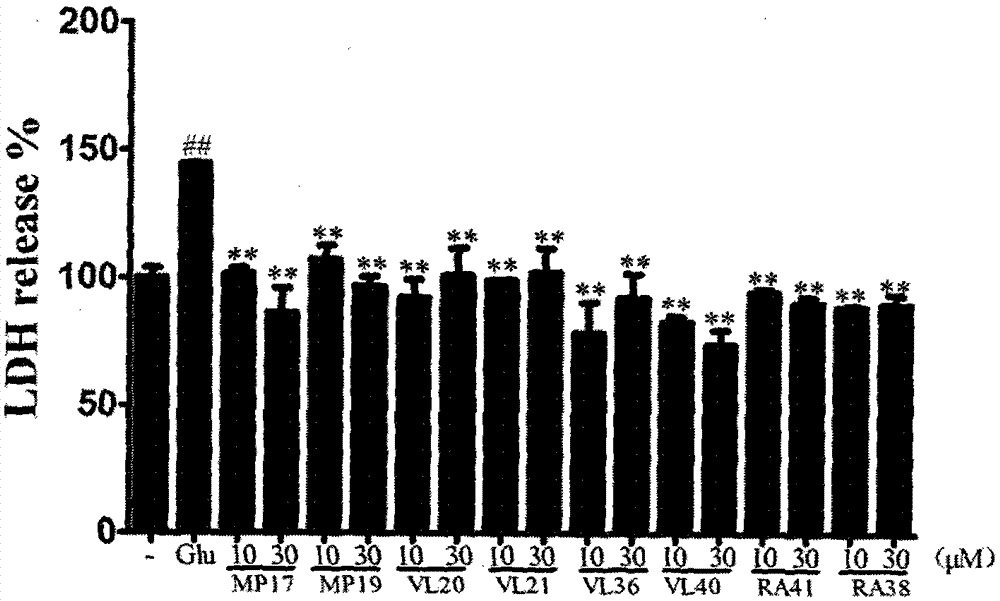
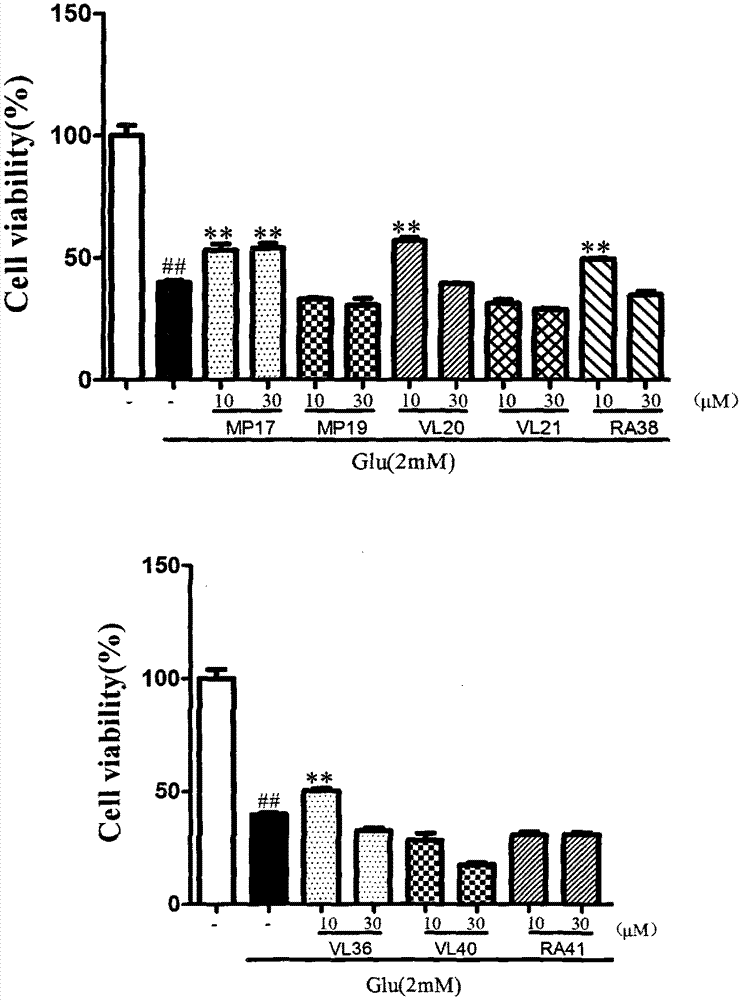
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038]
[0039] (2E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-N-(3-{[ethyl(methyl)carbamoyl]amino}phenyl)-2-acrylamide
[0040] Reagents: caffeic acid (109 mg, 0.53 mmol), 3-(3-aminophenyl)-1-ethyl-1-methylurea (111 mg, 0.53 mmol).
[0041] Purification: CHCl3 / MeOH (9.5:0.5). Silica gel column chromatography using CHCl3 / MeOH (9.5:0.5). Yellow solid, yield: 81 mg (43%).
[0042] mp 110-112°C;
[0043] 1 H NMR (CD 3 OD) δ: 1.17(t, 3H, J=7.2Hz, CH 3 ), 3.01 (s, 3H, CH 3 ), 3.43(q, 1H, J=7.2Hz, CH 2 ), 6.55(d, 1H, J=15.4Hz, CH=), 6.78(d, 1H, J=8.0Hz, Ar), 6.95(dd, 1H, J=1.6, 8.0Hz, Ar), 7.05(d , 1H, J=1.6Hz, Ar), 7.11(d, 1H, J=8.0Hz, Ar), 7.22(t, 1H, J=8.0Hz, Ar), 7.34(d, 1H, J=8.0Hz, Ar), 7.51(d, 1H, J=15.4Hz, CH=), 7.70(s, 1H, Ar) ppm;
[0044] 13 C NMR (Acetone-d 6 ( 19 h 21 N 3 o 4 ) Calc %: C 64.21, H 5.96, N 11.82; Trov %: C 64.47, H 6.08, N 11.69.
Embodiment 2
[0046]
[0047] (2E)-N-(3-{[Ethyl(methyl)carbamoyl]amino}phenyl)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-acrylamide
[0048] Reagents: ferulic acid (92 mg, 0.48 mmol), 3-(3-aminophenyl)-1-ethyl-1-methylurea (100 mg, 0.48 mmol).
[0049] Purification: silica gel column chromatography using CHCl 3 / MeOH (9.8:0.2). Yellow solid, yield: 71 mg (40%). mp112-115℃;
[0050] 1 H NMR (CD 3 OD) δ: 1.18(t, 3H, J=7.2Hz, CH 3 ), 3.02(s, 3H, CH 3 ), 3.44(q, 1H, J=7.2Hz, CH 2 ), 3.91 (s, 3H, OCH 3 ), 6.55(d, 1H, J=15.6Hz, CH=), 6.82(d, 1H, J=8.2Hz, Ar), 7.09(dd, 1H, J=1.8, 8.2Hz, Ar), 7.12(d , 1H, J=8.0Hz, Ar), 7.17(d, 1H, J=1.8Hz, Ar), 7.22(t, 1H, J=8.0Hz, Ar), 7.35(d, 1H, J=8.0Hz, Ar), 7.57(d, 1H, J=15.6Hz, CH=), 7.70(s, 1H, Ar) ppm;
[0051] 13 C NMR (Acetone-d 6 ( 20 h 23 N 3 o 4 ) Calc %: C 65.03, H 6.28, N 11.37; Trov %: C 65.32, H 6.44, N 11.53.
Embodiment 3
[0053]
[0054] 3-{[(2E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-acryloyl]amino}phenylethyl(methyl)carbamate
[0055] Reagents: caffeic acid (167 mg, 0.93 mmol), 3-aminophenylethyl (methyl) carbamic acid (180 mg, 0.93 mmol).
[0056] Purification: silica gel column chromatography using CHCl 3 / MeOH (9.5:0.5) was used as the eluent, followed by precipitation from ethyl acetate / n-hexane. Yellow solid, yield: 278 mg (84%).
[0057] mp 193-195°C;
[0058] 1 H NMR (Acetone-d 6 )δ: 1.15(t, 1.5H, J=7.0Hz, CH 3 rotamer), 1.24(t, 1.5H, J=7.0Hz, CH 3 rotamer), 2.95(s, 1.5H, CH 3 rotamer), 3.08(s, 1.5H, CH 3 rotamer), 3.37(q, 1H, J=7.0Hz, CH 2 rotamer), 3.49 (q, 1H, J=7.0Hz, CH 2 rotamer), 6.59 (d, 1H, J=15.4Hz, CH=), 6.81-6.84 (m, 1H, Ar), 6.87 (d, 1H, J=8.0Hz, Ar), 6.99 (dd, 1H, J =8.0, 2.1Hz, Ar), 7.10(d, 1H, J=2.1Hz, Ar), 7.28(dd, 1H, J=8.4, 8.0Hz, Ar), 7.47(d, 1H, J=8.4Hz, Ar), 7.54 (d, 1H, J=15.4Hz, CH=), 7.73 (s, 1H, Ar) ppm;
[0059] 13 C NMR (Acetone-d 6 )δ: 164.18, 153.83, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com