CSP (Common Spatial Patterns) and cross-correlation based motor imagery electroencephalogram classification method
An EEG signal and motor imagery technology, applied in the information field, can solve problems such as the decline in classification accuracy, noise sensitivity, and the inability of different individuals to adapt to individual differences.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0036] refer to figure 1, the concrete realization of the present invention is as follows:
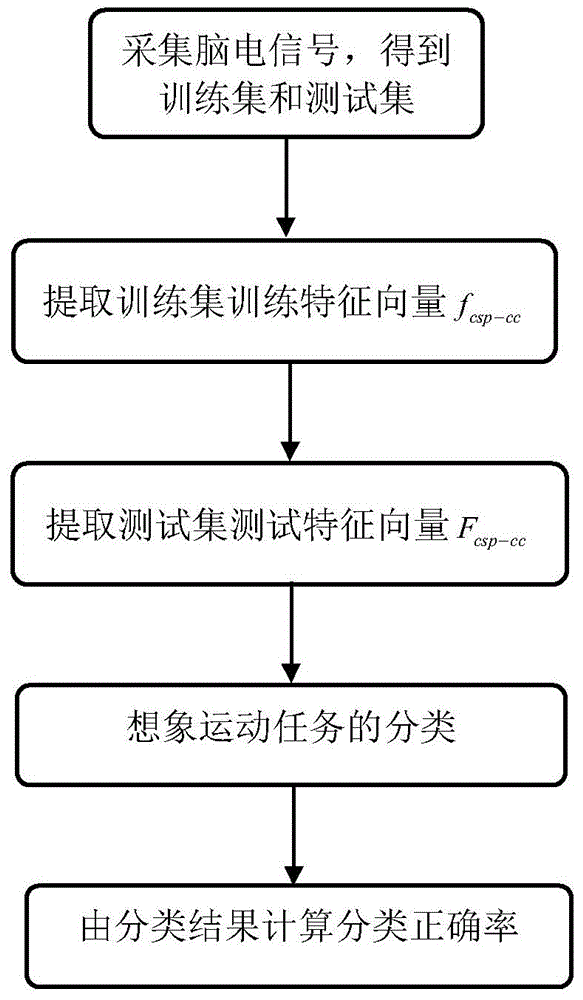
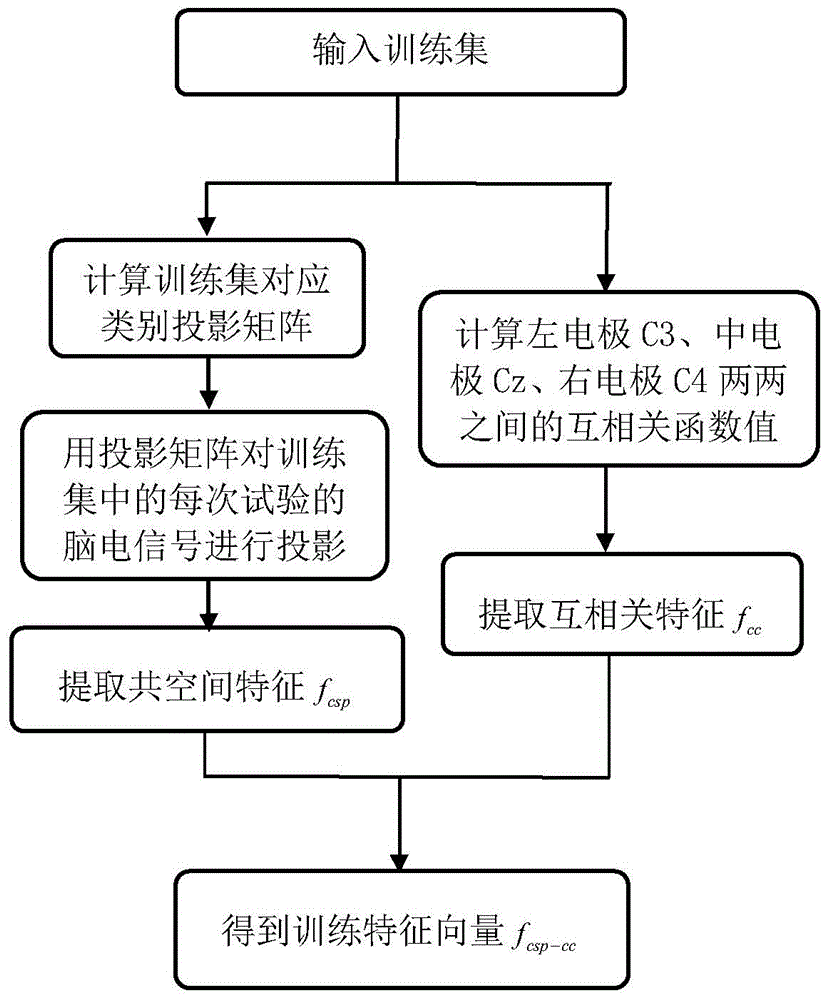
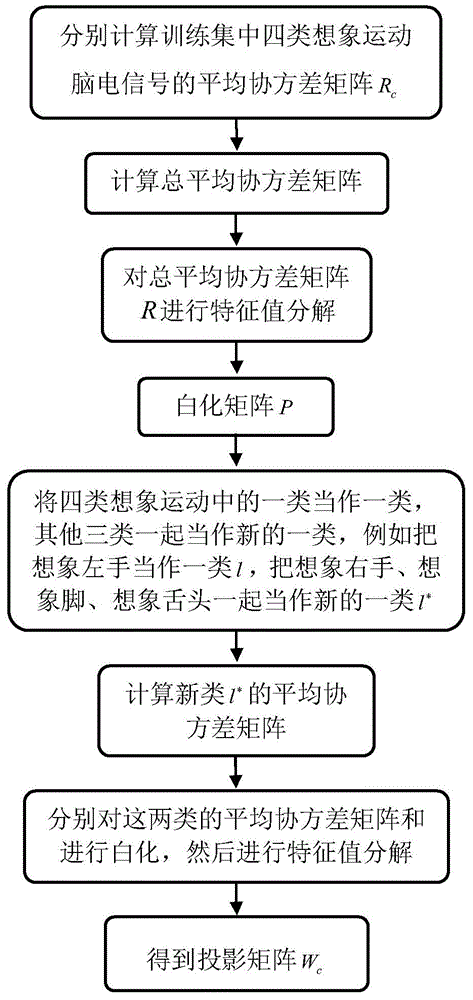
[0037] Step 1. Collect EEG signals and obtain the training set Φ 1 and the test set Φ 2 .
[0038] (1a) Acquisition of EEG signals
[0039] (1a1) Set the sampling rate of the EEG signal acquisition system to 250Hz,
[0040] (1a2) install electrodes on the left electrode C3, the middle electrode Cz and the right electrode C4 of the electrode cap and the corresponding positions of the 8 electrodes around these three electrodes, such as Figure 4 As shown, the subject wears an electrode cap, sits on a chair and looks at the monitor 1m away from him, and collects four kinds of imaginary movements of the subject imagining the left hand, right hand, foot and tongue according to the test sequence and the imaginary movement prompts appearing on the monitor EEG signal at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com