Synchronization information sending method, synchronization information detection method and user equipment
A technology for synchronizing information and sending equipment, applied in the direction of synchronization devices, wireless communications, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as not knowing the resources found in neighboring cells, no solution, and not synchronous transmission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
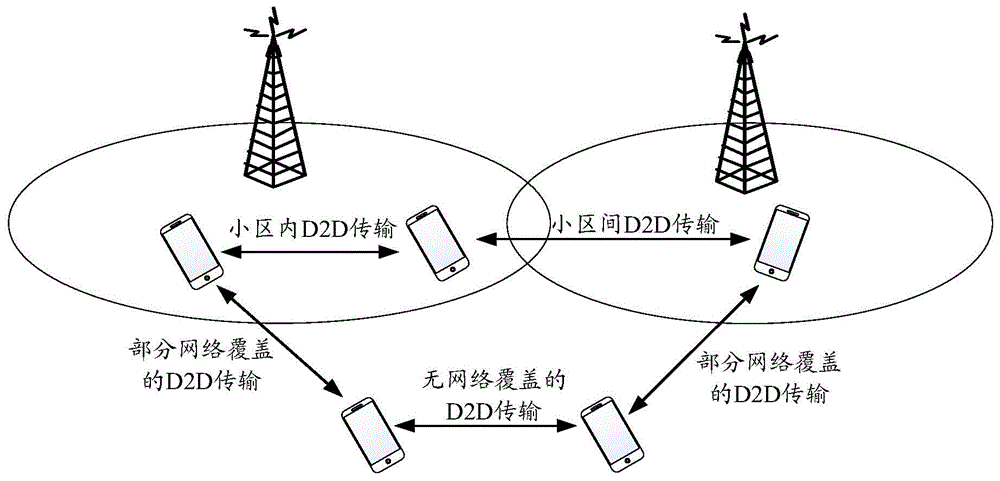
[0318] Embodiment 1. It is assumed that both UE1 and UE2 are within network coverage and belong to different synchronous cells; UE3 and UE4 are outside network coverage. Among them, UE1, UE2, and UE3 send synchronization signals, and UE4 receives synchronization signals. For details, see Figure 5 shown.
[0319] 1. UE1-UE3 respectively send synchronization signals on agreed physical resources according to the synchronization reference obtained from the reference synchronization source.
[0320] Specifically, UE1 and UE2 obtain synchronization references from downlink synchronization signals of cell 1 and cell 2 respectively; UE3 obtains synchronization references from GPS.
[0321] 2. UE1-UE3 determine whether to send synchronization information on the synchronization channel corresponding to the synchronization signal according to their own network connection status and / or reference synchronization source information, and determine whether to send synchronization informatio...
Embodiment 2
[0329] Embodiment 2, it is assumed that UE1 is within network coverage and belongs to cell 1; UE2, UE3, and UE4 are outside network coverage. Among them, UE1, UE2, and UE3 send synchronization signals, and UE4 receives synchronization signals. For details, see Figure 6 shown.
[0330] 1. UE1-UE3 respectively send synchronization signals on agreed physical resources according to the synchronization reference obtained from the reference synchronization source.
[0331] Specifically, UE1 and UE2 obtain the synchronization reference from cell 1 and cell 2 respectively; UE3 obtains the synchronization reference from the cluster head UE. Generally, in the case of no network, there will be a cluster head in a mutually adjacent cluster to send a synchronization signal, so that the surrounding UEs can obtain mutual synchronization by synchronizing with it, and then perform D2D transmission.
[0332] 2. UE1-UE3 determine the synchronization information carried by the synchronization ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com