Thermoelectric device using substrate and method for manufacturing same
A technology of a thermoelectric device and a manufacturing method, which is applied in the manufacture/processing of thermoelectric devices, thermoelectric devices using only Peltier or Seebeck effect, thermoelectric device components, etc., can solve the problem of reduced thermoelectric efficiency, large heat loss, and no flexibility and other problems, to achieve the effect of minimizing heat loss, maximizing thermoelectric efficiency, and reducing weight
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] Hereinafter, exemplary embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings, but the present invention is not limited or limited to these exemplary embodiments.
[0037] In describing the present invention, when it is determined that detailed descriptions of known techniques related to the present invention may obscure the gist of the present invention, the detailed descriptions will be omitted.
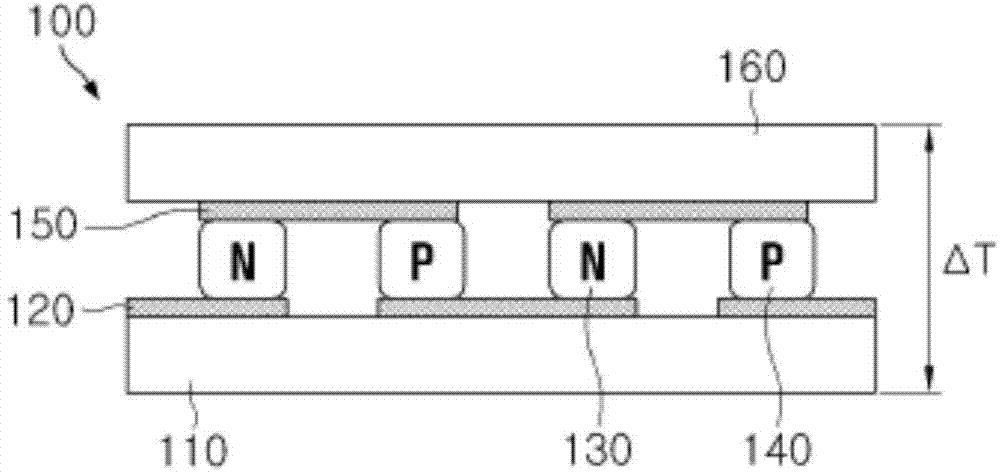
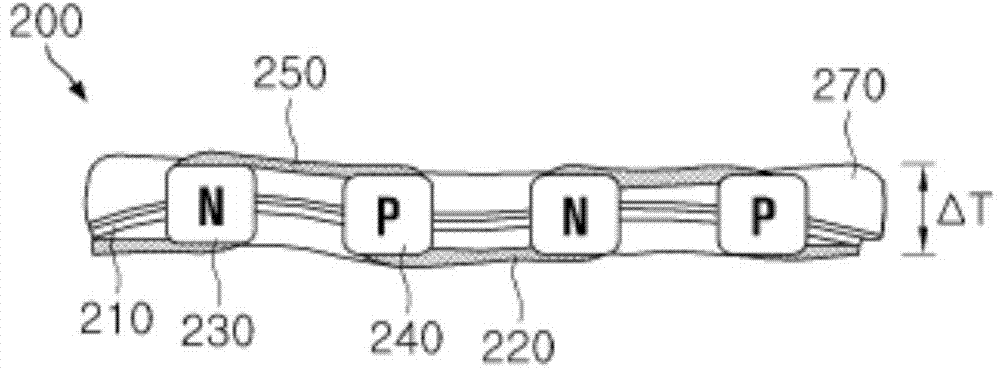
[0038] figure 2 is a cross-sectional view of a flexible thermoelectric device according to the present invention. see figure 2 , the flexible thermoelectric device 200 according to the present invention is configured to include: a grid-type substrate 210; an N-type thermoelectric material 230 and a P-type thermoelectric material 240 formed on the grid-type substrate 210; and a first electrode 220 and a second electrode 250, the first electrode 220 and the second electrode 250 electrically connect the N-type thermoelectr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com