Method for constructing superconducting magnets for magnetic resonance imaging
A technology of magnetic resonance imaging and superconducting magnets, applied in superconducting magnets/coils, magnetic objects, measuring magnetic variables, etc., can solve the problems of magnet uniformity and other indicators, design results deviate from the optimal solution, etc., to avoid taking The effect of adjusting the error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
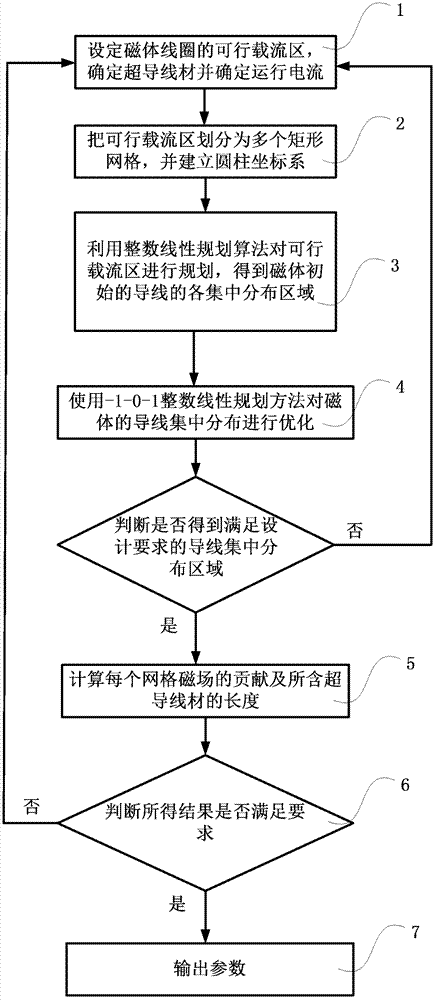
[0027] figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of an embodiment of the method for constructing a superconducting magnet for magnetic resonance imaging of the present invention, as figure 1 Shown:
[0028] Step 1. Estimate the maximum range of the feasible current-carrying area of the magnet coil, including the minimum inner radius and maximum outer radius of the feasible current-carrying area. According to the magnetic field design requirements, space constraints and the maximum magnetic induction intensity of the feasible current-carrying area, determine the superconducting wire And determine the operating current Iop;
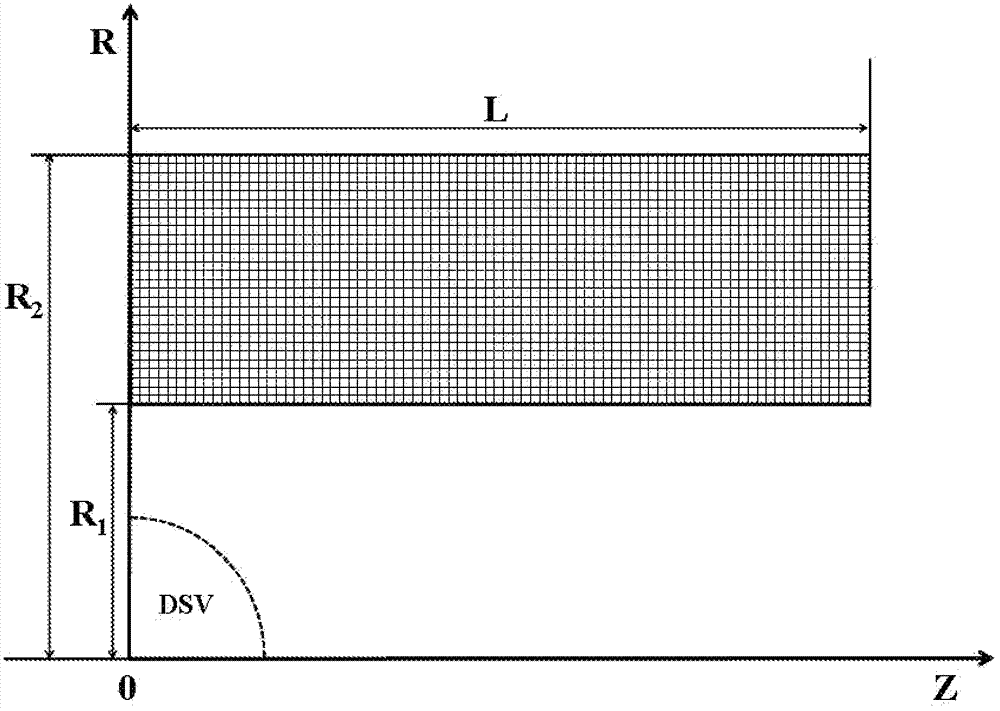
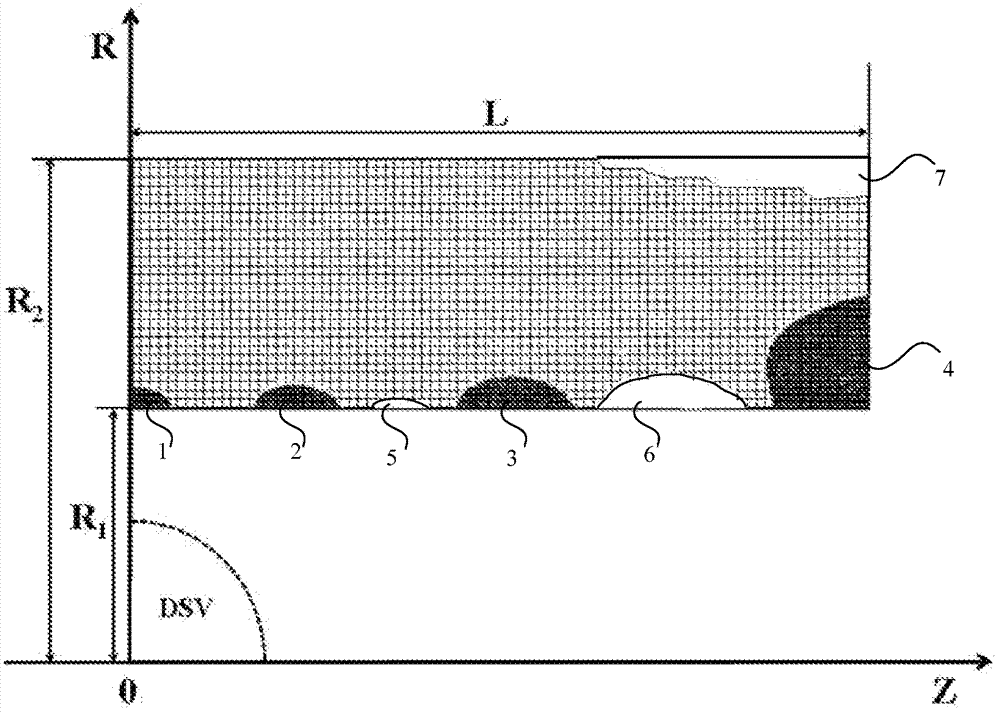
[0029] Step 2, with the center of the magnet as the origin, establish a cylindrical coordinate system (r, z, α), where r is the radial distance, the z-axis is the height, α is the azimuth angle, and the magnet axis is the z-axis direction; according to the Select the size of the superconducting wire, and divide the feasible current-carrying region into mult...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com