SAR (synthetic aperture radar) image change detection method based on high-order neighborhood TMF (triplet Markov random field) model
An image change detection, high-order neighborhood technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the non-stationary characteristics of SAR images that cannot be accurately reflected, the four-neighbor system cannot suppress the influence of noise, and cannot well distinguish homogeneous areas from non-stationary areas. Homogeneous regions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
[0035] refer to figure 1 , the implementation steps of the present invention are as follows:
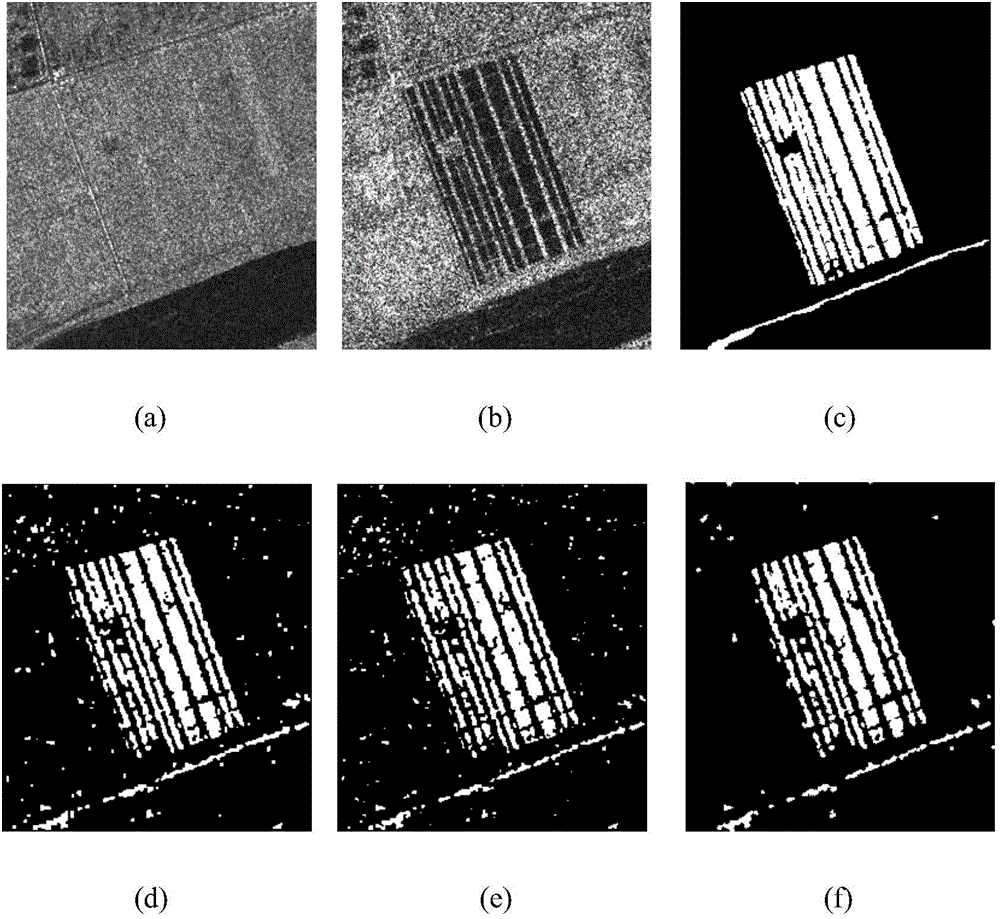
[0036] Step 1, input the registered two-temporal image I of size M×N 0 and I 1 , the registration accuracy is within one pixel.
[0037] Step 2, use the logarithmic ratio method to compare the two-temporal image I 0 and I 1 Process and construct difference image: y s =|log(I 0s / I 1s )|, where, s represents the position of the pixel, I 0s and I 1s Respectively represent the two temporal phase images I 0 and I 1 value at s, y s Indicates the value of the difference image Y at s, 0≤s≤M×N.
[0038] Step 3, using the threshold method to divide the pixels in the difference image Y into two types: non-changing part and changing part.
[0039]The threshold method is a mature existing method, including the OSTU method, the Kittler minimum error classification method, etc. In...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com