Transistor-Eingangsanpassung mit Transformator
A technology of transformers and power transistors, applied in the field of input matching, which can solve problems such as not suppressing the maximum available gain at low frequencies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
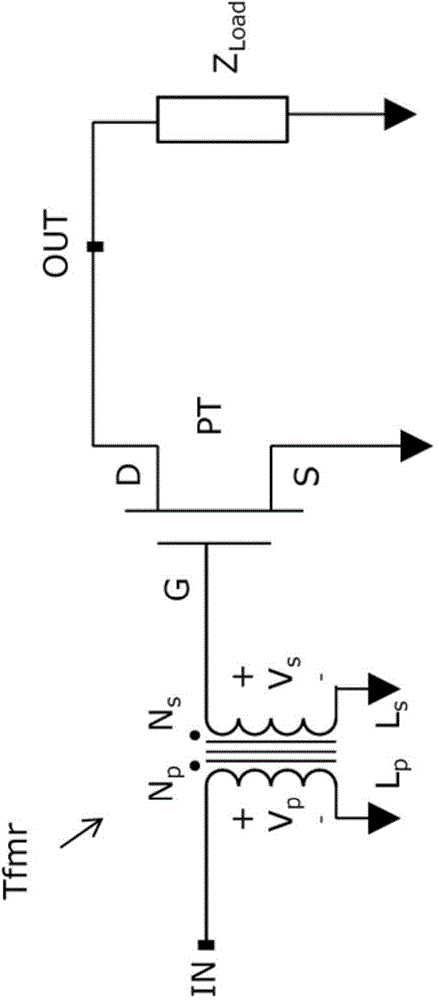
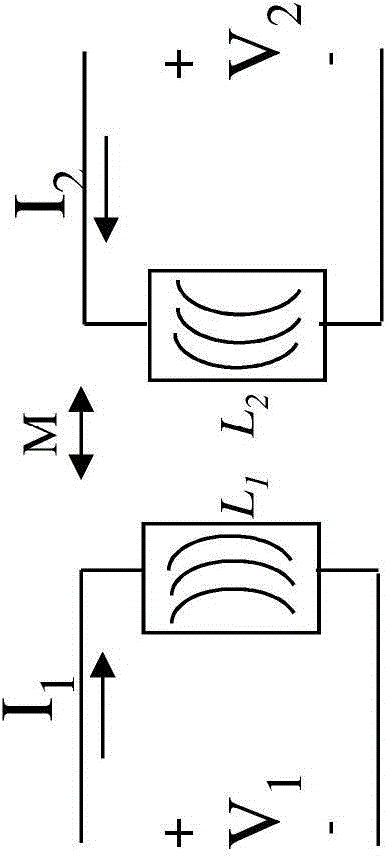
[0022] According to embodiments described herein, a transformer principle is used at the input of the RF power transistor to match the input impedance and create a high pass frequency response that suppresses low frequency gain. In a transformer, a changing alternating current in the primary (P) winding produces a changing magnetic flux which induces a changing voltage in the secondary (S) winding. At low frequency and DC, the package's input lead is isolated from the input (gate) of the RF power transistor by a transformer that operates effectively only at high frequencies, so that the transformer forms a high-pass network. This configuration effectively reduces and suppresses both the maximum available gain and the forward voltage (S21 ) gain hit at low frequencies. The impedance at the input leads of the package no longer depends on the input impedance of the RF power transistor, but on the electrical characteristics of the primary winding.
[0023] By effectively suppress...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com