Method for modifying polydimethylsiloxane by hydrophobic coating self-assembly by using ion complementary peptide
A dimethylsiloxane, hydrophobic coating technology, applied in coatings, chemical instruments and methods, laboratory containers, etc., can solve the problems of low anti-protein adsorption performance, unstable coatings, etc. Enhanced protein adsorption performance, enhanced coating stability, and inhibition of non-specific adsorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] 1. Preparation of surface modifier
[0028] The ion-complementary peptide EAR16-II was added to 10mmol / L phosphate buffer with a pH value of 9.5, and 1.0g of ion-complementary peptide EAR16-II was added to each liter of phosphate buffer to prepare a surface modifier.
[0029] 2. Modified polydimethylsiloxane
[0030] The polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic chip was ultrasonically treated with an ultrasonic cleaner in 1.0mol / L NaOH aqueous solution for 15 minutes, then ultrasonically treated with deionized water until neutral, and then washed with 10mmol / L pH value of 9.5 Washing with phosphate buffer solution to obtain the polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic chip after NaOH activation treatment. The surface modifier is injected into the channel of the polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic chip after the NaOH activation treatment to obtain a surface-modified polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic chip.
Embodiment 2
[0032] In step 1 of this example, the ion-complementary peptide EAR16-II and methylcellulose were added to 10 mmol / L phosphate buffer with a pH value of 9.5, and 1.0 g of ion-complementary peptide EAR16 was added to each liter of phosphate buffer -II and 0.5g methylcellulose, formulated as a surface modifier. The other steps were the same as in Implementation 1 to obtain a surface-modified polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic chip.
Embodiment 3
[0034] In step 1 of this example, the ion-complementary peptide EAR16-II and dodecyl-β-D-maltoside were added to 10 mmol / L phosphate buffer with a pH value of 9.5, and each liter of phosphate buffer was added 1.0 g of ion-complementary peptide EAR16-II and 0.5 g of dodecyl-β-D-maltoside were prepared as surface modifiers. The other steps were the same as in Implementation 1 to obtain a surface-modified polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic chip.
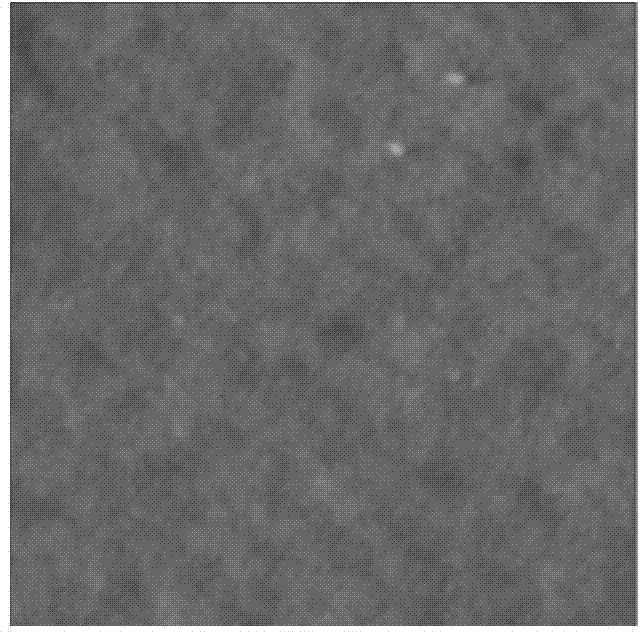
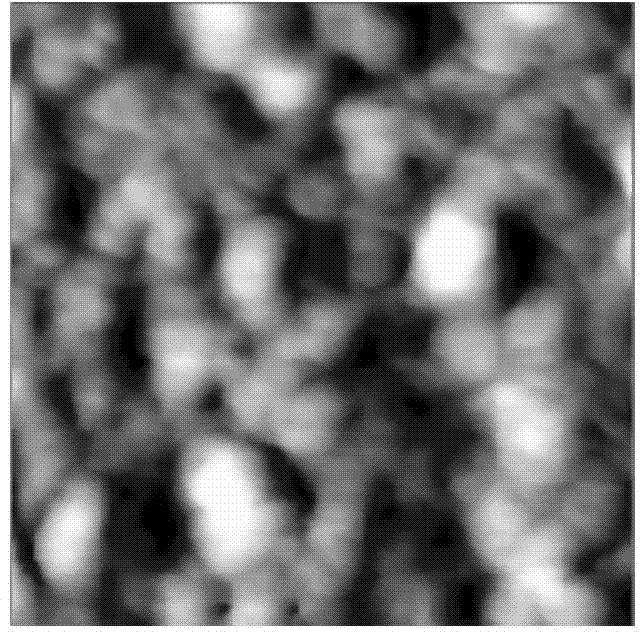
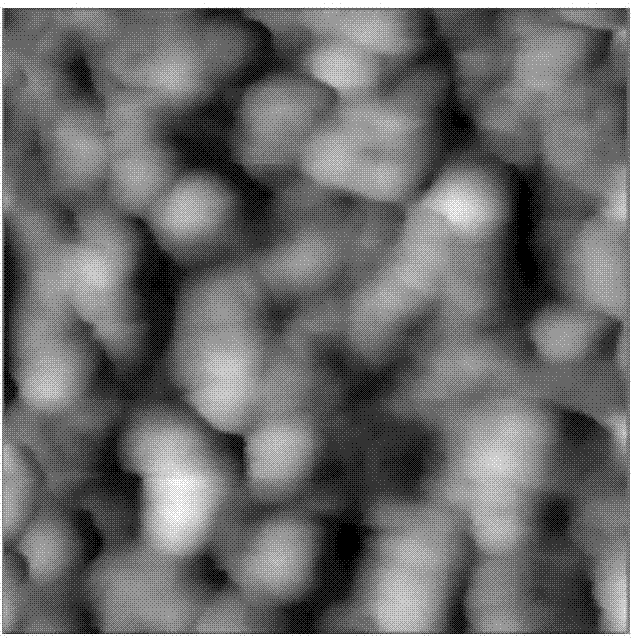
[0035] The methods of atomic force microscopy, Fourier transform attenuated total reflection infrared spectroscopy and contact angle measurement were used to analyze the polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic chip and the surface-modified polydimethylsiloxane obtained in Examples 1-3. Oxane microfluidic chip for characterization, the results are as follows Figure 1-5 .
[0036] Depend on Figure 1~4 It can be seen that the surface of the polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic chip is smooth, and the ion-complementary peptide EAR16-II on the po...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com