energy-saving window
An energy-saving window and window frame technology, applied in the field of energy-saving windows, can solve problems such as heating or cooling, inability to use, and lowering indoor temperature, and achieve the effect of improving energy-saving effect and saving energy consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1: The structure of energy-saving windows
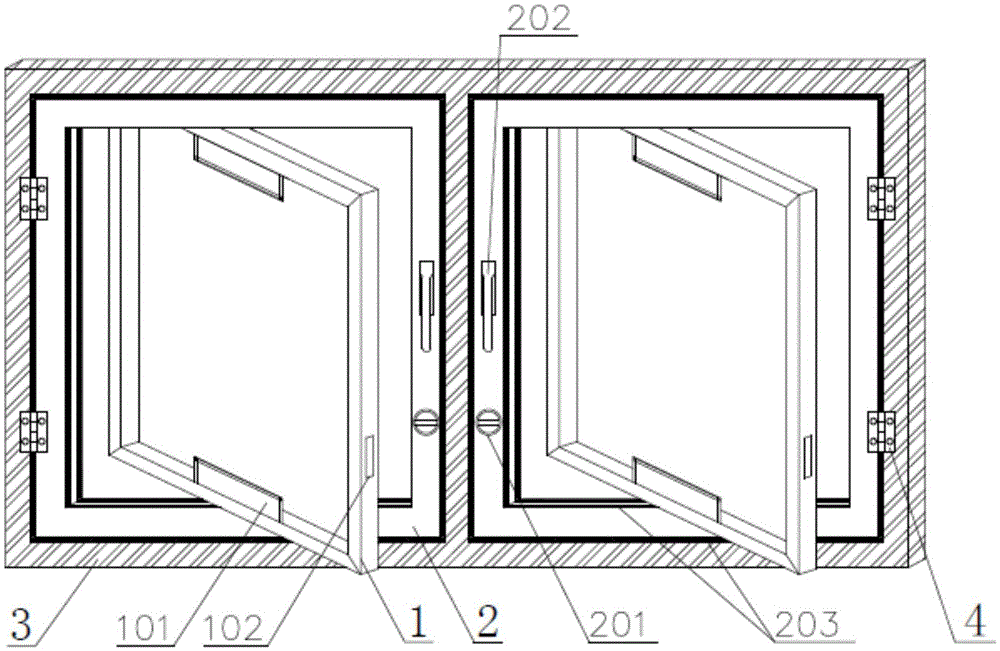
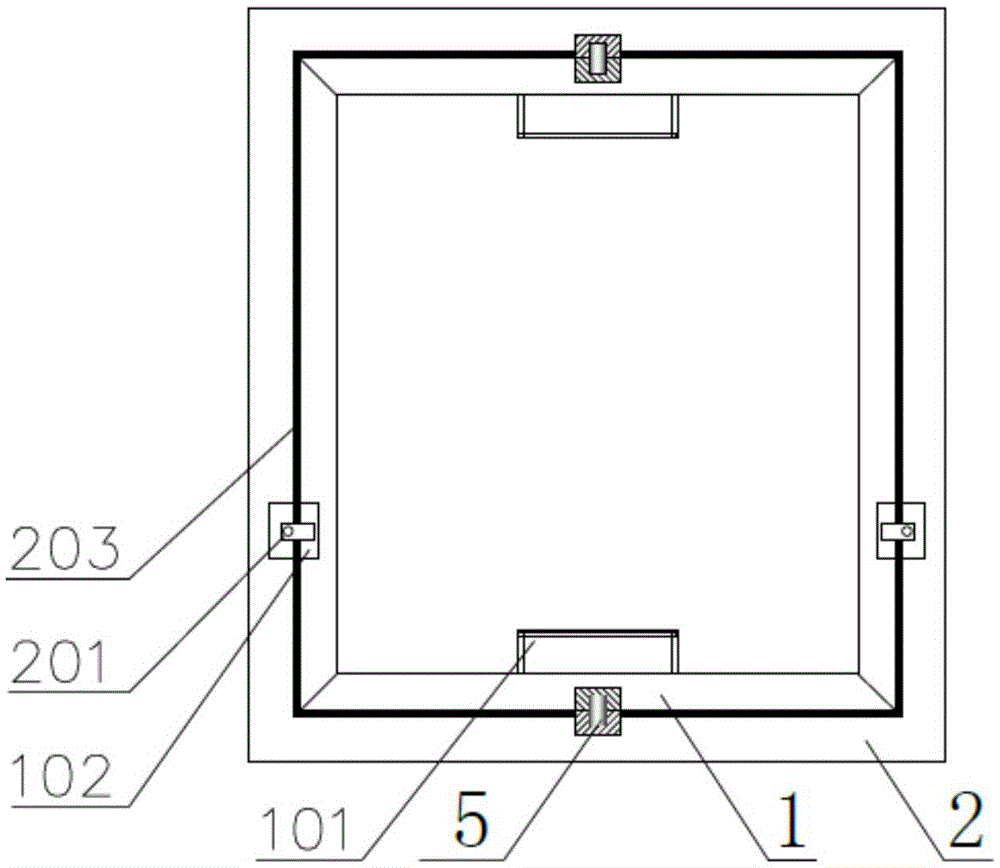
[0047] see figure 1 and figure 2 The energy-saving window described in this embodiment includes a rotating window frame 1, a casement window frame 2, a fixed window frame 3, a hinge 4 and a rotating shaft 5, and one side of the casement window frame 2 is installed on the Inside the fixed window frame 3, the casement window frame 2 rotates 90° around the two hinges 4, the central axis of the rotating window frame 1 coincides with the central axis of the casement window frame 2, and the rotating window frame 1 and the casement window frame 2. Connected by two rotating shafts 5 placed on the central axis, the rotating window frame 1 can rotate 360° in the casement window frame 2 with the rotating shaft 5 as the center line, wherein:
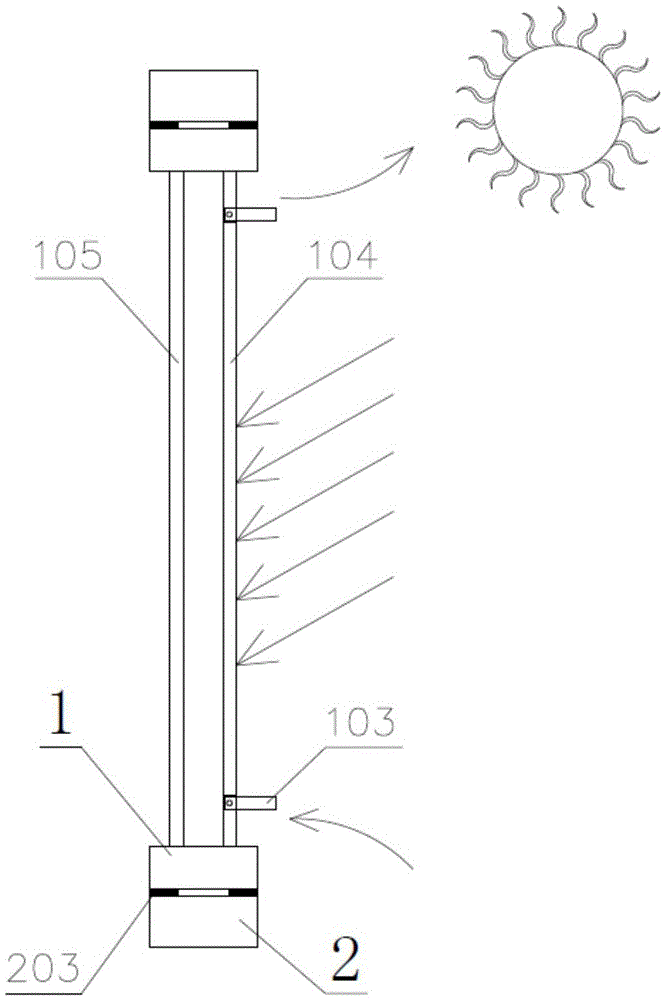
[0048] The rotating window frame 1 includes an air vent 101, a lock slot 102, a turning page 103, heat-absorbing glass 104 and ordinary glass 105, and the heat-absorbing glass 104 and ord...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Example 2: Optimizing and screening the thickness of the air interlayer, the thickness of the heat-absorbing glass, and the size of the vent
[0080] The dry-bulb temperature and solar radiation at 12:00 noon on January 31 in a typical meteorological year in Lhasa are selected as the outdoor meteorological parameters for steady-state simulation, and the rest are the same as the above conditions.
[0081] (1) Air interlayer thickness
[0082] Choose 6mm ordinary colorless glass, 6mm heat-absorbing glass, and vents with length×width dimensions of 300mm×150mm, and simulate the working conditions with air interlayer thicknesses of 6mm, 12mm and 16mm respectively, and the results are shown in Table 3:
[0083] Table 3 Heat supply of vents under different air layer thicknesses
[0084]
[0085] It can be seen from the above table that the heat supply of the ventilation opening is the largest when the thickness of the air space is 12mm, and the heat supply is 291W, so the ...
Embodiment 3
[0098] Example 3: Taking Lhasa City as an example, the window with the optimal size structure in Example 2 was compared with the ordinary window to simulate the energy saving in winter
[0099]Using the optimized energy-saving window model in Example 2 to simulate the heat transfer throughout the day in winter conditions, compare the heat transfer of a single window frame with the same specification of 1800mm in height and 900mm in width, using ordinary 6mm transparent glass.
[0100] like Image 6 , Figure 8 As shown, the vents are opened from 7:00 to 17:00. Due to the action of solar radiation, the air layer is heated to form thermal convection. The vents on the upper part of the heat-absorbing glass supply heat to the room, and the wind speed of the vents follows the heat supply to the sun. As the radiation increases, the wind speed and heat supply both reach the maximum around 13:00, which are 0.54m / s and 349W respectively. At this time, the total heat transfer also reac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com