Polyamide powder for laser sintering and preparation method thereof
A polyamide powder and laser sintering technology, applied in the field of selective laser sintering technology, can solve problems such as inability to achieve effects, and achieve the effects of good powder fluidity, concentrated particle size distribution, and simple and feasible process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
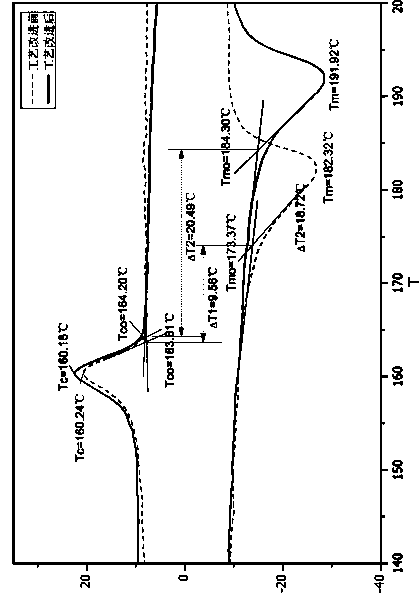
[0023] Add 3kg of PA1212 pellets and 24kg of ethanol to a 30L magnetically stirred reactor, feed high-purity nitrogen to a pressure of 0.3MPa, and start stirring; raise the temperature in the kettle to 145°C at a speed of 1.5°C / min. Insulate for 1 hour; after the constant temperature is over, use cooling water to lower the temperature to lower the temperature in the kettle to 90℃ at a cooling rate of 2.0℃ / min, then reheat to raise the temperature in the kettle to 110℃, and then cool the temperature in the kettle at a rate of 0.15℃ / min The temperature was lowered to 90°C until the precipitation was completed; the flow rate of cooling water was increased to lower the temperature in the kettle to room temperature, the material was taken out, centrifuged, and the powder solid was vacuum-dried for 8 hours. Gained solid powder properties are shown in Table 1 and figure 1 .
[0024] This embodiment sieving particle size distribution is:
[0025] <32μm: 0.6% (weight)
[0026] <38μm...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Add 3kg of PA1212 pellets and 24kg of ethanol to a 30L magnetically stirred reactor, feed high-purity nitrogen to a pressure of 0.3MPa, and start stirring; raise the temperature in the kettle to 145°C at a speed of 1.5°C / min. Insulate for 1 hour; after the constant temperature is over, use cooling water to lower the temperature in the kettle to 90℃ at a rate of 2.0℃ / min, reheat to raise the temperature in the kettle to 108℃, and then lower the temperature in the kettle at a rate of 0.12℃ / min When the temperature is lowered to 90°C, the precipitation is completed; the flow rate of cooling water is increased to lower the temperature in the kettle to room temperature, the material is taken out, centrifuged, and the powder solid is vacuum-dried for 8 hours. Gained solid powder properties are shown in Table 1 and figure 2 .
Embodiment 3
[0044] Add 3kg of PA1212 pellets and 24kg of ethanol to a 30L magnetically stirred reactor, feed high-purity nitrogen to a pressure of 0.3MPa, and start stirring; raise the temperature in the kettle to 145°C at a speed of 1.5°C / min. Insulate for 1 hour; after the constant temperature is over, use cooling water to lower the temperature in the kettle to 90℃ at a rate of 2.0℃ / min, then reheat to raise the temperature in the kettle to 106℃, and then lower the temperature in the kettle at a rate of 0.09℃ / min When the temperature is lowered to 90°C, the precipitation is completed; the flow rate of cooling water is increased to lower the temperature in the kettle to room temperature, the material is taken out, centrifuged, and the powder solid is vacuum-dried for 8 hours. Gained solid powder properties are shown in Table 1 and image 3 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com