Camera elements and camera devices
A technology for imaging elements and pixels, applied in electrical elements, radiation control devices, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of reducing drift components, reducing sensitivity, controlling acceptor concentration and donor concentration, etc., to achieve dark current suppression, thermal noise and other problems. inhibiting effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
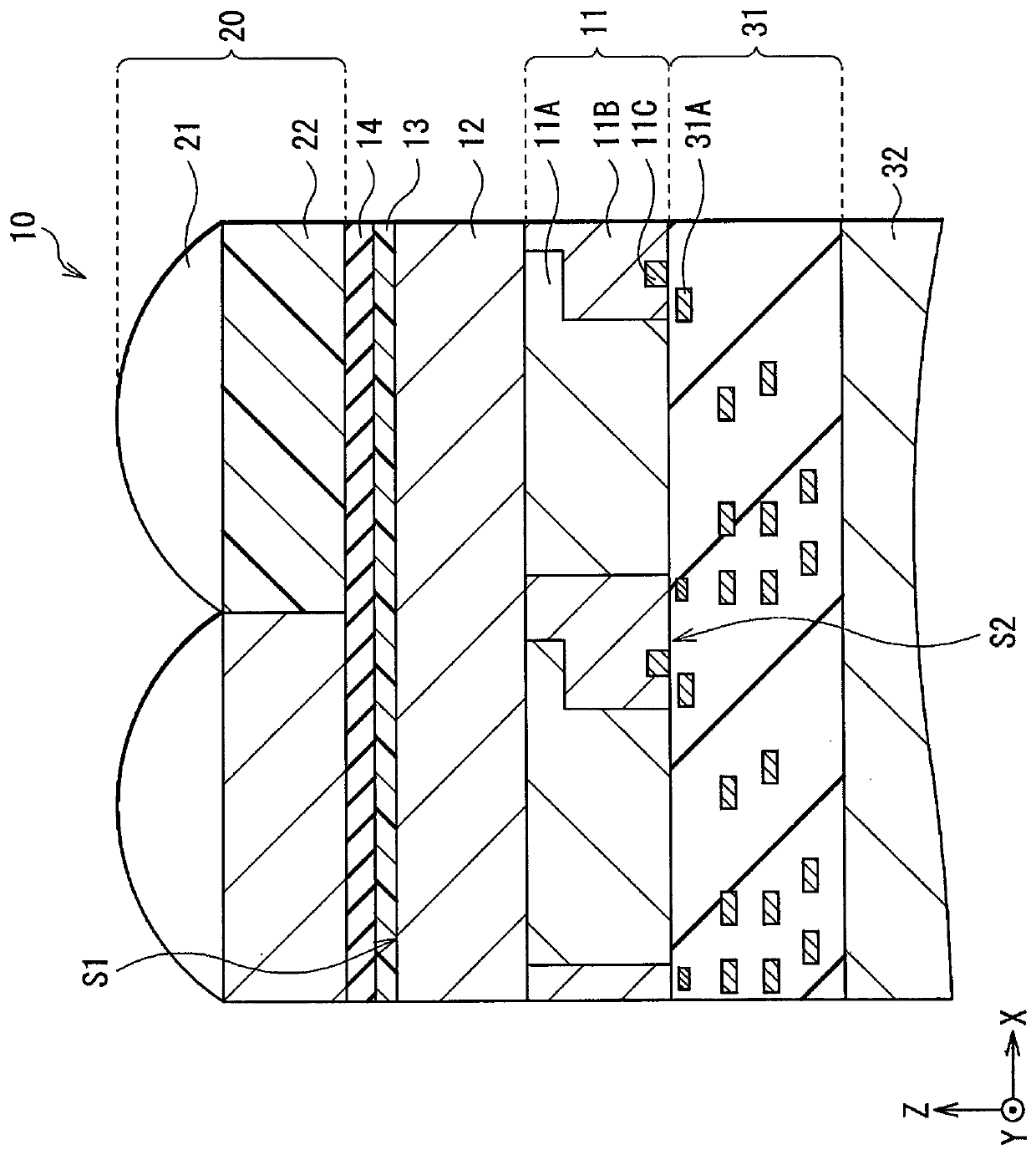
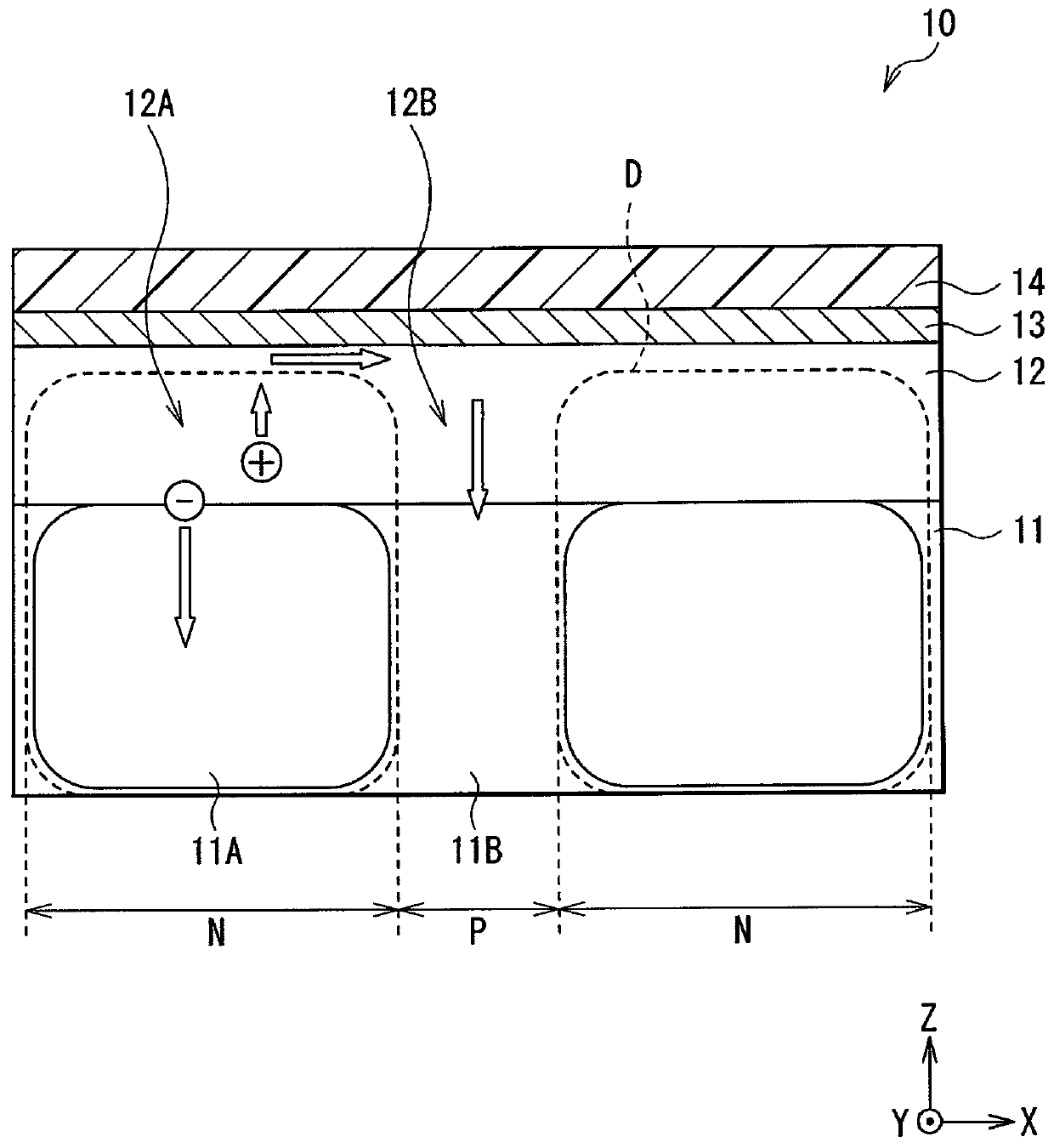
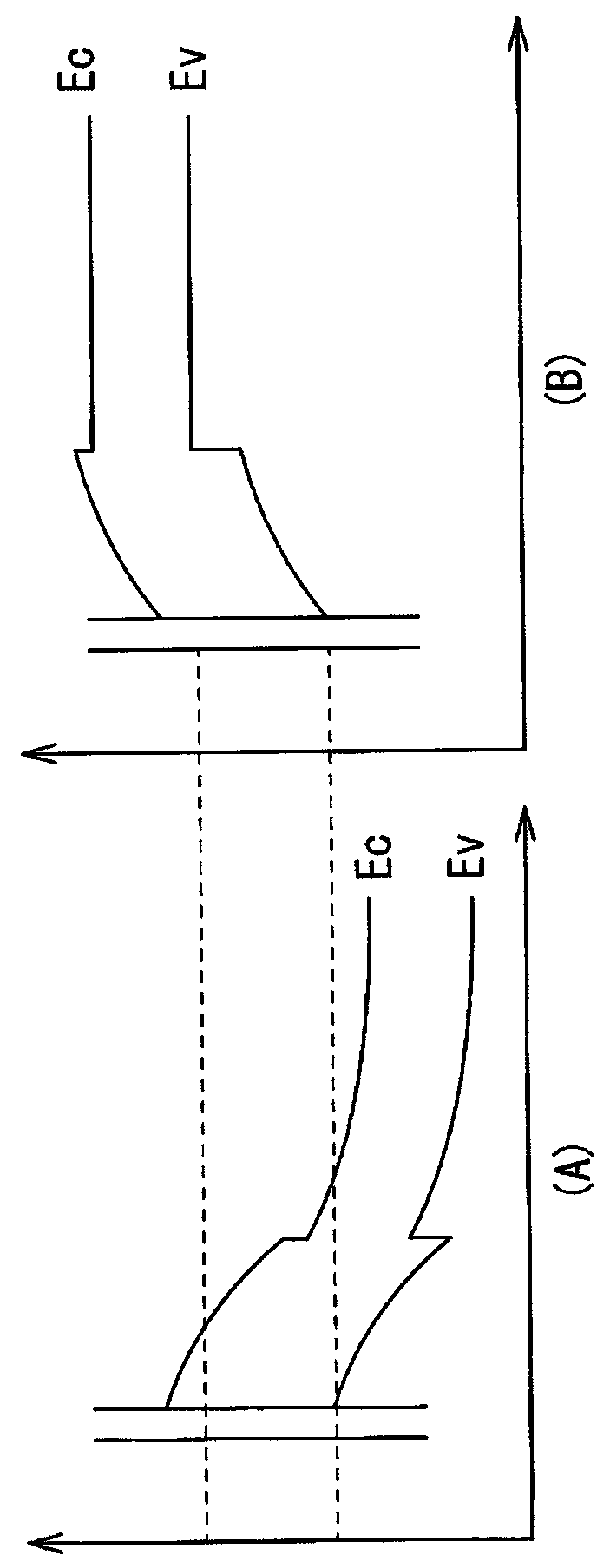
[0067] Figure 6 A cross-sectional structure of an imaging element (imaging element 10B) according to Modification 2 of the above-described embodiment is shown in the figure. In the imaging element 10B, a conductive film 44A and a conductive film 44B spaced apart are formed on the insulating film 13 , and the conductive film 44B formed on the ineffective portion 12B is formed of a light-shielding material. This is a point different from the above-mentioned embodiment. Except for this point, the imaging element 10B has the same configuration as that of the imaging element 10 , and also has the same functions and effects.
[0068] As described above, in the imaging element 10B, the conductive film 44B formed on the invalid portion 12B is formed of a light-shielding material. Therefore, in addition to the effects of the above-described embodiment and Modification 1, there is also an effect that color mixing due to light entering adjacent pixels obliquely can be prevented.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com