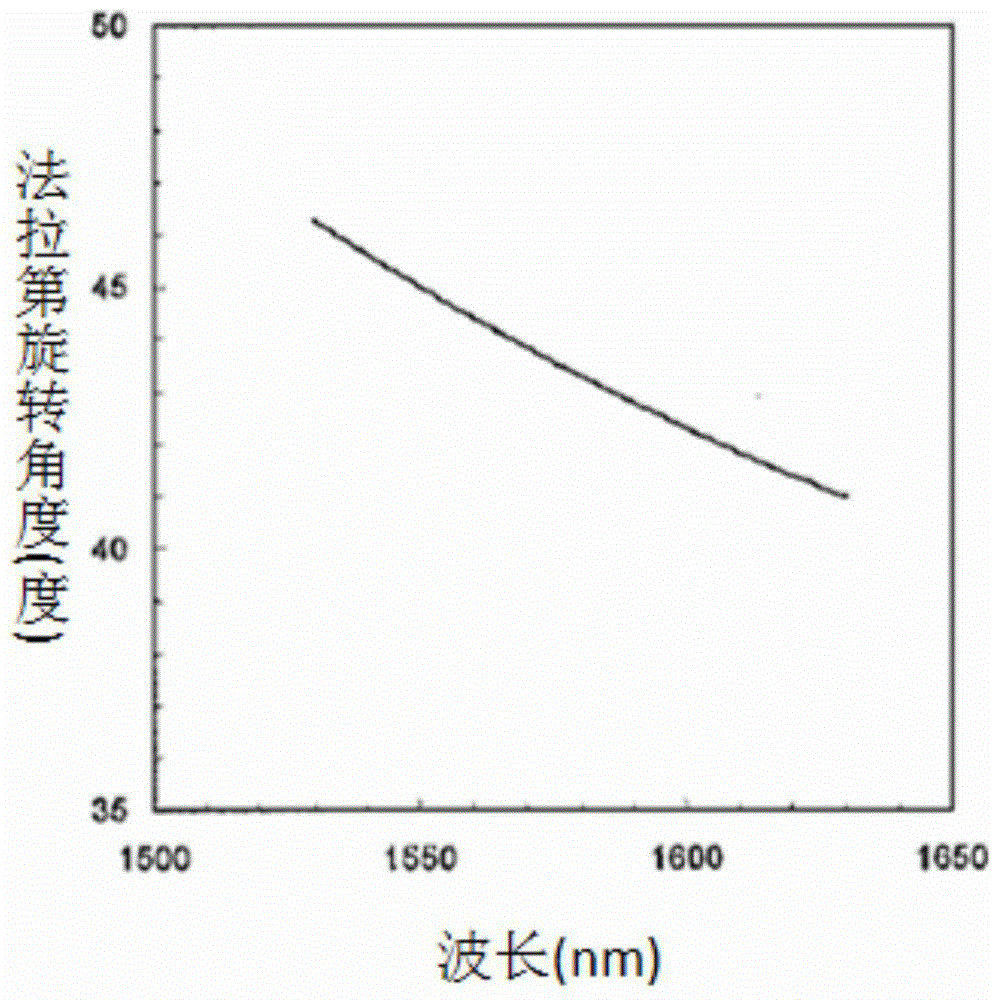
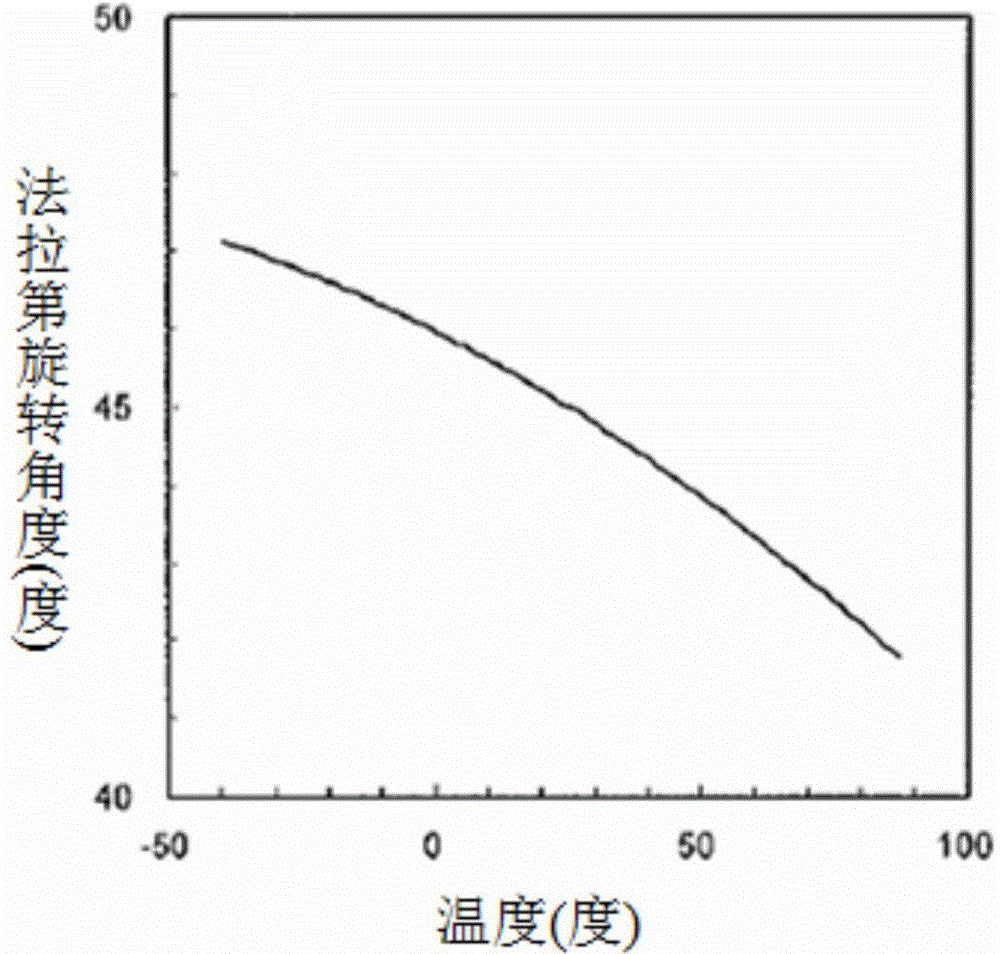
Faraday rotating lens irrelevant to wavelength and temperature
A Faraday rotating mirror and Faraday rotator technology, applied in nonlinear optics, instruments, optics, etc., can solve the problem that broadband wavelength and large temperature range cannot be effective at the same time, and achieve the effect of eliminating the effect of rotation angle dispersion and temperature-related effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
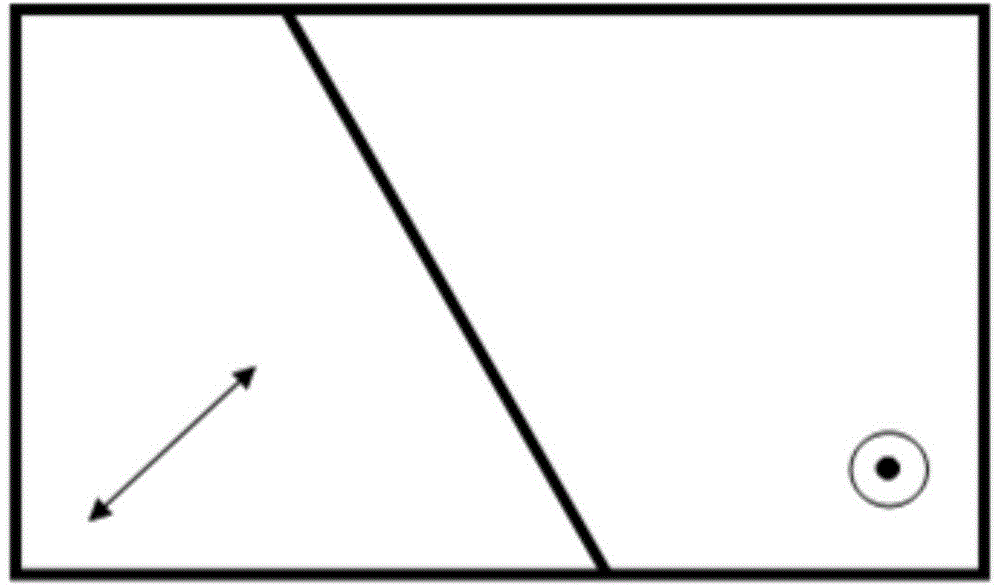
[0030] Figure 5 The wavelength- and temperature-independent Faraday rotating mirror includes a single-mode single-fiber collimator 11, a Nomarski prism 12, whose optical axis X1 is consistent with the x-axis, and whose optical axis X2 is in the y-z plane, a Faraday Rotator 13, a dielectric optical thin film plane reflector 14.
[0031] Figure 5The light 100 emitted from the single-mode single-fiber collimator 11 is transmitted along the z-axis of the Cartesian coordinate system, and when it hits the Nomarski prism 12, it is first divided into two beams of linearly polarized ordinary light 111 and non-linearly polarized light whose polarization directions are perpendicular to each other. Ordinary light 121 converges when passing through the two wedge-angle interfaces of the prism, passes through the Faraday rotator 13, and the vibrating plane rotates about 45 degrees to become light beams 112 and 122, and intersect on the plane mirror 14, the light beams 112 and 122 are resp...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Figure 9 The wavelength- and temperature-independent Faraday rotator in contains a single-mode single-fiber collimator 21, a polarizing beam shifter 22 whose optical axis X3 is in the y-z plane, and a Wollaston prism 23 whose optical axis X4 is parallel to the x-axis, the optical axis X5 is in the y-z plane, and its edges are parallel to the x-axis, a Faraday rotator 24 , and a dielectric optical film flat mirror 25 .
[0037] Figure 4 The light 300 emitted from the single-mode single-fiber collimator 21 is transmitted along the z-axis of the Cartesian coordinate system, and is incident on the polarized beam shifter 22 to be divided into two beams of linearly polarized extraordinary light 311 and ordinary light whose polarization directions are perpendicular to each other. The light 321 converges after passing through the Wollaston prism 23, passes through the Faraday rotator 24, and the vibrating plane rotates about 45 degrees to become two converging beams of light...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com